La formula di sdoppiamento - Francescopoli.net
La formula di sdoppiamento - Francescopoli.net
La formula di sdoppiamento - Francescopoli.net
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
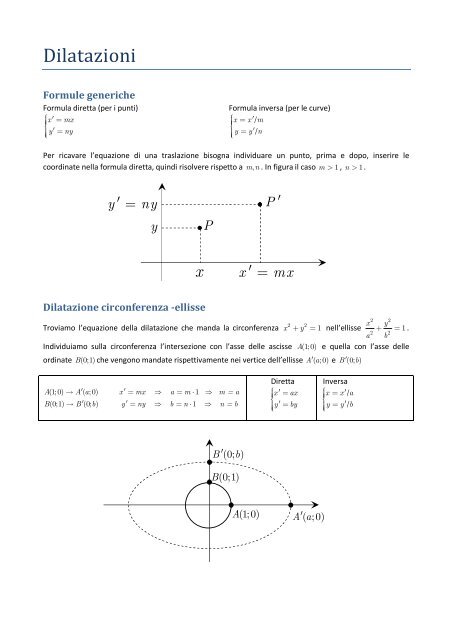
Dilatazioni<br />
Formule generiche<br />
Formula <strong>di</strong>retta (per i punti)<br />
x <br />
<br />
mx<br />
y ny<br />
<br />
Formula inversa (per le curve)<br />
<br />
x x <br />
<br />
/ m<br />
<br />
y<br />
y/<br />
n<br />
<br />
Per ricavare l’equazione <strong>di</strong> una traslazione bisogna in<strong>di</strong>viduare un punto, prima e dopo, inserire le<br />
coor<strong>di</strong>nate nella <strong>formula</strong> <strong>di</strong>retta, quin<strong>di</strong> risolvere rispetto a m,<br />
n . In figura il caso m 1 , n 1.<br />
y <br />
ny<br />
y<br />
P<br />
P <br />
x x mx<br />
Dilatazione circonferenza -ellisse<br />
2 2<br />
2 2<br />
x y<br />
Troviamo l’equazione della <strong>di</strong>latazione che manda la circonferenza x y 1 nell’ellisse 1 .<br />
2 2<br />
a b<br />
In<strong>di</strong>viduiamo sulla circonferenza l’intersezione con l’asse delle ascisse A (1; 0) e quella con l’asse delle<br />
or<strong>di</strong>nate B(0;1)<br />
che vengono mandate rispettivamente nei vertice dell’ellisse A ( a; 0) e B<br />
(0; b)<br />
A(1; 0) A( a; 0) x mx a m 1 m = a<br />
B(0;1) B(0; b) y<br />
ny b n 1<br />
n = b<br />
Diretta<br />
x <br />
<br />
ax<br />
y by<br />
<br />
Inversa<br />
<br />
x x <br />
<br />
/ a<br />
<br />
y<br />
y/<br />
b<br />
<br />
B (0; b)<br />
B(0;1)<br />
A (1;0) A(<br />
a; 0)
Tangente alla circonferenza <strong>di</strong> centro l’origine e raggio unitario<br />
Per scrivere la tangente alla circonferenza<br />
x<br />
2 2<br />
y 1 nel suo punto P ( x , y ) calcoliamo<br />
0 0 0<br />
il coefficiente angolare m della retta che<br />
r<br />
contiene il raggio, e da questo il coefficiente<br />
angolare della tangente<br />
m :<br />
t<br />
1<br />
y0<br />
m r<br />
P ( x ; y )<br />
0 0 0<br />
m<br />
r<br />
y<br />
1 x<br />
<br />
x m y<br />
0 0<br />
mt<br />
0 r 0<br />
1<br />
x0<br />
Sostituiamo il valore trovato nell’equazione del<br />
fascio <strong>di</strong> rette y y m( x x ) <strong>di</strong> centro<br />
0 0<br />
P ( x , y ) :<br />
0 0 0<br />
x<br />
y y ( x x ) xx yy x y xx yy 1<br />
0<br />
2 2<br />
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0<br />
y0<br />
2 2<br />
Avendo sfruttato che per ogni punto sulla circonferenza <strong>di</strong> raggio unitario si ha x y . Dilatando la<br />
0 0<br />
1<br />
retta ottenuta si ottiene la tangente all’ellisse. Usando la relazione <strong>formula</strong> inversa per le curve si ha:<br />
x <br />
x<br />
a<br />
y<br />
y 1<br />
0 0<br />
b<br />
Vogliamo però esprimere la retta tangente in funzione delle coor<strong>di</strong>nate del punto P( x , y ) appartenente<br />
0 0 0<br />
all’ellisse, immagine <strong>di</strong> P ( x , y ) . Usando la <strong>formula</strong> <strong>di</strong>retta per i punti si ha x ax e y by :<br />
0 0 0<br />
0 0 0 0<br />
x x <br />
a a<br />
y<br />
y<br />
b b<br />
0 0<br />
1<br />
Facendo cadere gli apici che ora non occorrono più si arriva alla cosiddetta <strong>formula</strong> <strong>di</strong> <strong>sdoppiamento</strong>, che<br />
permette <strong>di</strong> scrivere l’equazione della tangente ad un ellisse in un suo punto ( x , y )<br />
0 0<br />
xx<br />
a<br />
yy<br />
1<br />
b<br />
0 0<br />
2 2