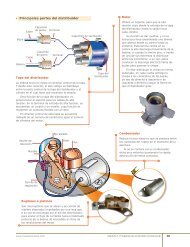
Tipos de cámara de combustión Para que un motor cumpla y ...
Tipos de cámara de combustión Para que un motor cumpla y ...
Tipos de cámara de combustión Para que un motor cumpla y ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
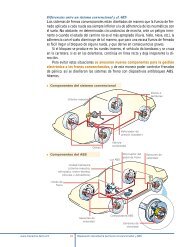
F<strong>un</strong>cionamiento <strong>de</strong>l <strong>de</strong>l sistema <strong>de</strong><br />
combustible convencional<br />
Cuadro explicativo 2.1 2.1<br />
COMPONENTES<br />
FUNCIONAMIENTO<br />
Bomba <strong>de</strong> combustible<br />
mecánica<br />
En este caso, es<br />
accionada por la rotación<br />
<strong>de</strong>l eje <strong>de</strong> levas. Un<br />
diafragma interior <strong>de</strong> la<br />
bomba se mueve hacia<br />
arriba y hacia abajo, para<br />
aspirar el combustible y<br />
bombearlo a través <strong>de</strong> la<br />
línea <strong>de</strong> combustible.<br />
3 4<br />
El combustible pasa por <strong>un</strong> fi ltro<br />
<strong>que</strong> retiene las partículas no<br />
<strong>de</strong>seadas y regula la presión<br />
<strong>de</strong> combustible entregada<br />
por la bomba (por<strong>que</strong> su<br />
f<strong>un</strong>cionamiento <strong>de</strong>pen<strong>de</strong> <strong>de</strong> las<br />
RPM <strong>de</strong> giro <strong>de</strong>l <strong>motor</strong>).<br />
Carburador<br />
Este dispositivo con<br />
ensambles mecánicos<br />
realiza la mezcla <strong>de</strong><br />
aire-combustible.<br />
Contiene <strong>un</strong> <strong>de</strong>pósito<br />
<strong>de</strong> gasolina, <strong>de</strong>s<strong>de</strong><br />
el cual la suministra<br />
a la(s) esprea(s)<br />
correspondiente(s); el<br />
nivel <strong>de</strong>l combustible<br />
se controla por<br />
medio <strong>de</strong> <strong>un</strong> fl otador<br />
interconstruido en el<br />
propio carburador.<br />
Una vez <strong>que</strong> el combustible es<br />
bombeado, fi ltrado y regulado,<br />
se almacena temporalmente en<br />
<strong>un</strong> <strong>de</strong>pósito auxiliar <strong>de</strong>ntro <strong>de</strong>l<br />
carburador; y ahí, su nivel es<br />
controlado mediante <strong>un</strong> fl otador.<br />
Cuando el <strong>de</strong>pósito está lleno, el<br />
fl otador activa a <strong>un</strong>a válvula <strong>de</strong> paso<br />
o <strong>de</strong> <strong>de</strong>rivación, <strong>que</strong> hace <strong>que</strong> la<br />
presión <strong>de</strong> combustible exce<strong>de</strong>nte<br />
regrese al tan<strong>que</strong>.<br />
El carburador consigue la mezcla<br />
aire-combustible en la proporción<br />
a<strong>de</strong>cuada. Su f<strong>un</strong>cionamiento se<br />
basa en el efecto Venturi, <strong>que</strong><br />
hace <strong>que</strong> toda corriente <strong>de</strong> aire<br />
<strong>que</strong> pasa por <strong>un</strong>a canalización<br />
genere <strong>un</strong>a <strong>de</strong>presión (succión);<br />
esto se aprovecha para arrastrar el<br />
combustible proporcionado por el<br />
carburador.