- Page 1 and 2:
Second Edition JOCHEN SCHILLER
- Page 4 and 5:
Jochen H. Schiller Mobile Communica
- Page 6:
To my students and Cora
- Page 9 and 10:
viii Mobile communications 2.5 Mult
- Page 11 and 12:
x Mobile communications 5.4 Routing
- Page 13 and 14:
xii Mobile communications 9.1.3 Fas
- Page 15 and 16:
About the author Jochen Schiller is
- Page 17 and 18:
xvi Mobile communications the book
- Page 19 and 20:
xviii Mobile communications ● Mor
- Page 22 and 23:
Introduction 1 What will computers
- Page 24 and 25:
1.1 Applications Although many appl
- Page 26 and 27:
LAN, WLAN 780 kbit/s GSM/EDGE 384 k
- Page 28 and 29:
your wireless travel guide to ‘pu
- Page 30 and 31:
can predict the future of communica
- Page 32 and 33:
handover, i.e., changing of the bas
- Page 34 and 35:
networks. It works at the license-f
- Page 36 and 37:
gross data rates of 54 Mbit/s. This
- Page 38 and 39:
● Interference: Radio transmissio
- Page 40 and 41:
on the end-systems communicate with
- Page 42 and 43:
After chapter 3, the reader can sel
- Page 44 and 45:
The reader can find review exercise
- Page 46 and 47:
Wireless transmission 2 This book f
- Page 48 and 49:
Wireless transmission 27 digital au
- Page 50 and 51:
UMTS (TDD) 1900-1920 2020-2025 Cord
- Page 52 and 53:
2.2 Signals Signals are the physica
- Page 54 and 55:
Wireless transmission 33 side world
- Page 56 and 57:
Ground plane λ/4 A more advanced s
- Page 58 and 59:
Wireless transmission 37 Depending
- Page 60 and 61:
Scattering Diffraction Wireless tra
- Page 62 and 63:
An additional effect shown in Figur
- Page 64 and 65:
many radio stations around the worl
- Page 66 and 67:
t c Wireless transmission 45 k 1 k
- Page 68 and 69:
Wireless transmission 47 This funct
- Page 70 and 71:
cannot be guaranteed, so ASK is typ
- Page 72 and 73:
Wireless transmission 51 ● if the
- Page 74 and 75:
2.6.6 Multi-carrier modulation Spec
- Page 76 and 77:
Just as spread spectrum helps to de
- Page 78 and 79:
appears as random noise: this seque
- Page 80 and 81:
Wireless transmission 59 7 to a bin
- Page 82 and 83:
User data Hopping sequence Received
- Page 84 and 85:
● Handover needed: The mobile sta
- Page 86 and 87:
As electromagnetic waves are the ba
- Page 88:
Wireless transmission 67 Halsall, F
- Page 91 and 92:
70 Mobile communications 3.1 Motiva
- Page 93 and 94:
72 Mobile communications if the sen
- Page 95 and 96:
74 Mobile communications but listen
- Page 97 and 98:
76 Figure 3.5 Classical Aloha multi
- Page 99 and 100:
78 Figure 3.7 Demand assignment mul
- Page 101 and 102:
80 Figure 3.10 MACA can avoid hidde
- Page 103 and 104:
82 Figure 3.13 Inhibit sense multip
- Page 105 and 106:
84 Mobile communications ● Both s
- Page 107 and 108:
86 Figure 3.16 Reconstruction of A
- Page 109 and 110:
88 Figure 3.19 Spread Aloha multipl
- Page 111 and 112:
90 Table 3.1 Comparison of SDMA, TD
- Page 113 and 114:
92 Mobile communications 3.8 Refere
- Page 115 and 116:
94 Figure 4.1 Worldwide subscribers
- Page 117 and 118:
96 Mobile communications added CDMA
- Page 119 and 120:
98 Figure 4.3 Bearer and tele servi
- Page 121 and 122:
100 Mobile communications can be us
- Page 123 and 124:
102 Mobile communications ● Base
- Page 125 and 126:
104 Mobile communications can also
- Page 127 and 128:
106 Figure 4.5 GSM TDMA frame, slot
- Page 129 and 130:
108 Mobile communications ● Contr
- Page 131 and 132:
110 Figure 4.7 Protocol architectur
- Page 133 and 134:
112 Mobile communications (within 1
- Page 135 and 136:
114 Mobile communications ● Inter
- Page 137 and 138:
116 Figure 4.10 Message flow for MT
- Page 139 and 140:
118 Figure 4.11 Types of handover i
- Page 141 and 142:
120 Mobile communications e.g., UMT
- Page 143 and 144:
122 Figure 4.15 Data encryption Mob
- Page 145 and 146:
124 Mobile communications For n cha
- Page 147 and 148:
126 Table 4.5 Reliability classes i
- Page 149 and 150:
128 Figure 4.16 GPRS architecture r
- Page 151 and 152:
130 Mobile communications reach an
- Page 153 and 154:
132 Figure 4.19 DECT protocol layer
- Page 155 and 156:
134 Mobile communications 4.2.2.2 M
- Page 157 and 158:
136 Figure 4.21 TETRA frame structu
- Page 159 and 160:
138 Mobile communications Now the r
- Page 161 and 162:
140 Figure 4.23 The IMT-2000 family
- Page 163 and 164:
142 Figure 4.24 Main components of
- Page 165 and 166:
144 Figure 4.26 Spreading and scram
- Page 167 and 168:
146 Figure 4.28 UTRA FDD (W-CDMA) f
- Page 169 and 170:
148 Figure 4.29 UTRA TDD (TD-CDMA)
- Page 171 and 172:
150 Mobile communications 4.4.4.1 R
- Page 173 and 174:
152 Figure 4.31 UMTS core network t
- Page 175 and 176:
154 Figure 4.33 Marco-diversity sup
- Page 177 and 178:
156 Figure 4.35 Overview of differe
- Page 179 and 180:
158 Mobile communications is quite
- Page 181 and 182:
160 Mobile communications 24 Who wo
- Page 183 and 184:
162 Mobile communications ETSI (199
- Page 186 and 187:
Satellite communication introduces
- Page 188 and 189:
Satellite systems 167 ● Satellite
- Page 190 and 191:
Satellite systems are, and will con
- Page 192 and 193:
Another effect of satellite communi
- Page 194 and 195:
Satellite systems 173 ● Medium ea
- Page 196 and 197:
5.3.3 MEO MEOs can be positioned so
- Page 198 and 199:
quality for handover frequency. The
- Page 200 and 201:
A very ambitious and maybe never re
- Page 202:
6 Considered as an interworking uni
- Page 205 and 206:
184 Mobile communications transmiss
- Page 207 and 208:
186 Mobile communications It is onl
- Page 209 and 210:
188 Figure 6.3 DAB frame structure
- Page 211 and 212:
190 Figure 6.5 Dynamic reconfigurat
- Page 213 and 214:
192 Mobile communications system or
- Page 215 and 216:
194 Figure 6.8 Different contents o
- Page 217 and 218:
196 Figure 6.10 Mobile Internet ser
- Page 219 and 220:
198 Mobile communications 6.7 Revie
- Page 222 and 223:
Wireless LAN 7 This chapter present
- Page 224 and 225:
Many different, and sometimes compe
- Page 226 and 227:
Almost all networks described in th
- Page 228 and 229:
Clearly, the two basic variants of
- Page 230 and 231:
the AP. The stations and the AP whi
- Page 232 and 233:
DLC PHY LLC MAC PLCP PMD MAC manage
- Page 234 and 235:
7.3.3.2 Direct sequence spread spec
- Page 236 and 237:
DIFS medium busy DIFS PIFS SIFS ●
- Page 238 and 239:
station 1 station 2 station 3 stati
- Page 240 and 241:
sender receiver other stations DIFS
- Page 242 and 243:
medium busy point co-ordinator wire
- Page 244 and 245: ytes bits 2 Frame control 2 Protoco
- Page 246 and 247: ytes 2 Frame ACK Duration Control b
- Page 248 and 249: station 1 station 2 medium beacon i
- Page 250 and 251: data (as shown in the example). Thi
- Page 252 and 253: Unfortunately, many products implem
- Page 254 and 255: Channel Frequency [MHz] US/Canada E
- Page 256 and 257: Data rate Modulation Coding Coded C
- Page 258 and 259: 4 rate 1 reserved PLCP preamble 12
- Page 260 and 261: ● 802.11h (Spectrum managed 802.1
- Page 262 and 263: synchronization priority detection
- Page 264 and 265: 7.4.1.3 Yield phase During the yiel
- Page 266 and 267: WATM aspects come from the telecomm
- Page 268 and 269: 7.4.2.3 WATM services The following
- Page 270 and 271: MATM terminal radio segment fixed n
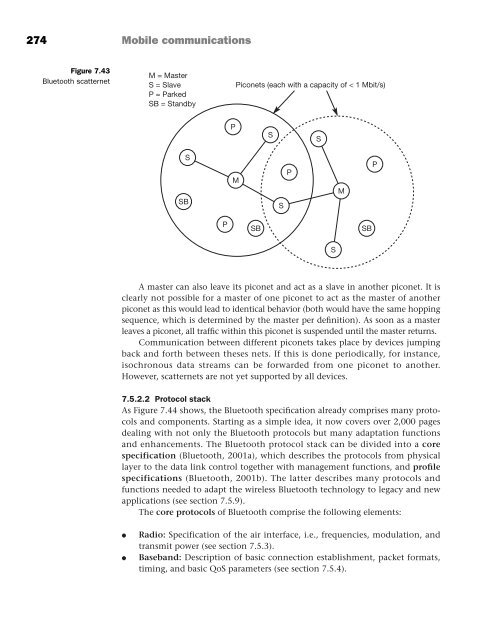
- Page 272 and 273: users out of private WATM networks.
