Syllabus - Father Michael McGivney Catholic Academy
Syllabus - Father Michael McGivney Catholic Academy
Syllabus - Father Michael McGivney Catholic Academy
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
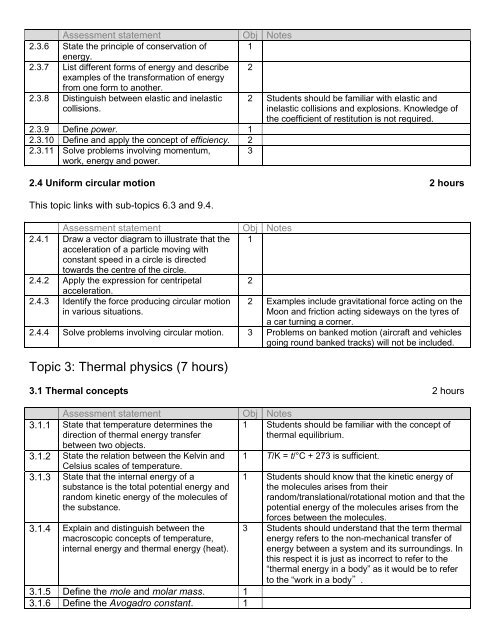
Assessment statement Obj Notes2.3.6 State the principle of conservation of 1energy.2.3.7 List different forms of energy and describe 2examples of the transformation of energyfrom one form to another.2.3.8 Distinguish between elastic and inelasticcollisions.2 Students should be familiar with elastic andinelastic collisions and explosions. Knowledge ofthe coefficient of restitution is not required.2.3.9 Define power. 12.3.10 Define and apply the concept of efficiency. 22.3.11 Solve problems involving momentum, 3work, energy and power.2.4 Uniform circular motion 2 hoursThis topic links with sub-topics 6.3 and 9.4.Assessment statement2.4.1 Draw a vector diagram to illustrate that theacceleration of a particle moving withconstant speed in a circle is directedtowards the centre of the circle.2.4.2 Apply the expression for centripetalacceleration.2.4.3 Identify the force producing circular motionin various situations.Obj Notes122 Examples include gravitational force acting on theMoon and friction acting sideways on the tyres ofa car turning a corner.2.4.4 Solve problems involving circular motion. 3 Problems on banked motion (aircraft and vehiclesgoing round banked tracks) will not be included.Topic 3: Thermal physics (7 hours)3.1 Thermal concepts 2 hoursAssessment statement3.1.1 State that temperature determines thedirection of thermal energy transferbetween two objects.3.1.2 State the relation between the Kelvin andCelsius scales of temperature.3.1.3 State that the internal energy of asubstance is the total potential energy andrandom kinetic energy of the molecules ofthe substance.3.1.4 Explain and distinguish between themacroscopic concepts of temperature,internal energy and thermal energy (heat).3.1.5 Define the mole and molar mass. 13.1.6 Define the Avogadro constant. 1Obj Notes1 Students should be familiar with the concept ofthermal equilibrium.1 T/K = t/°C + 273 is sufficient.1 Students should know that the kinetic energy ofthe molecules arises from theirrandom/translational/rotational motion and that thepotential energy of the molecules arises from theforces between the molecules.3 Students should understand that the term thermalenergy refers to the non-mechanical transfer ofenergy between a system and its surroundings. Inthis respect it is just as incorrect to refer to the“thermal energy in a body” as it would be to referto the “work in a body”.