Nomenclature-1 - Moravian College Chemistry Department
Nomenclature-1 - Moravian College Chemistry Department
Nomenclature-1 - Moravian College Chemistry Department
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
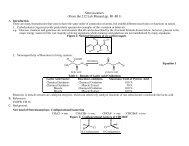
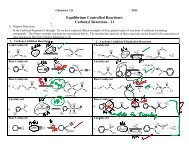
<strong>Nomenclature</strong>-1 2b. http://elchem.kaist.ac.kr/jhkwak/OkanaganPdb97/nomenclature/index.htmDeveloped by Professor emeritus at Okanagan <strong>College</strong> of the University of British Columbia, CanadaProvides naming rules and examplesSections:1. Introductions to these pages2. The IUPAC Systematic Approach to <strong>Nomenclature</strong>3. The AlkanesUnbranched AlkanesBranched AlkanesMonocyclic Alkanesc. http://www.acdlabs.com/iupac/nomenclatureDeveloped by Advanced <strong>Chemistry</strong> Development LaboratoriesGives detailed IUPAC rules for nomenclature.Sections:Recommendations 1979:A. Hydrocarbons:Acyclic Hydrocarbons/ A-1. Saturated Unbranched-chain Compounds and Univalent Radicals &/ A-2. Saturated BranchedchainCompounds and Univalent RadicalsMonocyclic Hydrocarbons/ A-11. Unsubstituted Compounds and RadicalsSummary of Rules for Naming Alkanes1. Find the longest continuous chain of CARBON atoms or the largest ring of CARBON atoms and use it to determine the base alkanename. Note: Atoms that are part of a ring cannot also be part of a chain. (See CGWW p. 26 for a list of base names.)2. Identify each substituent group attached to the base carbon chain and name it using the group name (See CGWW p. 26). If there are two ormore identical substituents in a molecule, they are named as "di-, tri-, tetra- etc. (See example in 7. below)3. For acyclic alkanes (not containing rings), number the base carbon chain from the end nearest the point of attachment of a substituent andassign each substituent a number based on its position of attachment to the main chain.4. For cycloalkanes, number the ring positions such that the sum of the position numbers will be minimum.5. Designate each substituent with the number of its position on the chain or ring. If more than one substituent is attached to the same position,each substituent should be numbered separately even if both substituents at a position have the same name. (See the example in 7. Below.)6. When two or more substituents are attached to the base chain or ring, list them alphabetically ignoring the di-, tri-, tetra etc. prefixes.7. In complex names, position numbers are separated from each other with commas and from words with dashes. e.gAcyclicCyclic3-ethyl-2,2,4-trimethylhexane4-ethyl-1-methyl-1,2-dipropylcyclohexane