STRUCTURE OF COURSES, M.A. SOCIOLOGY SEMESTER – I ...
STRUCTURE OF COURSES, M.A. SOCIOLOGY SEMESTER – I ...
STRUCTURE OF COURSES, M.A. SOCIOLOGY SEMESTER – I ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
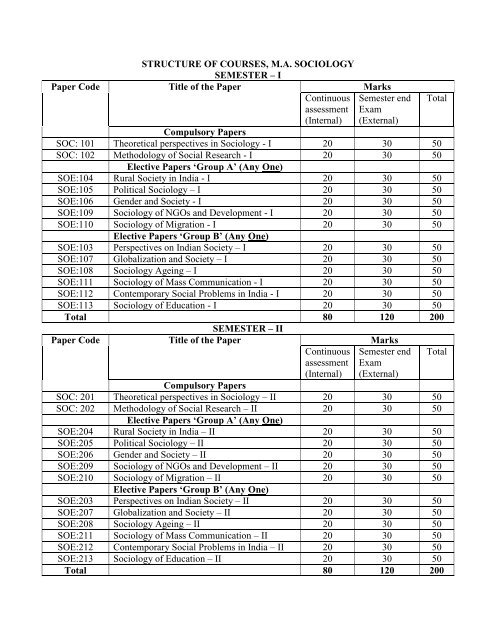
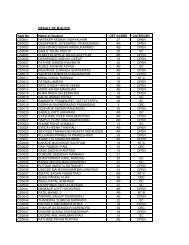
Paper Code<br />
<strong>STRUCTURE</strong> <strong>OF</strong> <strong>COURSES</strong>, M.A. <strong>SOCIOLOGY</strong><br />
<strong>SEMESTER</strong> <strong>–</strong> I<br />
Title of the Paper<br />
Marks<br />
Continuous Semester end Total<br />
assessment Exam<br />
(Internal) (External)<br />
SOC: 101<br />
Compulsory Papers<br />
Theoretical perspectives in Sociology - I 20 30 50<br />
SOC: 102 Methodology of Social Research - I<br />
Elective Papers ‘Group A’ (Any One)<br />
20 30 50<br />
SOE:104 Rural Society in India - I 20 30 50<br />
SOE:105 Political Sociology <strong>–</strong> I 20 30 50<br />
SOE:106 Gender and Society - I 20 30 50<br />
SOE:109 Sociology of NGOs and Development - I 20 30 50<br />
SOE:110 Sociology of Migration - I<br />
Elective Papers ‘Group B’ (Any One)<br />
20 30 50<br />
SOE:103 Perspectives on Indian Society <strong>–</strong> I 20 30 50<br />
SOE:107 Globalization and Society <strong>–</strong> I 20 30 50<br />
SOE:108 Sociology Ageing <strong>–</strong> I 20 30 50<br />
SOE:111 Sociology of Mass Communication - I 20 30 50<br />
SOE:112 Contemporary Social Problems in India - I 20 30 50<br />
SOE:113 Sociology of Education - I 20 30 50<br />
Total<br />
<strong>SEMESTER</strong> <strong>–</strong> II<br />
80 120 200<br />
Paper Code<br />
Title of the Paper<br />
Marks<br />
Continuous Semester end Total<br />
assessment Exam<br />
Compulsory Papers<br />
(Internal) (External)<br />
SOC: 201 Theoretical perspectives in Sociology <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
SOC: 202 Methodology of Social Research <strong>–</strong> II<br />
Elective Papers ‘Group A’ (Any One)<br />
20 30 50<br />
SOE:204 Rural Society in India <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
SOE:205 Political Sociology <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
SOE:206 Gender and Society <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
SOE:209 Sociology of NGOs and Development <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
SOE:210 Sociology of Migration <strong>–</strong> II<br />
Elective Papers ‘Group B’ (Any One)<br />
20 30 50<br />
SOE:203 Perspectives on Indian Society <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
SOE:207 Globalization and Society <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
SOE:208 Sociology Ageing <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
SOE:211 Sociology of Mass Communication <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
SOE:212 Contemporary Social Problems in India <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
SOE:213 Sociology of Education <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
Total 80 120 200
Paper Code<br />
<strong>SEMESTER</strong> <strong>–</strong> III<br />
Title of the Paper<br />
Continuous<br />
assessment<br />
(Internal)<br />
Marks<br />
Semester end<br />
Exam<br />
(External)<br />
Compulsory Papers<br />
SOC: 301 Classical Sociological Tradition - I 20 30 50<br />
SOC: 302 Sociology of change and Development - I 20 30 50<br />
Elective Papers ‘Group A’ (Any One)<br />
SOE:303 Social Demography - I 20 30 50<br />
SOE:305 Social movements in India - I 20 30 50<br />
SOE:307 Sociology of Information Society - I 20 30 50<br />
SOE:308 Urban Society in India - I 20 30 50<br />
SOE:309 Sociology of Disaster Management - I 20 30 50<br />
Elective Papers ‘Group B’ (Any One)<br />
SOE:304 Criminology - I 20 30 50<br />
SOE:306 Environment and Society - I 20 30 50<br />
SOE:310 Health and Society - I 20 30 50<br />
SOE:311 Tribal Sociology - I 20 30 50<br />
SOE:312 Social Psychology - I 20 30 50<br />
Total 80 120 200<br />
Paper Code<br />
<strong>SEMESTER</strong> <strong>–</strong> IV<br />
Title of the Paper<br />
Continuous<br />
assessment<br />
(Internal)<br />
Marks<br />
Semester end<br />
Exam<br />
(External)<br />
Compulsory Papers<br />
SOC: 401 Classical Sociological Tradition - II 20 30 50<br />
SOC: 402 Sociology of change and Development - II 20 30 50<br />
Elective Papers ‘Group A’ (Any One)<br />
SOE:403 Social Demography <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
SOE:405 Social movements in India <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
SOE:407 Sociology of Information Society <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
SOE:408 Urban Society in India <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
SOE:409 Sociology of Disaster Management <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
Elective Papers ‘Group B’ (Any One)<br />
SOE:404 Criminology <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
