Roxana - Gabriela HORINCAR Refresh Strategies and Online ... - LIP6
Roxana - Gabriela HORINCAR Refresh Strategies and Online ... - LIP6
Roxana - Gabriela HORINCAR Refresh Strategies and Online ... - LIP6
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
items with the publication frequency of λ = 10 items/hour, an aggregator that refreshes<br />
that source less than once an hour r = 1 will lose items, as the source becomes saturated<br />
before being refreshed.<br />
Definition 2.1.7. Saturation coefficient<br />
Given the publication window size Ws, the publication frequency λ <strong>and</strong> the refresh rate r<br />
of the source s, we define the saturation coefficient SatCoeff(n, s) ∈ [0, 1] of source s in<br />
relation with aggregator n as the percentage of items published by s <strong>and</strong> lost by n:<br />
�<br />
Ws·r<br />
1 −<br />
SatCoeff(n, s) =<br />
λ if Ws · r < λ<br />
0 otherwise<br />
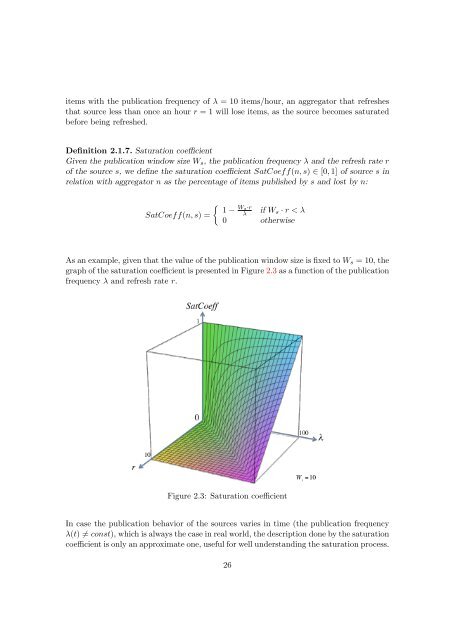
As an example, given that the value of the publication window size is fixed to Ws = 10, the<br />
graph of the saturation coefficient is presented in Figure 2.3 as a function of the publication<br />
frequency λ <strong>and</strong> refresh rate r.<br />
Figure 2.3: Saturation coefficient<br />
In case the publication behavior of the sources varies in time (the publication frequency<br />
λ(t) �= const), which is always the case in real world, the description done by the saturation<br />
coefficient is only an approximate one, useful for well underst<strong>and</strong>ing the saturation process.<br />
26