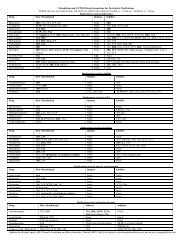
ECMO and Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy - PPAG
ECMO and Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy - PPAG
ECMO and Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy - PPAG
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
What happened to.….• SCUF – Slow <strong>Continuous</strong> UltraFiltration• Convective removal, no replacement fluid• CAVH – <strong>Continuous</strong> ArterioVenous Hemofiltration• Convective removal, patient blood pressure determinesflow, 2 vessels, replacement fluid• CVVHD – <strong>Continuous</strong> VenoVenous HemoDialysis• Diffusive removal, pump driven, usually no replacementfluid, dialysate delivered countercurrent to blood• CVVH – <strong>Continuous</strong> VenoVenous Hemofiltration• Convective removal, pump driven, replacement fluid• CVVHDF – <strong>Continuous</strong> VenoVenousHemoDiaFiltration• Diffusive + Convective Removal, pump driven,replacement fluid, dialysate delivered countercurrent tobloodCRRT - Principles• Blood flows through a semipermeablemembrane driven either by patient bloodpressure (AV mode) or by a peristalticpump (VV mode)• Semipermeable membrane of the filter istypically synthetic <strong>and</strong> high-flux• Solute clearance can be achieved bydiffusion, convection, or a combinationDiffusion• Solutes such as urea, phosphate, <strong>and</strong> uremictoxins are driven by their electrochemicalgradient to move across the membrane into thesterile dialysate, which is runningcountercurrent to blood on the other side of themembrane capillaries• Different than IHD• CRRT – dialysate flow is slow• Typically 0.6 - 2 L/hr• IHD – dialysate flow is fast• Typically 500 mL/min or 30 L/hr