SSK Unit 4.2 Planning Guide
SSK Unit 4.2 Planning Guide
SSK Unit 4.2 Planning Guide
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
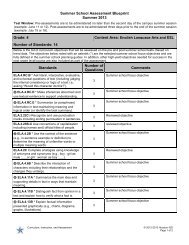
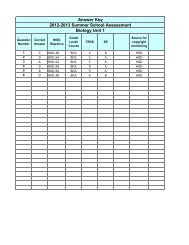
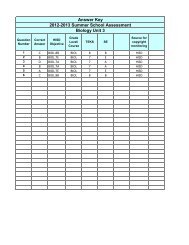
• Poetic forms and poetic techniques often reflect the poem’s purpose.1. What are some of the poetic forms?2. What are some examples of poetic techniques?3. How do authors reveal the purpose of a poem?Assessment ConnectionsHISD PLANNING GUIDEEnglish Language Arts Grade 8SUMMER SCHOOL• Performance- Students publish an expository essay of sufficient length that includes organized and accuratelyconveyed information, effective introductory and concluding paragraphs and a variety of sentence structures, acontrolling idea or thesis, an organizing structure (e.g. inductive/deductive, compare/contrast) appropriate to purpose,audience, and context, relevant information and valid inferences, rhetorical devices, and transitions betweenparagraphs.Formative Assessment- Expository Essay Rubric• Students select poetry of various forms and write introductions to ascertain their knowledge of various forms ofpoetry.Formative Assessment- May I Introduce You• Students complete a cold read and assessment to ascertain their skills at making inferences while reading poetry andanalyzing figurative language.Formative Assessment- Barter• Students make connections between two poems to ascertain their ability to make connections across texts.Formative Assessment- Don’t Quit and Don’t Give Up• Students use released STAAR items to gain familiarity with the stems.STAAR Released Items: Reading (Selection 1, Items: 1-4, 7 and Selection 2, Items: 4, 6, 7)Texas English Language Proficiency Assessment System (TELPAS): End-of-year assessment in listening,speaking, reading, and writing for all students coded as LEP (ELL) and for students who are LEP but have parentaldenials for Language Support Programming (coded WH). For the Writing TELPAS, teachers provide five writingsamples – one narrative about a past event, two academic (from science, social studies, or mathematics), and twoothers.Instructional ConsiderationsThis Curriculum <strong>Unit</strong> <strong>Planning</strong> <strong>Guide</strong> is designed to support HISD teachers in planning daily lessons that meet the needsof students based on data generated during the school year. Teachers should utilize data to individualize instruction andto select focus genres and objectives. To ensure effective planning and instruction, refer to the components outlined bythe Houston ISD Instructional Practice Rubric.VocabularyPrerequisitesStudents should possess dictionary skills, be able to use context clues to ascertain meaning, and demonstrate ability tomake meaning of text.Background Knowledge for TeacherExplicitly teach how to use a dictionary and thesaurus. See Literature Grade 8 and Common Context Clues in BestPractices Toolkit in Resources.Instructional Accommodations for Diverse Learners The regular use of a bilingual dictionary leads to faster acquisition of English.Continue to use Vocabulary Notebooks. Develop vocabulary by listening to selections read aloud.Vocabulary integration allows students to learn and understand new vocabulary through creating personal meaning.Vocabulary integration includes: Choral pronunciation Contextual read-alouds Graphic organizers - English Language Proficiency Standards (ELPS) - Literacy Leads the Way Best Practices - Aligned to Upcoming State Readiness Standard- State Process Standard R - State Readiness Standard S - State Supporting Standard© Houston ISD Curriculum2013 – 2014Page 2 of 6