Olympiad 3
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Exercise 18. If the area of a regular hexagon ABCDEF is 54 √ 3 cm 2 and<br />
AB = x cm, find x.<br />
Exercise 19. The Angle bisector theorem.<br />
Theorem 1. Consider triangle ABC.<br />
Let the angle bisector of angle A intersect<br />
side BC at a point D between<br />
B and C. The angle bisector theorem<br />
states that<br />
BD<br />
CD = AB<br />
AC<br />
Prove this theorem.<br />
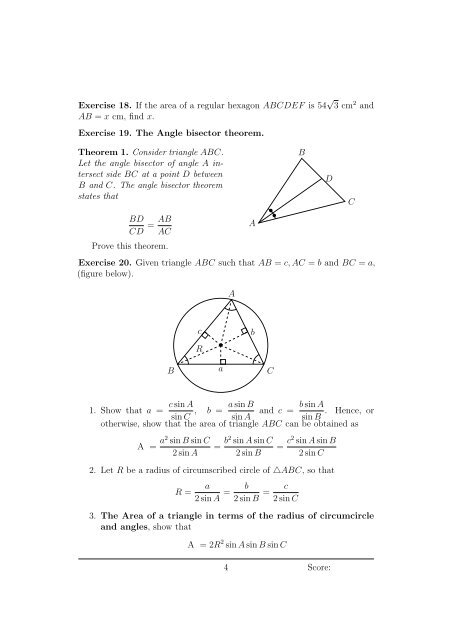
Exercise 20. Given triangle ABC such that AB = c, AC = b and BC = a,<br />
(figure below).<br />
A<br />
A<br />
• •<br />
B<br />
D<br />
C<br />
c<br />
R<br />
•<br />
b<br />
B<br />
a<br />
C<br />
1. Show that a = c sin A<br />
sin C , b = a sin B<br />
b sin A<br />
and c =<br />
sin A<br />
sin B . Hence, or<br />
otherwise, show that the area of triangle ABC can be obtained as<br />
A = a2 sin B sin C<br />
2 sin A<br />
= b2 sin A sin C<br />
2 sin B<br />
= c2 sin A sin B<br />
2 sin C<br />
2. Let R be a radius of circumscribed circle of △ABC, so that<br />
R =<br />
a<br />
2 sin A = b<br />
2 sin B = c<br />
2 sin C<br />
3. The Area of a triangle in terms of the radius of circumcircle<br />
and angles, show that<br />
A = 2R 2 sin A sin B sin C<br />
4 Score: