LessonThreeNeSGeometricBeautyofSnowflakesPrt3Rvsd121016.pptx
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
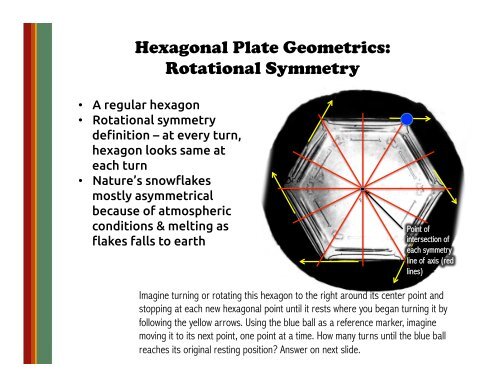
Hexagonal Plate Geometrics:<br />
Rotational Symmetry<br />
• A regular hexagon<br />
• Rotational symmetry<br />
definition – at every turn,<br />
hexagon looks same at<br />
each turn<br />
• Nature’s snowflakes<br />
mostly asymmetrical<br />
because of atmospheric<br />
conditions & melting as<br />
flakes falls to earth<br />
Point of<br />
intersection of<br />
each symmetry<br />
line of axis (red<br />
lines)<br />
Imagine turning or rotating this hexagon to the right around its center point and<br />
stopping at each new hexagonal point until it rests where you began turning it by<br />
following the yellow arrows. Using the blue ball as a reference marker, imagine<br />
moving it to its next point, one point at a time. How many turns until the blue ball<br />
reaches its original resting position? Answer on next slide.