mobile ad hoc networks providing efficient multicasting techniques
mobile ad hoc networks providing efficient multicasting techniques
mobile ad hoc networks providing efficient multicasting techniques
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
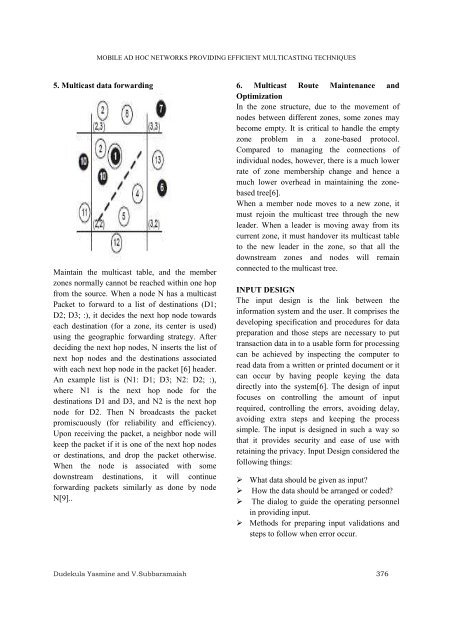
MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS PROVIDING EFFICIENT MULTICASTING TECHNIQUES5. Multicast data forwardingMaintain the multicast table, and the memberzones normally cannot be reached within one hopfrom the source. When a node N has a multicastPacket to forward to a list of destinations (D1;D2; D3; :), it decides the next hop node towardseach destination (for a zone, its center is used)using the geographic forwarding strategy. Afterdeciding the next hop nodes, N inserts the list ofnext hop nodes and the destinations associatedwith each next hop node in the packet [6] he<strong>ad</strong>er.An example list is (N1: D1; D3; N2: D2; :),where N1 is the next hop node for thedestinations D1 and D3, and N2 is the next hopnode for D2. Then N bro<strong>ad</strong>casts the packetpromiscuously (for reliability and efficiency).Upon receiving the packet, a neighbor node willkeep the packet if it is one of the next hop nodesor destinations, and drop the packet otherwise.When the node is associated with somedownstream destinations, it will continueforwarding packets similarly as done by nodeN[9]..6. Multicast Route Maintenance andOptimizationIn the zone structure, due to the movement ofnodes between different zones, some zones maybecome empty. It is critical to handle the emptyzone problem in a zone-based protocol.Compared to managing the connections ofindividual nodes, however, there is a much lowerrate of zone membership change and hence amuch lower overhe<strong>ad</strong> in maintaining the zonebasedtree[6].When a member node moves to a new zone, itmust rejoin the multicast tree through the newle<strong>ad</strong>er. When a le<strong>ad</strong>er is moving away from itscurrent zone, it must handover its multicast tableto the new le<strong>ad</strong>er in the zone, so that all thedownstream zones and nodes will remainconnected to the multicast tree.INPUT DESIGNThe input design is the link between theinformation system and the user. It comprises thedeveloping specification and procedures for datapreparation and those steps are necessary to puttransaction data in to a usable form for processingcan be achieved by inspecting the computer tore<strong>ad</strong> data from a written or printed document or itcan occur by having people keying the dat<strong>ad</strong>irectly into the system[6]. The design of inputfocuses on controlling the amount of inputrequired, controlling the errors, avoiding delay,avoiding extra steps and keeping the processsimple. The input is designed in such a way sothat it provides security and ease of use withretaining the privacy. Input Design considered thefollowing things: What data should be given as input? How the data should be arranged or coded? The dialog to guide the operating personnelin <strong>providing</strong> input. Methods for preparing input validations andsteps to follow when error occur.Dudekula Yasmine and V.Subbaramaiah 376