Web-DSS-Chapter-03
Web-DSS-Chapter-03
Web-DSS-Chapter-03
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
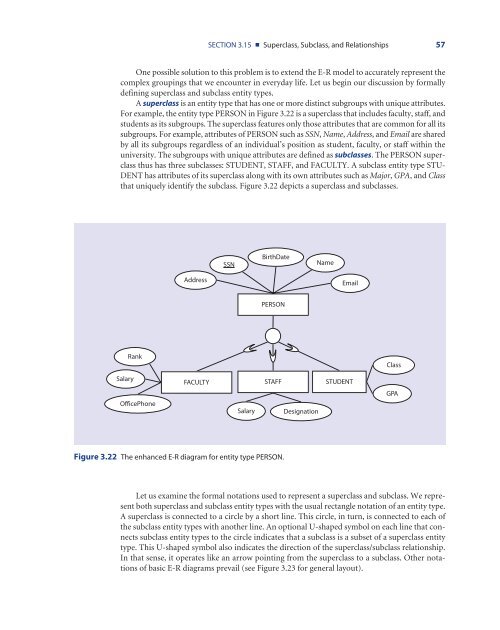
SECTION 3.15 ■ Superclass, Subclass, and Relationships 57One possible solution to this problem is to extend the E-R model to accurately represent thecomplex groupings that we encounter in everyday life. Let us begin our discussion by formallydefining superclass and subclass entity types.A superclass is an entity type that has one or more distinct subgroups with unique attributes.For example, the entity type PERSON in Figure 3.22 is a superclass that includes faculty, staff, andstudents as its subgroups. The superclass features only those attributes that are common for all itssubgroups. For example, attributes of PERSON such as SSN, Name, Address, and Email are sharedby all its subgroups regardless of an individual’s position as student, faculty, or staff within theuniversity. The subgroups with unique attributes are defined as subclasses. The PERSON superclassthus has three subclasses: STUDENT, STAFF, and FACULTY. A subclass entity type STU-DENT has attributes of its superclass along with its own attributes such as Major, GPA, and Classthat uniquely identify the subclass. Figure 3.22 depicts a superclass and subclasses.SSNBirthDateNameAddressEmailPERSONSalaryRankOfficePhoneFACULTY STAFF STUDENTSalaryDesignationClassGPAFigure 3.22 The enhanced E-R diagram for entity type PERSON.Let us examine the formal notations used to represent a superclass and subclass. We representboth superclass and subclass entity types with the usual rectangle notation of an entity type.A superclass is connected to a circle by a short line. This circle, in turn, is connected to each ofthe subclass entity types with another line. An optional U-shaped symbol on each line that connectssubclass entity types to the circle indicates that a subclass is a subset of a superclass entitytype. This U-shaped symbol also indicates the direction of the superclass/subclass relationship.In that sense, it operates like an arrow pointing from the superclass to a subclass. Other notationsof basic E-R diagrams prevail (see Figure 3.23 for general layout).