Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division - McGraw-Hill Australia
Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division - McGraw-Hill Australia
Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division - McGraw-Hill Australia
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
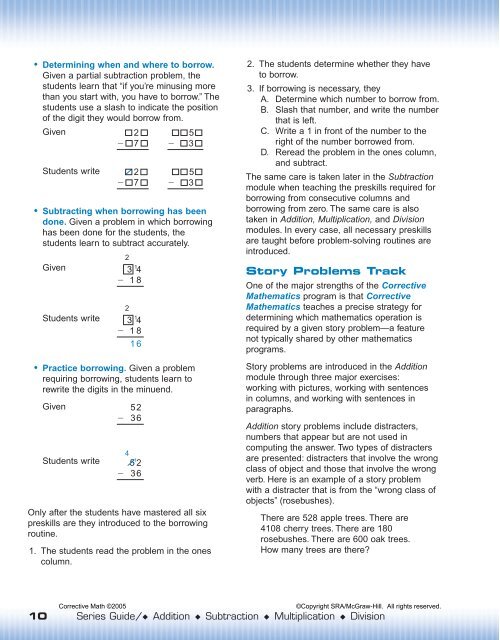
• Determining when and where to borrow.Given a partial subtraction problem, thestudents learn that “if you’re minusing morethan you start with, you have to borrow.” Thestudents use a slash to indicate the positionof the digit they would borrow from.GivenStudents write• Subtracting when borrowing has beendone. Given a problem in which borrowinghas been done for the students, thestudents learn to subtract accurately.GivenStudents write23 1 4 1823 1 4 18• Practice borrowing. Given a problemrequiring borrowing, students learn torewrite the digits in the minuend.GivenStudents write2 72 71652 3645 1 2 365 35 3Only after the students have mastered all sixpreskills are they introduced to the borrowingroutine.1. The students read the problem in the onescolumn.2. The students determine whether they haveto borrow.3. If borrowing is necessary, theyA. Determine which number to borrow from.B. Slash that number, and write the numberthat is left.C. Write a 1 in front of the number to theright of the number borrowed from.D. Reread the problem in the ones column,and subtract.The same care is taken later in the <strong>Subtraction</strong>module when teaching the preskills required forborrowing from consecutive columns andborrowing from zero. The same care is alsotaken in <strong>Addition</strong>, <strong>Multiplication</strong>, and <strong>Division</strong>modules. In every case, all necessary preskillsare taught before problem-solving routines areintroduced.Story Problems TrackOne of the major strengths of the CorrectiveMathematics program is that CorrectiveMathematics teaches a precise strategy fordetermining which mathematics operation isrequired by a given story problem—a featurenot typically shared by other mathematicsprograms.Story problems are introduced in the <strong>Addition</strong>module through three major exercises:working with pictures, working with sentencesin columns, and working with sentences inparagraphs.<strong>Addition</strong> story problems include distracters,numbers that appear but are not used incomputing the answer. Two types of distractersare presented: distracters that involve the wrongclass of object and those that involve the wrongverb. Here is an example of a story problemwith a distracter that is from the “wrong class ofobjects” (rosebushes).There are 528 apple trees. There are4108 cherry trees. There are 180rosebushes. There are 600 oak trees.How many trees are there?Corrective Math ©2005©Copyright SRA/<strong>McGraw</strong>-<strong>Hill</strong>. All rights reserved.10 Series Guide/◆ <strong>Addition</strong> ◆ <strong>Subtraction</strong> ◆ <strong>Multiplication</strong> ◆ <strong>Division</strong>