Safe Handling of Hazardous Drugs
YU0w0
YU0w0
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
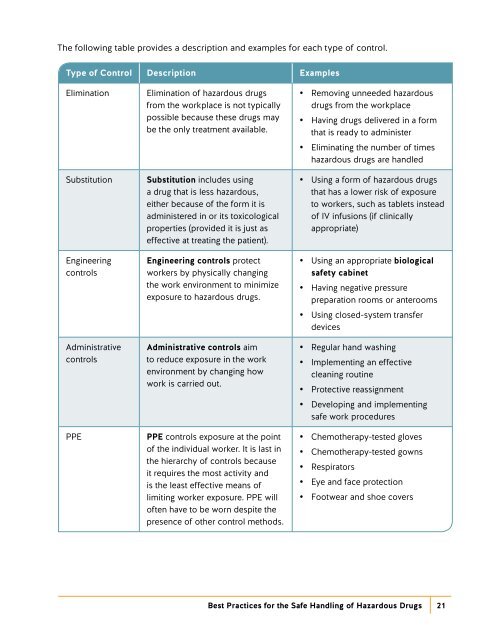
The following table provides a description and examples for each type <strong>of</strong> control.<br />
Type <strong>of</strong> Control Description Examples<br />
Elimination<br />
Substitution<br />
Engineering<br />
controls<br />
Administrative<br />
controls<br />
PPE<br />
Elimination <strong>of</strong> hazardous drugs<br />
from the workplace is not typically<br />
possible because these drugs may<br />
be the only treatment available.<br />
Substitution includes using<br />
a drug that is less hazardous,<br />
either because <strong>of</strong> the form it is<br />
administered in or its toxicological<br />
properties (provided it is just as<br />
effective at treating the patient).<br />
Engineering controls protect<br />
workers by physically changing<br />
the work environment to minimize<br />
exposure to hazardous drugs.<br />
Administrative controls aim<br />
to reduce exposure in the work<br />
environment by changing how<br />
work is carried out.<br />
PPE controls exposure at the point<br />
<strong>of</strong> the individual worker. It is last in<br />
the hierarchy <strong>of</strong> controls because<br />
it requires the most activity and<br />
is the least effective means <strong>of</strong><br />
limiting worker exposure. PPE will<br />
<strong>of</strong>ten have to be worn despite the<br />
presence <strong>of</strong> other control methods.<br />
••<br />
Removing unneeded hazardous<br />
drugs from the workplace<br />
••<br />
Having drugs delivered in a form<br />
that is ready to administer<br />
••<br />
Eliminating the number <strong>of</strong> times<br />
hazardous drugs are handled<br />
••<br />
Using a form <strong>of</strong> hazardous drugs<br />
that has a lower risk <strong>of</strong> exposure<br />
to workers, such as tablets instead<br />
<strong>of</strong> IV infusions (if clinically<br />
appropriate)<br />
••<br />
Using an appropriate biological<br />
safety cabinet<br />
••<br />
Having negative pressure<br />
preparation rooms or anterooms<br />
••<br />
Using closed-system transfer<br />
devices<br />
••<br />
Regular hand washing<br />
••<br />
Implementing an effective<br />
cleaning routine<br />
••<br />
Protective reassignment<br />
••<br />
Developing and implementing<br />
safe work procedures<br />
••<br />
Chemotherapy-tested gloves<br />
••<br />
Chemotherapy-tested gowns<br />
••<br />
Respirators<br />
••<br />
Eye and face protection<br />
••<br />
Footwear and shoe covers<br />
Best Practices for the <strong>Safe</strong> <strong>Handling</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Hazardous</strong> <strong>Drugs</strong> 21