Fibre Channel Fundamentals (PDF) - Unylogix Technologies Inc.
Fibre Channel Fundamentals (PDF) - Unylogix Technologies Inc.
Fibre Channel Fundamentals (PDF) - Unylogix Technologies Inc.
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
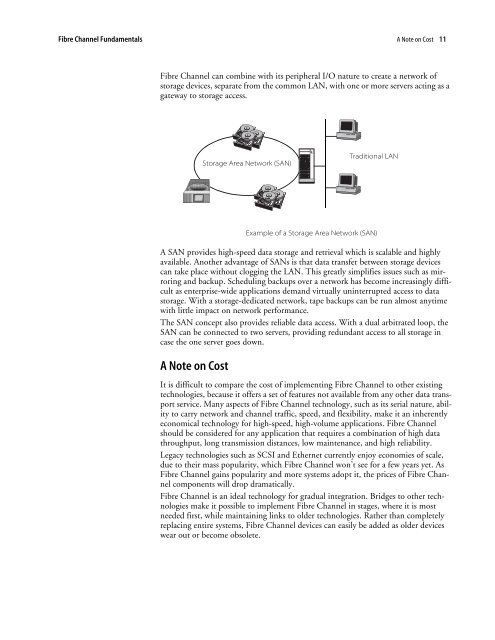
<strong>Fibre</strong> <strong>Channel</strong> <strong>Fundamentals</strong> A Note on Cost 11<strong>Fibre</strong> <strong>Channel</strong> can combine with its peripheral I/O nature to create a network ofstorage devices, separate from the common LAN, with one or more servers acting as agateway to storage access.Storage Area Network (SAN)Traditional LANA SAN provides high-speed data storage and retrieval which is scalable and highlyavailable. Another advantage of SANs is that data transfer between storage devicescan take place without clogging the LAN. This greatly simplifies issues such as mirroringand backup. Scheduling backups over a network has become increasingly difficultas enterprise-wide applications demand virtually uninterrupted access to datastorage. With a storage-dedicated network, tape backups can be run almost anytimewith little impact on network performance.The SAN concept also provides reliable data access. With a dual arbitrated loop, theSAN can be connected to two servers, providing redundant access to all storage incase the one server goes down.A Note on CostExample of a Storage Area Network (SAN)It is difficult to compare the cost of implementing <strong>Fibre</strong> <strong>Channel</strong> to other existingtechnologies, because it offers a set of features not available from any other data transportservice. Many aspects of <strong>Fibre</strong> <strong>Channel</strong> technology, such as its serial nature, abilityto carry network and channel traffic, speed, and flexibility, make it an inherentlyeconomical technology for high-speed, high-volume applications. <strong>Fibre</strong> <strong>Channel</strong>should be considered for any application that requires a combination of high datathroughput, long transmission distances, low maintenance, and high reliability.Legacy technologies such as SCSI and Ethernet currently enjoy economies of scale,due to their mass popularity, which <strong>Fibre</strong> <strong>Channel</strong> won’t see for a few years yet. As<strong>Fibre</strong> <strong>Channel</strong> gains popularity and more systems adopt it, the prices of <strong>Fibre</strong> <strong>Channel</strong>components will drop dramatically.<strong>Fibre</strong> <strong>Channel</strong> is an ideal technology for gradual integration. Bridges to other technologiesmake it possible to implement <strong>Fibre</strong> <strong>Channel</strong> in stages, where it is mostneeded first, while maintaining links to older technologies. Rather than completelyreplacing entire systems, <strong>Fibre</strong> <strong>Channel</strong> devices can easily be added as older deviceswear out or become obsolete.