Dissociable correlates of recollection and familiarity ... - ResearchGate
Dissociable correlates of recollection and familiarity ... - ResearchGate
Dissociable correlates of recollection and familiarity ... - ResearchGate
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
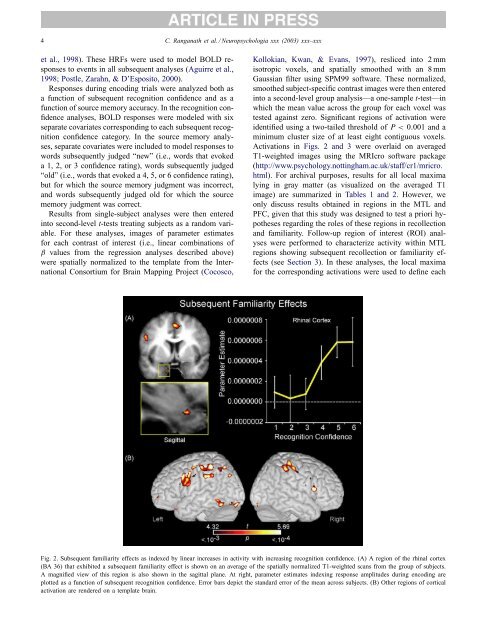
4 C. Ranganath et al. / Neuropsychologia xxx (2003) xxx–xxxet al., 1998). These HRFs were used to model BOLD responsesto events in all subsequent analyses (Aguirre et al.,1998; Postle, Zarahn, & D’Esposito, 2000).Responses during encoding trials were analyzed both asa function <strong>of</strong> subsequent recognition confidence <strong>and</strong> as afunction <strong>of</strong> source memory accuracy. In the recognition confidenceanalyses, BOLD responses were modeled with sixseparate covariates corresponding to each subsequent recognitionconfidence category. In the source memory analyses,separate covariates were included to model responses towords subsequently judged “new” (i.e., words that evokeda 1, 2, or 3 confidence rating), words subsequently judged“old” (i.e., words that evoked a 4, 5, or 6 confidence rating),but for which the source memory judgment was incorrect,<strong>and</strong> words subsequently judged old for which the sourcememory judgment was correct.Results from single-subject analyses were then enteredinto second-level t-tests treating subjects as a r<strong>and</strong>om variable.For these analyses, images <strong>of</strong> parameter estimatesfor each contrast <strong>of</strong> interest (i.e., linear combinations <strong>of</strong>β values from the regression analyses described above)were spatially normalized to the template from the InternationalConsortium for Brain Mapping Project (Cocosco,Kollokian, Kwan, & Evans, 1997), resliced into 2 mmisotropic voxels, <strong>and</strong> spatially smoothed with an 8 mmGaussian filter using SPM99 s<strong>of</strong>tware. These normalized,smoothed subject-specific contrast images were then enteredinto a second-level group analysis—a one-sample t-test—inwhich the mean value across the group for each voxel wastested against zero. Significant regions <strong>of</strong> activation wereidentified using a two-tailed threshold <strong>of</strong> P