SaltRx 2 User Guide HR2-109 - Hampton Research
SaltRx 2 User Guide HR2-109 - Hampton Research
SaltRx 2 User Guide HR2-109 - Hampton Research
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
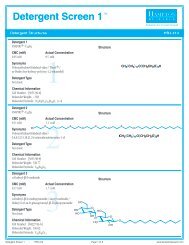
<strong>SaltRx</strong>TM2Solutions for Crystal Growth<strong>User</strong> <strong>Guide</strong> <strong>HR2</strong>-<strong>109</strong> (pg 2)Figure 4Typical observations in acrystallization experimentClear DropSkin /PrecipitatePrecipitatePrecipitate /PhaseQuasiCrystalsMicrocrystalsNeedleClusterPlatesRod ClusterSingleCrystalExamine The DropCarefully examine the drops under a stereo microscope (10 to100x magnification) immediately after setting up the screen. Recordall observations and be particularly careful to scan the focalplane for small crystals. Observe the drops once each day for thefirst week, then once a week there after. Records should indicatewhether the drop is clear, contains precipitate, and or crystals. Itis helpful to describe the drop contents using descriptive terms.Adding magnitude is also helpful. Example: 4+ yellow/brownfine precipitate, 2+ small bipyramid crystals, clear drop, 3+ needleshaped crystals in 1+ white precipitate. One may also employa standard numerical scoring scheme (Clear = 0, Precipitate = 1,Crystal = 10, etc). Figure 4 shows typical examples of what onemight observe in a crystallization experiment.Interpreting <strong>SaltRx</strong> 2Clear drops indicate that either the relative supersaturation of thesample and reagent is too low or the drop has not yet completedequilibration. If the drop remains clear after 3 to 4 weeks considerrepeating the <strong>SaltRx</strong> 2 condition and doubling the sampleconcentration. If more than 70 of the 96 <strong>SaltRx</strong> 2 drops are clearconsider doubling the sample concentration and repeating theentire screen.Drops containing precipitate indicate that either the relative supersaturationof the sample and reagent is too high, the samplehas denatured, or the sample is heterogeneous. To reduce therelative supersaturation, dilute the sample twofold and repeat the<strong>SaltRx</strong> 2 condition. If more than 70 of the 96 <strong>SaltRx</strong> 2 dropscontain precipitate and no crystals are present, consider dilutingthe sample concentration in half and repeating the entire screen.If sample denaturation is suspect, take measures to stabilize thesample (add reducing agent, ligands, glycerol, salt, or other stabilizingagents). If the sample is impure, aggregated, or heterogeneoustake measures to pursue homogeneity. It is possible toobtain crystals from precipitate so do not discard nor ignore adrop containing precipitate. If possible, examine drops containingprecipitate under polarizing optics to differentiate precipitatefrom microcrystalline material.If the drop contains a macromolecular crystal the relative supersaturationof the sample and reagent is appropriate for crystallization.The next step is to optimize the preliminary conditions(pH, salt type, salt concentration, precipitant type, precipitantconcentration, sample concentration, temperature, additives, andother crystallization variables) which produced the crystal in orderto improve crystal size and quality.Compare the observations between the 4°C and room temperatureincubation to determine the effect of temperature on samplesolubility.Different results in the same drops at different temperatures indicatethat sample solubility is temperature dependent and that oneshould include temperature as a variable in subsequent screensand optimization experiments.Retain and observe plates until the drops are dried out. Crystalgrowth can occur within 15 minutes or one year.<strong>SaltRx</strong> 2 Formulation<strong>SaltRx</strong> 2 reagents are formulated using the highest purity chemicals,ultrapure water (18.2 Megohm-cm, 5 ppb TOC) and are sterilefiltered using 0.22 micron filters into sterile containers (nopreservatives added).<strong>SaltRx</strong> 2 reagents are readily reproduced using <strong>Hampton</strong> <strong>Research</strong>Optimize stock solutions of salts, polymers and buffers.Optimize stock reagents make reproducing <strong>SaltRx</strong> 2 reagents fast,convenient and easy. Dilutions can be performed directly into thecrystallization plate using Optimize stock reagents.<strong>SaltRx</strong> 2 reagents containing buffers are formulated by creatinga 1.0 M stock buffer, titrated to the desired pH using hydrochloricacid or sodium hydroxide. The buffer is then diluted with theother reagent components and water. No further pH adjustmentis required.<strong>SaltRx</strong> 2 reagents are stable at room temperature and are best ifused within 12 months of receipt.If the sample contains phosphate, borate, or carbonate buffers itis possible to obtain inorganic crystals (false positives) when using<strong>SaltRx</strong> 2 reagents containing divalent cations. To avoid falsepositives use phosphate, borate, or carbonate buffers at concentrationsof 10 mM or less or exchange the phosphate, borate, orcarbonate buffer with a more soluble buffer that does not complexwith divalent cations such as HEPES sodium.References and Readings1. Crystallization of nucleic acids and proteins, Edited by A. Ducruixand R. Giege, The Practical Approach Series, Oxford Univ.Press, 1992.2. Current approaches to macromolecular crystallization.McPherson, A. Eur. J. Biochem. 189, 1-23, 1990.