Cyber Defense eMagazine August Edition for 2021
Cyber Defense eMagazine August Edition for 2021 #CDM #CYBERDEFENSEMAG @CyberDefenseMag by @Miliefsky a world-renowned cyber security expert and the Publisher of Cyber Defense Magazine as part of the Cyber Defense Media Group as well as Yan Ross, US Editor-in-Chief, Pieruligi Paganini, Co-founder & International Editor-in-Chief, Stevin Miliefsky, President and many more writers, partners and supporters who make this an awesome publication! Thank you all and to our readers! OSINT ROCKS! #CDM #CDMG #OSINT #CYBERSECURITY #INFOSEC #BEST #PRACTICES #TIPS #TECHNIQUES
Cyber Defense eMagazine August Edition for 2021 #CDM #CYBERDEFENSEMAG @CyberDefenseMag by @Miliefsky a world-renowned cyber security expert and the Publisher of Cyber Defense Magazine as part of the Cyber Defense Media Group as well as Yan Ross, US Editor-in-Chief, Pieruligi Paganini, Co-founder & International Editor-in-Chief, Stevin Miliefsky, President and many more writers, partners and supporters who make this an awesome publication! Thank you all and to our readers! OSINT ROCKS! #CDM #CDMG #OSINT #CYBERSECURITY #INFOSEC #BEST #PRACTICES #TIPS #TECHNIQUES
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
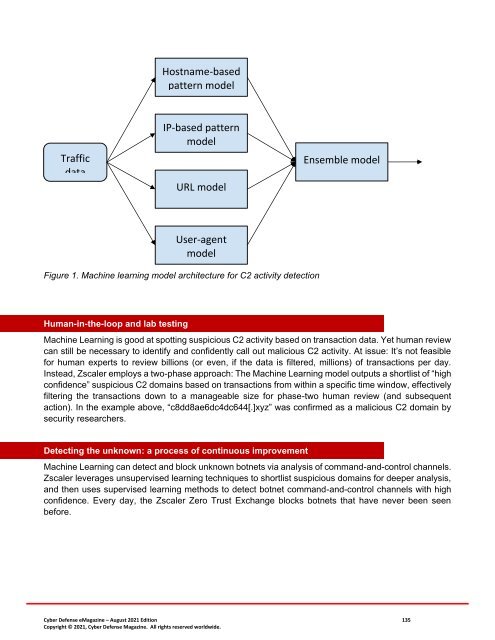
Hostname-based<br />
pattern model<br />
Traffic<br />
data<br />
IP-based pattern<br />
model<br />
URL model<br />
Ensemble model<br />
User-agent<br />
model<br />
Figure 1. Machine learning model architecture <strong>for</strong> C2 activity detection<br />
Human-in-the-loop and lab testing<br />
Machine Learning is good at spotting suspicious C2 activity based on transaction data. Yet human review<br />
can still be necessary to identify and confidently call out malicious C2 activity. At issue: It’s not feasible<br />
<strong>for</strong> human experts to review billions (or even, if the data is filtered, millions) of transactions per day.<br />
Instead, Zscaler employs a two-phase approach: The Machine Learning model outputs a shortlist of “high<br />
confidence” suspicious C2 domains based on transactions from within a specific time window, effectively<br />
filtering the transactions down to a manageable size <strong>for</strong> phase-two human review (and subsequent<br />
action). In the example above, “c8dd8ae6dc4dc644[.]xyz” was confirmed as a malicious C2 domain by<br />
security researchers.<br />
Detecting the unknown: a process of continuous improvement<br />
Machine Learning can detect and block unknown botnets via analysis of command-and-control channels.<br />
Zscaler leverages unsupervised learning techniques to shortlist suspicious domains <strong>for</strong> deeper analysis,<br />
and then uses supervised learning methods to detect botnet command-and-control channels with high<br />
confidence. Every day, the Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange blocks botnets that have never been seen<br />
be<strong>for</strong>e.<br />
<strong>Cyber</strong> <strong>Defense</strong> <strong>eMagazine</strong> – <strong>August</strong> <strong>2021</strong> <strong>Edition</strong> 135<br />
Copyright © <strong>2021</strong>, <strong>Cyber</strong> <strong>Defense</strong> Magazine. All rights reserved worldwide.