Davide Cherubini - PhD Thesis - UniCA Eprints
Davide Cherubini - PhD Thesis - UniCA Eprints
Davide Cherubini - PhD Thesis - UniCA Eprints
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
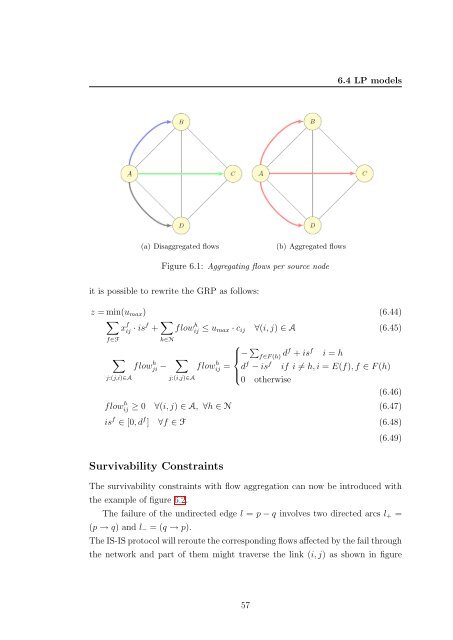
6.4 LP models(a) Disaggregated flows(b) Aggregated flowsFigure 6.1: Aggregating flows per source nodeit is possible to rewrite the GRP as follows:z = min(u max ) (6.44)∑x f ij · isf + ∑ flowij h ≤ u max · c ij ∀(i, j) ∈ A (6.45)f∈F h∈N⎧∑⎪⎨ − ∑ f∈F (h) df + is f i = hflowji h − flowij h = dj:(j,i)∈Aj:(i,j)∈A⎪⎩− is f if i ≠ h, i = E(f), f ∈ F (h)0 otherwise(6.46)flowij h ≥ 0 ∀(i, j) ∈ A, ∀h ∈ N (6.47)is f ∈ [0, d f ] ∀f ∈ F (6.48)(6.49)Survivability ConstraintsThe survivability constraints with flow aggregation can now be introduced withthe example of figure 6.2.The failure of the undirected edge l = p − q involves two directed arcs l + =(p → q) and l − = (q → p).The IS-IS protocol will reroute the corresponding flows affected by the fail throughthe network and part of them might traverse the link (i, j) as shown in figure57