The two dimensional heat equation - Trinity University
The two dimensional heat equation - Trinity University
The two dimensional heat equation - Trinity University
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
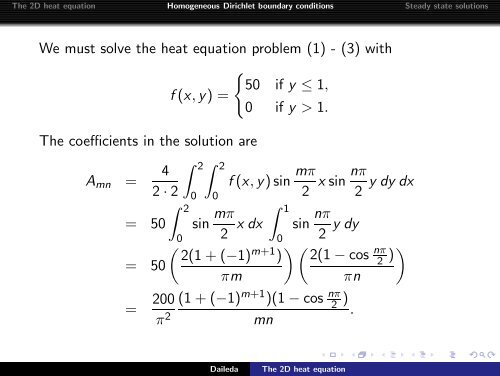
<strong>The</strong> 2D <strong>heat</strong> <strong>equation</strong> Homogeneous Dirichlet boundary conditions Steady state solutionsWe must solve the <strong>heat</strong> <strong>equation</strong> problem (1) - (3) with{50 if y ≤ 1,f(x,y) =0 if y > 1.<strong>The</strong> coefficients in the solution areA mn =42·2∫ 2 ∫ 20∫ 20f(x,y)sin mπ2 x sin nπ 2∫ 12 x dx sin nπ 2 y dy= 50 sin mπ0 0( 2(1+(−1) m+1 )() 2(1−cosnπ= 50πm πn= 200 (1+(−1) m+1 )(1−cos nπ 2 )π 2 .mny dy dx2 ))Daileda<strong>The</strong> 2D <strong>heat</strong> <strong>equation</strong>