Time-Domain Terahertz - Toptica
Time-Domain Terahertz - Toptica
Time-Domain Terahertz - Toptica
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
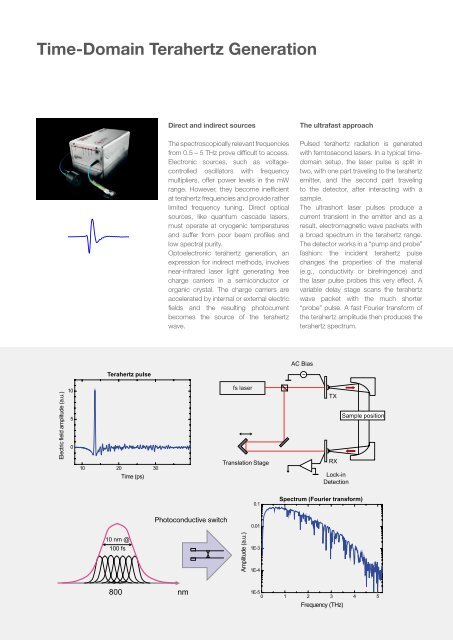
<strong>Time</strong>-<strong>Domain</strong> <strong>Terahertz</strong> GenerationDirect and indirect sourcesThe spectroscopically relevant frequenciesfrom 0.5 – 5 THz prove difficult to access.electronic sources, such as voltagecontrolledoscillators with frequencymultipliers, offer power levels in the mWrange. However, they become inefficientat terahertz frequencies and provide ratherlimited frequency tuning. direct opticalsources, like quantum cascade lasers,must operate at cryogenic temperaturesand suffer from poor beam profiles andlow spectral purity.optoelectronic terahertz generation, anexpression for indirect methods, involvesnear-infrared laser light generating freecharge carriers in a semiconductor ororganic crystal. The charge carriers areaccelerated by internal or external electricfields and the resulting photocurrentbecomes the source of the terahertzwave.The ultrafast approachPulsed terahertz radiation is generatedwith femtosecond lasers. In a typical timedomainsetup, the laser pulse is split intwo, with one part traveling to the terahertzemitter, and the second part travelingto the detector, after interacting with asample.The ultrashort laser pulses produce acurrent transient in the emitter and as aresult, electromagnetic wave packets witha broad spectrum in the terahertz range.The detector works in a “pump and probe”fashion: the incident terahertz pulsechanges the properties of the material(e.g., conductivity or birefringence) andthe laser pulse probes this very effect. Avariable delay stage scans the terahertzwave packet with the much shorter“probe” pulse. A fast Fourier transform ofthe terahertz amplitude then produces theterahertz spectrum.AC Bias<strong>Terahertz</strong> pulse~Electric field amplitude (a.u.)105010 20 30<strong>Time</strong> (ps)fs laserTranslation StageTXRXLock-inDetectionSample position0.1Spectrum (Fourier transform)Photoconductive switch0.0110 nm @100 fsAmplitude (a.u.)1E-31E-4800 nm1E-50 1 2 3 4 5Frequency (THz)