ACCT 346 DeVry Week 6 Quiz 2 Different Sets
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>ACCT</strong> <strong>346</strong> <strong>DeVry</strong> <strong>Week</strong> 6 <strong>Quiz</strong> 2 <strong>Different</strong> <strong>Sets</strong><br />
Downloading is very simple, you can download this Course here:<br />
http://mindsblow.us/question-details/<strong>ACCT</strong>-<strong>346</strong>-<strong>DeVry</strong>-<strong>Week</strong>-6-<strong>Quiz</strong>-2-<strong>Different</strong>-<strong>Sets</strong>/4189<br />
Or<br />
Contact us at:<br />
help@mindblows.us<br />
<strong>ACCT</strong> <strong>346</strong> <strong>DeVry</strong> <strong>Week</strong> 6 <strong>Quiz</strong> (2 <strong>Different</strong> <strong>Sets</strong>)<br />
<strong>ACCT</strong> <strong>346</strong> <strong>DeVry</strong> <strong>Week</strong> 6 <strong>Quiz</strong> (Version 1)<br />
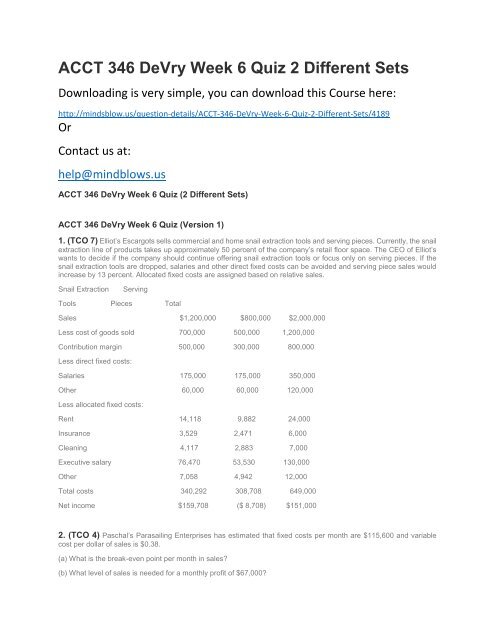
1. (TCO 7) Elliot’s Escargots sells commercial and home snail extraction tools and serving pieces. Currently, the snail<br />
extraction line of products takes up approximately 50 percent of the company’s retail floor space. The CEO of Elliot’s<br />
wants to decide if the company should continue offering snail extraction tools or focus only on serving pieces. If the<br />
snail extraction tools are dropped, salaries and other direct fixed costs can be avoided and serving piece sales would<br />
increase by 13 percent. Allocated fixed costs are assigned based on relative sales.<br />
Snail Extraction<br />
Serving<br />
Tools Pieces Total<br />
Sales $1,200,000 $800,000 $2,000,000<br />
Less cost of goods sold 700,000 500,000 1,200,000<br />
Contribution margin 500,000 300,000 800,000<br />
Less direct fixed costs:<br />
Salaries 175,000 175,000 350,000<br />
Other 60,000 60,000 120,000<br />
Less allocated fixed costs:<br />
Rent 14,118 9,882 24,000<br />
Insurance 3,529 2,471 6,000<br />
Cleaning 4,117 2,883 7,000<br />
Executive salary 76,470 53,530 130,000<br />
Other 7,058 4,942 12,000<br />
Total costs 340,292 308,708 649,000<br />
Net income $159,708 ($ 8,708) $151,000<br />
2. (TCO 4) Paschal’s Parasailing Enterprises has estimated that fixed costs per month are $115,600 and variable<br />
cost per dollar of sales is $0.38.<br />
(a) What is the break-even point per month in sales?<br />
(b) What level of sales is needed for a monthly profit of $67,000?
