SIDE-BY-SIDE TEKS COMPARISON GRADE 3 - Project Share
SIDE-BY-SIDE TEKS COMPARISON GRADE 3 - Project Share
SIDE-BY-SIDE TEKS COMPARISON GRADE 3 - Project Share
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
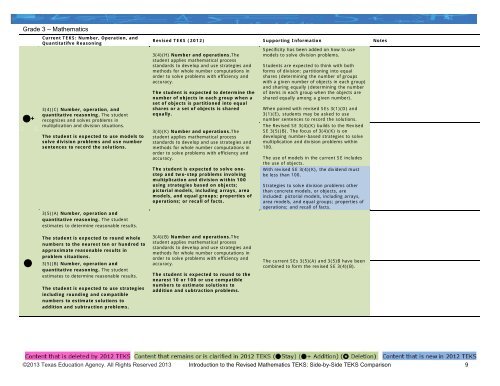
Grade 3 – Mathematics+Current <strong>TEKS</strong>: Number, Operation, andQuantitatifve Reasoning3(4)(C) Number, operation, andquantitative reasoning. The studentrecognizes and solves problems inmultiplication and division situations.The student is expected to use models tosolve division problems and use numbersentences to record the solutions.3(5)(A) Number, operation andquantitative reasoning. The studentestimates to determine reasonable results.Revised <strong>TEKS</strong> (2012) Supporting Information Notes3(4)(H) Number and operations.Thestudent applies mathematical processstandards to develop and use strategies andmethods for whole number computations inorder to solve problems with efficiency andaccuracy.The student is expected to determine thenumber of objects in each group when aset of objects is partitioned into equalshares or a set of objects is sharedequally.3(4)(K) Number and operations.Thestudent applies mathematical processstandards to develop and use strategies andmethods for whole number computations inorder to solve problems with efficiency andaccuracy.The student is expected to solve onestepand two-step problems involvingmultiplication and division within 100using strategies based on objects;pictorial models, including arrays, areamodels, and equal groups; properties ofoperations; or recall of facts.Specificity has been added on how to usemodels to solve division problems.Students are expected to think with bothforms of division: partitioning into equalshares (determining the number of groupswith a given number of objects in each group)and sharing equally (determining the numberof items in each group when the objects areshared equally among a given number).When paired with revised SEs 3(1)(D) and3(1)(E), students may be asked to usenumber sentences to record the solutions.The Revised SE 3(4)(K) builds to the RevisedSE 3(5)(B). The focus of 3(4)(K) is ondeveloping number-based strategies to solvemultiplication and division problems within100.The use of models in the current SE includesthe use of objects.With revised SE 3(4)(K), the dividend mustbe less than 100.Strategies to solve division problems otherthan concrete models, or objects, areincluded: pictorial models, including arrays,area models, and equal groups; properties ofoperations; and recall of facts.The student is expected to round wholenumbers to the nearest ten or hundred toapproximate reasonable results inproblem situations.•3(5)(B) Number, operation andquantitative reasoning. The studentestimates to determine reasonable results.The student is expected to use strategiesincluding rounding and compatiblenumbers to estimate solutions toaddition and subtraction problems.3(4)(B) Number and operations.Thestudent applies mathematical processstandards to develop and use strategies andmethods for whole number computations inorder to solve problems with efficiency andaccuracy.The student is expected to round to thenearest 10 or 100 or use compatiblenumbers to estimate solutions toaddition and subtraction problems.The current SEs 3(5)(A) and 3(5)B have beencombined to form the revised SE 3(4)(B).©2013 Texas Education Agency. All Rights Reserved 2013 Introduction to the Revised Mathematics <strong>TEKS</strong>: Side-by-Side <strong>TEKS</strong> Comparison 9