- Page 274 and 275: 2 EMAS EMAS WMT RAS -E -N T MT MS 3
- Page 276 and 277: ● Fixed wireless ATM terminals (s
- Page 278 and 279: layers. To cover special characteri
- Page 280 and 281: etween audio and video equipment, A
- Page 282 and 283: DLC control SAP Radio resource cont
- Page 284 and 285: 5150 5470 36 5180 16.6 MHz 100 5500
- Page 286 and 287: 2 ms MAC frame broadcast 2 ms MAC f
- Page 288 and 289: 2 LCH PDU type 2 LCH PDU type 10 se
- Page 290 and 291: WLAN solutions, besides QoS, is the
- Page 292 and 293: ● Bridging of networks: Using wir
- Page 296 and 297: audio apps. vCal/vCard NW apps. tel
- Page 298 and 299: 625 µs f k M f k M f k+1 S f k M f
- Page 300 and 301: division duplex scheme). A simple a
- Page 302 and 303: SCO MASTER f 0 ACL f 4 SCO f 6 ACL
- Page 304 and 305: detach standby transmit AMA park PM
- Page 306 and 307: Operating mode Average current [mA]
- Page 308 and 309: Connectionless PDU 2 2 ≥2 0-65533
- Page 310 and 311: user can use all services as intend
- Page 312 and 313: 7.5.10 IEEE 802.15 In 1999 the IEEE
- Page 314 and 315: Compared to Bluetooth the MAC layer
- Page 316 and 317: Criterion IEEE 802.11b IEEE 802.11a
- Page 318 and 319: will continue the work that was pre
- Page 320 and 321: Borisov, N., Goldberg, I., Wagner,
- Page 322: IEEE (2001) Port-based Network Acce
- Page 325 and 326: 304 Mobile communications 8.1 Mobil
- Page 327 and 328: 306 Mobile communications ● Compa
- Page 329 and 330: 308 Mobile communications ● Corre
- Page 331 and 332: 310 Mobile communications At first
- Page 333 and 334: 312 Mobile communications 8.1.4.2 A
- Page 335 and 336: 314 Figure 8.6 Registration reply T
- Page 337 and 338: 316 Figure 8.8 IP-in-IP encapsulati
- Page 339 and 340: 318 Figure 8.11 Protocol fields for
- Page 341 and 342: 320 Mobile communications packets h
- Page 343 and 344: 322 Mobile communications ● Firew
- Page 345 and 346:
324 Mobile communications 8.1.10 IP
- Page 347 and 348:
326 Figure 8.15 Basic architecture
- Page 349 and 350:
328 Figure 8.17 Basic DHCP configur
- Page 351 and 352:
330 Mobile communications (Drohms,
- Page 353 and 354:
332 Figure 8.20 Example ad-hoc netw
- Page 355 and 356:
334 Mobile communications Let us go
- Page 357 and 358:
336 Table 8.2 Part of a routing tab
- Page 359 and 360:
338 Mobile communications ● N 4 d
- Page 361 and 362:
340 Mobile communications interfere
- Page 363 and 364:
342 Figure 8.22 Building hierarchie
- Page 365 and 366:
344 Mobile communications when it c
- Page 367 and 368:
346 Mobile communications 17 What a
- Page 369 and 370:
348 Mobile communications Mink, S.,
- Page 372 and 373:
Mobile transport layer 9 Supporting
- Page 374 and 375:
Mobile transport layer 353 The send
- Page 376 and 377:
operable. Every enhancement to TCP,
- Page 378 and 379:
There are several advantages with I
- Page 380 and 381:
Mobile transport layer 359 retransm
- Page 382 and 383:
Mobile transport layer 361 lier tha
- Page 384 and 385:
Mobile transport layer 363 9.2.5 Tr
- Page 386 and 387:
Mobile transport layer 365 HTTP req
- Page 388 and 389:
Mobile transport layer 367 within a
- Page 390 and 391:
Mobile system wireless However, all
- Page 392 and 393:
This simple formula neglects retran
