Aromatic Compounds - 1 Summary of Class Discussion
Aromatic Compounds - 1 Summary of Class Discussion
Aromatic Compounds - 1 Summary of Class Discussion
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
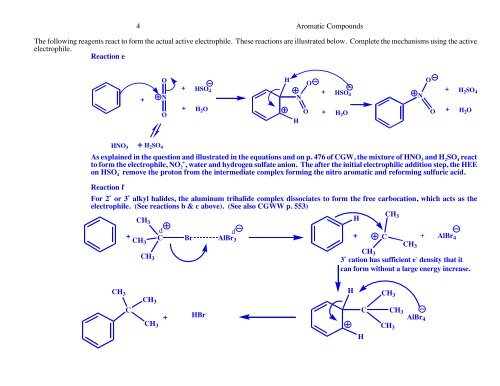
4 <strong>Aromatic</strong> <strong>Compounds</strong>The following reagents react to form the actual active electrophile. These reactions are illustrated below. Complete the mechanisms using the activeelectrophile.Reaction e+ONOHOO+ HSO 4 ++HSOH 2 SO 4N4 N+ H 2 O O + H 2 OO + H 2 OHHNO 3 + H 2 SO 4As explained in the question and illustrated in the equations and on p. 476 <strong>of</strong> CGW, the mixture <strong>of</strong> HNO 3 and H 2 SO 4 reactto form the electrophile, NO 2+ , water and hydrogen sulfate anion. The after the initial electrophilic addition step, the HEEon HSO 4- remove the proton from the intermediate complex forming the nitro aromatic and reforming sulfuric acid.Reaction fFor 2˚ or 3˚ alkyl halides, the aluminum trihalide complex dissociates to form the free carbocation, which acts as theelectrophile. (See reactions b & c above). (See also CGWW p. 553)CHCH 3H3dd++ C + AlBrCH 43CH 3CHCH 333˚ cation has sufficient e - density that itcan form without a large energy increase.C Br AlBr 3HCH 3CCH 3CH 3CH 3+HBrHCCH 3CH 3AlBr 4