3 What Is Energy?
3 What Is Energy?
3 What Is Energy?
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
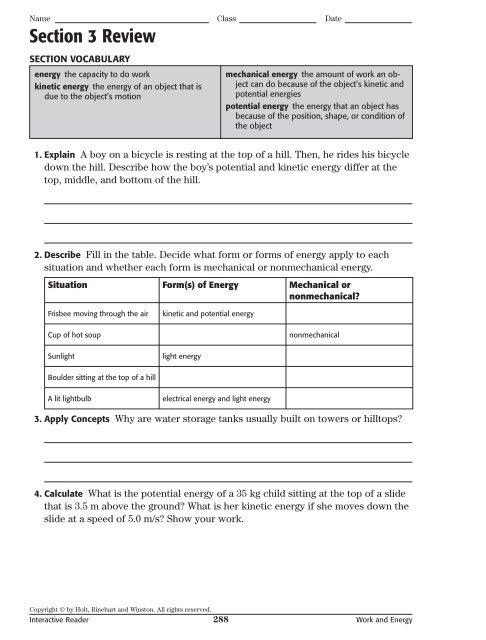
Name Class DateSection 3 ReviewSECTION VOCABULARYenergy the capacity to do workkinetic energy the energy of an object that isdue to the object’s motionmechanical energy the amount of work an objectcan do because of the object’s kinetic andpotential energiespotential energy the energy that an object hasbecause of the position, shape, or condition ofthe object1. Explain A boy on a bicycle is resting at the top of a hill. Then, he rides his bicycledown the hill. Describe how the boy’s potential and kinetic energy differ at thetop, middle, and bottom of the hill.2. Describe Fill in the table. Decide what form or forms of energy apply to eachsituation and whether each form is mechanical or nonmechanical energy.Situation Form(s) of <strong>Energy</strong> Mechanical ornonmechanical?Frisbee moving through the airkinetic and potential energyCup of hot soupnonmechanicalSunlightlight energyBoulder sitting at the top of a hillA lit lightbulbelectrical energy and light energy3. Apply Concepts Why are water storage tanks usually built on towers or hilltops?4. Calculate <strong>What</strong> is the potential energy of a 35 kg child sitting at the top of a slidethat is 3.5 m above the ground? <strong>What</strong> is her kinetic energy if she moves down theslide at a speed of 5.0 m/s? Show your work.Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.Interactive Reader 288 Work and <strong>Energy</strong>