Reformación y autoreformación de metano con vapor de agua
Reformación y autoreformación de metano con vapor de agua
Reformación y autoreformación de metano con vapor de agua
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
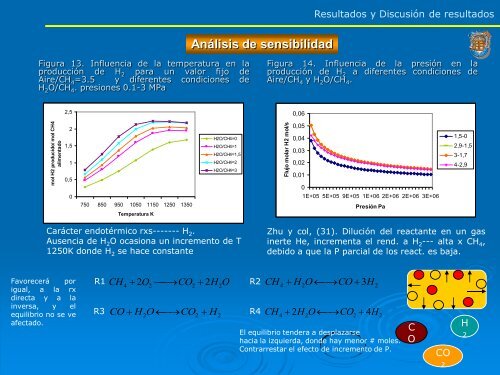
Figura 13. Influencia <strong>de</strong> la temperatura en la<br />
producción <strong>de</strong> H 2 para un valor fijo <strong>de</strong><br />
Aire/CH 4=3.5 y diferentes <strong>con</strong>diciones <strong>de</strong><br />
H 2O/CH 4. presiones 0.1-3 MPa<br />
mol H2 producido/ mol CH4<br />
alimentado<br />
2,5<br />
2<br />
1,5<br />
1<br />
0,5<br />
Favorecerá por<br />
igual, a la rx<br />
directa y a la<br />
inversa, y el<br />
equilibrio no se ve<br />
afectado.<br />
0<br />
750 850 950 1050 1150 1250 1350<br />
Temperatura K<br />
Análisis <strong>de</strong> sensibilidad<br />
H2O/CH4=0<br />
H2O/CH4=1<br />
H2O/CH4=1,5<br />
H2O/CH4=2<br />
H2O/CH4=3<br />
Carácter endotérmico rxs------- H 2.<br />
Ausencia <strong>de</strong> H 2O ocasiona un incremento <strong>de</strong> T<br />
1250K don<strong>de</strong> H 2 se hace <strong>con</strong>stante<br />
R1<br />
R3<br />
CH 4 2O2 <br />
CO2<br />
2H2O<br />
CO H O<br />
CO H<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
R2<br />
R4<br />
Figura 14. Influencia <strong>de</strong> la presión en la<br />
producción <strong>de</strong> H 2 a diferentes <strong>con</strong>diciones <strong>de</strong><br />
Aire/CH 4 y H 2O/CH 4.<br />
Flujo molar H2 mol/s<br />
0,06<br />
0,05<br />
0,04<br />
0,03<br />
0,02<br />
0,01<br />
0<br />
Resultados y Discusión <strong>de</strong> resultados<br />
1E+05 5E+05 9E+05 1E+06 2E+06 2E+06 3E+06<br />
Presión Pa<br />
1,5-0<br />
2,9-1,5<br />
3-1,7<br />
4-2,9<br />
Zhu y col, (31). Dilución <strong>de</strong>l reactante en un gas<br />
inerte He, incrementa el rend. a H 2--- alta x CH 4,<br />
<strong>de</strong>bido a que la P parcial <strong>de</strong> los react. es baja.<br />
CH H O<br />
CO 3H<br />
4<br />
4<br />
2<br />
CH 2H O<br />
CO 4H<br />
2<br />
El equilibrio ten<strong>de</strong>ra a <strong>de</strong>splazarse<br />
hacia la izquierda, don<strong>de</strong> hay menor # moles.<br />
Contrarrestar el efecto <strong>de</strong> incremento <strong>de</strong> P.<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
C<br />
O<br />
CO<br />
2<br />
H<br />
2