You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
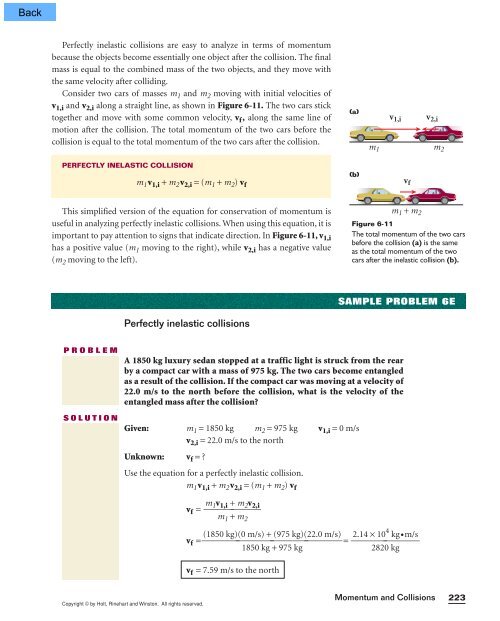
Perfectly inelastic collisions are easy to analyze in terms of momentumbecause the objects become essentially one object after the collision. The finalmass is equal to the combined mass of the two objects, and they move withthe same velocity after colliding.Consider two cars of masses m 1 and m 2 moving with initial velocities ofv 1,i and v 2,i along a straight line, as shown in Figure 6-11. The two cars sticktogether and move with some common velocity, v f , along the same line ofmotion after the collision. The total momentum of the two cars before thecollision is equal to the total momentum of the two cars after the collision.PERFECTLY INELASTIC COLLISIONm 1 m 2(b)m 1 v 1,i + m 2 v 2,i = (m 1 + m 2 ) v fv f(a)v 1,iv 2,iThis simplified version of the equation for conservation of momentum isuseful in analyzing perfectly inelastic collisions. When using this equation, it isimportant to pay attention to signs that indicate direction. In Figure 6-11, v 1,ihas a positive value (m 1 moving to the right), while v 2,i has a negative value(m 2 moving to the left).m 1 + m 2Figure 6-11The total momentum of the two carsbefore the collision (a) is the sameas the total momentum of the twocars after the inelastic collision (b).SAMPLE PROBLEM 6EPerfectly inelastic collisionsPROBLEMSOLUTIONA 1850 kg luxury sedan stopped at a traffic light is struck from the rearby a compact car with a mass of 975 kg. The two cars become entangledas a result of the collision. If the compact car was moving at a velocity of22.0 m/s to the north before the collision, what is the velocity of theentangled mass after the collision?Given: m 1 = 1850 kg m 2 = 975 kg v 1,i = 0 m/sv 2,i = 22.0 m/s to the northUnknown: v f = ?Use the equation for a perfectly inelastic collision.m 1 v 1,i + m 2 v 2,i = (m 1 + m 2 ) v fv f = ⎯ m 1v1,i + m⎯2v 2,im1+ m2v f = =⎯ 2.14 × 4(1850 kg)(0 m/s) + (975 kg)(22.0 m/s) 10kg •m/s⎯⎯⎯⎯ ⎯1850 kg + 975 kg2820kgv f = 7.59 m/s to the northCopyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.Momentum and Collisions223