Influence of Load and Sliding Speed on Friction Coefficient of IBAD ...
Influence of Load and Sliding Speed on Friction Coefficient of IBAD ...
Influence of Load and Sliding Speed on Friction Coefficient of IBAD ...
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
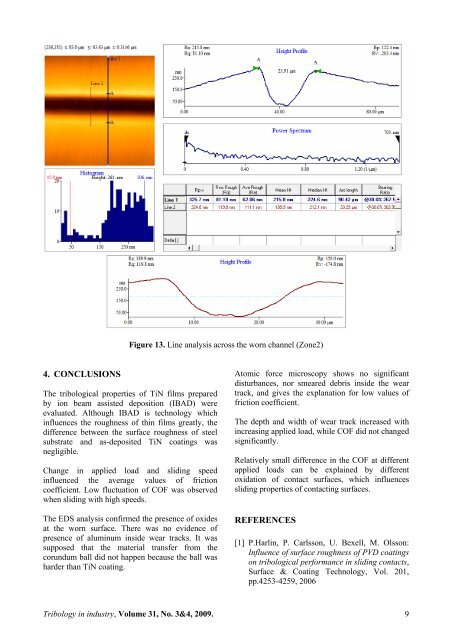
Figure 13. Line analysis across the worn channel (Z<strong>on</strong>e2)4. CONCLUSIONSThe tribological properties <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> TiN films preparedby i<strong>on</strong> beam assisted depositi<strong>on</strong> (<strong>IBAD</strong>) wereevaluated. Although <strong>IBAD</strong> is technology whichinfluences the roughness <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> thin films greatly, thedifference between the surface roughness <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> steelsubstrate <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> as-deposited TiN coatings wasnegligible.Change in applied load <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> sliding speedinfluenced the average values <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> fricti<strong>on</strong>coefficient. Low fluctuati<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> COF was observedwhen sliding with high speeds.The EDS analysis c<strong>on</strong>firmed the presence <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> oxidesat the worn surface. There was no evidence <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g>presence <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> aluminum inside wear tracks. It wassupposed that the material transfer from thecorundum ball did not happen because the ball washarder than TiN coating.Atomic force microscopy shows no significantdisturbances, nor smeared debris inside the weartrack, <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> gives the explanati<strong>on</strong> for low values <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g>fricti<strong>on</strong> coefficient.The depth <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> width <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> wear track increased withincreasing applied load, while COF did not changedsignificantly.Relatively small difference in the COF at differentapplied loads can be explained by differentoxidati<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> c<strong>on</strong>tact surfaces, which influencessliding properties <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> c<strong>on</strong>tacting surfaces.REFERENCES[1] P.Harlin, P. Carlss<strong>on</strong>, U. Bexell, M. Olss<strong>on</strong>:<str<strong>on</strong>g>Influence</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> surface roughness <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> PVD coatings<strong>on</strong> tribological performance in sliding c<strong>on</strong>tacts,Surface & Coating Technology, Vol. 201,pp.4253-4259, 2006Tribology in industry, Volume 31, No. 3&4, 2009. 9