(c) For the month of August, Paschal’s anticipates sales of $585,000. What is the expected level of profit?<br />
3. (TCO 6) Princess Cruise Lines has the following service departments; concierge, valet, and maintenance. Expense<br />
for these departments are allocated to Mediterranean and Trans-Atlantic cruises. Expenses for the departments are<br />
totaled (both variable and fixed components are combined) and as follows:<br />
Concierge $2,500,000<br />
Valet $1,750,000<br />
Maintenance $4,250,000<br />
The sea miles logged are 6,000,000 for the Mediterranean and 18,000,000 for the Trans-<br />
Atlanticvoyages.<br />
Based upon the sea miles logged, allocate the service department costs.<br />
4. (TCO 9) Thurman Munster, the owner of Adams Family RVs, is considering the addition of a service center his<br />
lot. The building and equipment are estimated to cost $1,100,000 and both the building and equipment will be<br />
depreciated over 10 years using the straight-line method. The building and equipment have zero estimated residual<br />
value at the end of 10 years. Munster’s required rate of return for this project is 12 percent. Net income related to each<br />
year of the investment is as follows:<br />
Revenue $450,000<br />
Less:<br />
Material cost $ 60,000<br />
Labor 100,000<br />
Depreciation 110,000<br />
Other 10,000 280,000<br />
Income before taxes 170,000<br />
Taxes at 40% 68,000<br />
Net income $102,000<br />
(a) Determine the net present value of the investment in the service center. Should Munster invest in the service center?<br />
(b) Calculate the internal rate of return of the investment to the nearest ½ percent.<br />
(c) Calculate the payback period of the investment.<br />
(d) Calculate the accounting rate of return.<br />
5. (TCO 5) The following information relates to Vice Versa Ventures for calendar year 20XX, the company’s first year<br />
of operations:<br />
Units produced 20,000<br />
Units sold 17,000<br />
Selling price per unit $35<br />
Direct material per unit $5<br />
Direct labor per unit $5<br />
Variable manufacturing overhead per unit $2<br />
Variable selling cost per unit $3<br />
Annual fixed manufacturing overhead $160,000
Annual fixed selling and administrative expense $80,000<br />
(a) Prepare an income statement using full costing.<br />
(b) Prepare an income statement using variable costing.<br />
6. (TCO 8) Leekee Shipyards has a new barnacle removing product for ocean going vessels. The company invests<br />
$1,200,000 in operating assets and plans to produce and sell 400,000 units per year. Leekee wants to make a return<br />
on investment of 20% each year. Leekee needs to know what price to charge for this product.<br />
Use the absorption costing approach to determine the markup necessary to make the desired return on investment<br />
based on the following information:<br />
Per Unit<br />
Total<br />
Direct Materials $ 2.00<br />
Direct Labor $ 1.50<br />
Variable Manufacturing Overhead $ 1.00<br />
Fixed Manufacturing Overhead $ 100,000<br />
Variable Selling and Administrative Expense $ 0.10<br />
Fixed Selling and Administrative Expense $ 100,000<br />
<strong>ACCT</strong> <strong>346</strong> <strong>DeVry</strong> <strong>Week</strong> 6 <strong>Quiz</strong> (Version 2)<br />
Question 1. Question : Which of the following costs is not relevant in decision making?<br />
Sunk cost<br />
Incremental cost<br />
Opportunity cost<br />
<strong>Different</strong>ial cost<br />
Question 2. Question : Which of the following does not take the time value of money into account?<br />
Internal rate of return<br />
Net present value<br />
Payback period<br />
None of the above<br />
Question 3. Question : Which of the following is not a capital budgeting decision?<br />
Purchasing new equipment<br />
Replacing old equipment<br />
Producing a film project<br />
Planning for retirement<br />
Question 4. Question : Which of the following is an example of a sunk cost?<br />
Direct materials<br />
Variable overhead<br />
Equipment depreciation
Future cost<br />
Question 5. Question : A revenue that differs between alternatives is called a(n):<br />
Incremental revenue.<br />
Irrelevant revenue.<br />
Joint revenue.<br />
Opportunity revenue.<br />
Question 6. Question : Capital expenditure decisions<br />
are also called capital budgeting decisions.<br />
involve the acquisition of long-lived assets.<br />
have a major, long-term effect on a firm’s operations.<br />
All of the above are correct<br />
Question 7. Question : The rate of return that equates the present value of future cash flows to the investment<br />
outlay is the<br />
hurdle rate.<br />
internal rate of return.<br />
payback return.<br />
accounting rate of return.<br />
Question 8. Question : Which of the following is never considered in incremental analysis?<br />
Incremental revenue<br />
Sunk costs<br />
Incremental profit<br />
<strong>Different</strong>ial costs<br />
Question 9. Question : Which of the following is often not a differential cost?<br />
Direct labor<br />
Direct material<br />
Variable manufacturing overhead<br />
Fixed manufacturing overhead<br />
Question 10. Question : The required rate of return used to calculate an investment’s net present value is related<br />
to the firm’s<br />
contribution margin.<br />
cost of capital.<br />
depreciation methods.<br />
fixed costs.