- Page 394:
Mobile transport layer 373 De Vivo,
- Page 397 and 398:
376 Mobile communications WAP combi
- Page 399 and 400:
378 Figure 10.1 Application, cache,
- Page 401 and 402:
380 Mobile communications 10.1.3 Li
- Page 403 and 404:
382 Mobile communications and, thus
- Page 405 and 406:
384 Mobile communications Typically
- Page 407 and 408:
386 Mobile communications What do s
- Page 409 and 410:
388 Mobile communications HTTP vers
- Page 411 and 412:
390 Figure 10.4 Additional applicat
- Page 413 and 414:
392 Figure 10.8 Client and network
- Page 415 and 416:
394 Figure 10.9 Components and inte
- Page 417 and 418:
396 Figure 10.11 WDP service primit
- Page 419 and 420:
398 Figure 10.12 WTLS establishing
- Page 421 and 422:
400 Mobile communications 10.3.4 Wi
- Page 423 and 424:
402 Figure 10.16 Basic transaction,
- Page 425 and 426:
404 Figure 10.19 WTP class 2 transa
- Page 427 and 428:
406 Figure 10.20 WSP/B session esta
- Page 429 and 430:
408 Figure 10.23 WSP/B completed tr
- Page 431 and 432:
410 Figure 10.25 WSP/B asynchronous
- Page 433 and 434:
412 Mobile communications Besides t
- Page 435 and 436:
414 Mobile communications many vend
- Page 437 and 438:
416 Mobile communications ... your
- Page 439 and 440:
418 Mobile communications using sta
- Page 441 and 442:
420 Mobile communications These lib
- Page 443 and 444:
422 Mobile communications connectio
- Page 445 and 446:
424 Mobile communications Altogethe
- Page 447 and 448:
426 Mobile communications Your s
- Page 449 and 450:
428 Mobile communications 10.3.10.3
- Page 451 and 452:
430 Figure 10.33 Sample protocol st
- Page 453 and 454:
432 Figure 10.35 i-mode push archit
- Page 455 and 456:
434 Mobile communications Synchroni
- Page 457 and 458:
436 Mobile communications ● Trans
- Page 459 and 460:
438 Figure 10.38 Example protocol s
- Page 461 and 462:
440 Mobile communications 10.8 Revi
- Page 463 and 464:
442 Mobile communications Bickmore,
- Page 465 and 466:
444 Mobile communications Liljeberg
- Page 467 and 468:
446 Mobile communications WAP Forum
- Page 470 and 471:
11.1 The architecture of future net
- Page 472 and 473:
devices, reconfigurable senders/rec
- Page 474:
Internet technology is really simpl
- Page 477 and 478:
456 Mobile communications ARQN ARQ
- Page 479 and 480:
458 Mobile communications CSMA Carr
- Page 481 and 482:
460 Mobile communications FHSS Freq
- Page 483 and 484:
462 Mobile communications ISDN Inte
- Page 485 and 486:
464 Mobile communications MSISDN Mo
- Page 487 and 488:
466 Mobile communications PTP Point
- Page 489 and 490:
468 Mobile communications S-SAP Ses
- Page 491 and 492:
470 Mobile communications WCAC Wire
- Page 493 and 494:
472 Mobile communications Example:
- Page 495 and 496:
474 Mobile communications ● Proto
- Page 498 and 499:
A bis interface 102 access burst 10
- Page 500 and 501:
CCH (control channels) 108 CCIR (Co
- Page 502 and 503:
embedded controllers 7 emergencies,
- Page 504 and 505:
HDB (home data base) 131 HDLC (high
- Page 506 and 507:
MCC (mobile country code) 114 MCI (
- Page 508 and 509:
personal identity number (PIN) 102
- Page 510 and 511:
SNDCP (subnetwork dependent converg
- Page 512 and 513:
very high frequency (VHF) 26 very l