A Practical Approach to Syncope
A Practical Approach to Syncope
A Practical Approach to Syncope
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
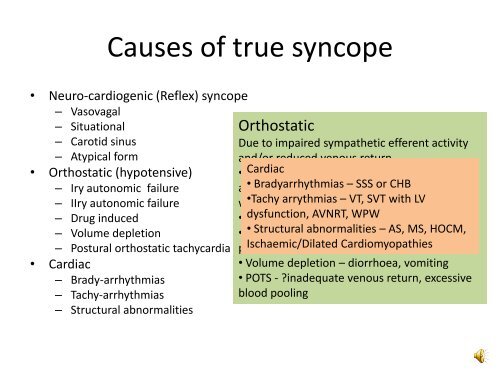
Causes of true syncope• Neuro-cardiogenic (Reflex) syncope– Vasovagal– Situational– Carotid sinus– Atypical form• Orthostatic (hypotensive)– Iry au<strong>to</strong>nomic failure– IIry au<strong>to</strong>nomic failure– Drug induced– Volume depletionDue <strong>to</strong> impaired sympathetic efferent activityDue <strong>to</strong> inappropiate function of reflexes thatand/or reduced venous returnmaintain BP in the upright posture leading <strong>to</strong>• Iry Cardiac ANF – multiple system atrophy, purehypotension (vasodeppressor) or bradycardiaau<strong>to</strong>nomic • Bradyarrhythmias failure, Lewy – SSS body or CHB dementia, ass.(cardioinhibi<strong>to</strong>ry)with •Tachy Parkinsons arrythmias – VT, SVT with LVVasovagal – prolonged standing/sitting,• IIry dysfunction, ANF – DM, AVNRT, amyloidosis, WPW ureamiaemotion, pain, blood.• Drug • Structural induced abnormalities – vasodila<strong>to</strong>rs, – AS, diuretics, MS, HOCM,Situational – cough, micturition, GI– Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome phenothiazines, Ischaemic/Dilated (POTS) antidepressantsCardiomyopathiesstimulation, laughing• Volume depletion – diorrhoea, vomitingCarotid sinus – hypersensitivity• POTS - ?inadequate venous return, excessiveAtypical – uncertain, absent triggersblood pooling• Cardiac– Brady-arrhythmias– Tachy-arrhythmias– Structural abnormalitiesNeurocardiogenicOrthostaticsyncope