SOE:406 Environment and Society <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
SOE:410 Health and Society <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
SOE:411 Tribal Sociology <strong>–</strong> II 20 30 50<br />
SOE:412 Social Psychology - II 20 30 50<br />
Total 80 120 200<br />
Note: Students must obtain minimum 40% marks in Continuous Assessment (Internal)<br />
and Semester End Examination (External ) separately for each paper for passing the<br />
examination.<br />
Total<br />
Total
M. A. I <strong>SEMESTER</strong><br />
SOC-101: Theoretical Perspectives in Sociology - I<br />
Unit I. Introduction<br />
a) Nature of sociological theory.<br />
b) Elements of sociological theory.<br />
c) Relationship between theory and research.<br />
Unit II. Structural functionalism<br />
a) The idea of social structure-A.R. Radcliffe Brown.<br />
b) Dimensions of Social System- T. Parsons.<br />
c) Codification, Critique and reformulation of functional Analysis- R.K. Merton.<br />
Unit III. Conflict theory<br />
a) Dialectical Conflict Theory- R Dahrendorf.<br />
b) Functional Analysis of Conflict- L. Coser.<br />
c) Conflict and Social change- R. Collins.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Abraham, M. Frncis 1992. Modem Sociological Theory. An Introduction Bombay:<br />
Oxford University Press.<br />
Alexander, Jeffrey C. 1987. Twenty lectures: Sociological theory since world war<br />
II.New York: Columbia University Press.<br />
Bottomore, Tom. 1984. The Frankfurt school. Chester, Sussex: Ellis Horwood and<br />
London: Tavistock Publications.<br />
Collins, Randall. 1997 (Indian edition). Sociological theory. Jaipur and New Delhi:<br />
Rawat.<br />
Craib, Ian. 1992. Modern social theory: From Parsons to Habermas (2nd<br />
edition).London: Harvester Press.<br />
Doshi S. L. 2002 : Adhunikata, Uttar-Adhunikata Evam Nava-Samajshastriya Siddhant,<br />
Rawat Publications, Jaipur.<br />
Giddens, Anthony 1983 : Central Problems in Social Theory : Action, Structure and<br />
Contradiction in Social Analysis, Micmillan, London<br />
Kuper, Adam and Jessica Kuper (eds.). 1996 (2nd edition). The social science<br />
encyclopaedia. London and New York: Routledge.<br />
Kuper, Adam. 1975. Anthropologists and anthropology: The British school, 1922-<br />
72.Harmondsworth, Middlesex: Penguin Books.<br />
Ritzer, George and Goodman D. 2004 (6th edition). Sociological theory. New York:<br />
McGraw-Hill.<br />
Sturrock, John (ed.). 1979. Structuralism and since: From Levi Strauss to<br />
Derida.Oxford: Oxford University Press.<br />
Turner, Jonathan H. 1995 (4th edition). The structure of sociological theory. Jaipur and<br />
New Delhi: Rawat.<br />
Zeitlin, Irving M. 1998 (Indian edition) . Rethinking sociology: A critique of<br />
contemporary theory. Jaipur and New Delhi: Rawat.
SOC - 102: Methodology of Social Research - I<br />
I. Philosophical Roots of Social Research:<br />
a) Methodologies in methodology in social research: major paradigms,<br />
quantitative and qualitative research, and participatory research methodology.<br />
b) Positivism and its critique: Contribution of Comte, Durkheim, and Popper to<br />
positivism, critique of positivism: Fayeraband and Giddens.<br />
c) Hermeneutical tradition: dominant tendencies.<br />
II. Nature of Social Reality and Approaches:<br />
a) Phenomenology, Ethnomethodology, symbolic interactionism, Interpretative<br />
understanding.<br />
b) Logic of inquiry in social science research: inductive and deductive.<br />
c) Theory building: Model building, paradigm, theory and fact, constructing a theory,<br />
Relationship between theory and research.<br />
d) Scientific method in social research: nature and steps.<br />
e) Hypothesis: Types, Sources and characteristics.<br />
f) The Problems in the study of social reality: Objectivity and Subjectivity.<br />
III. Application of Computers in Social Research: Use of Computers and Internet in<br />
Social Research<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Ahuja, Ram. 2001. Research Methods, Rawat Publications, Jaipur.<br />
Babbie, Earl. 2006. The Practice of Social Research (10 th edition). Chennai: Chennai<br />
Micro Print Pvt.Ltd.<br />
Bryman, Alan.2004. Social Research Methods. Oxford University press. New York.<br />
Creswell, J. W. 2003. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods<br />
Approaches. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.<br />
Durkheim, Emile. 1964. The Rules of Sociological Method. London: Collier MacMillan,<br />
1938. New York: The Free Press,<br />
Feyerabend, Paul. 1978. Against method. London/New York: Verso.<br />
Giddens, Anthony 1976. New Rules of sociological Research. Hutchinson, and Co.<br />
Kuhn, Thomas. 1970. The Structure of Scientific Revolutions, Chicago: The University<br />
of Chicago Press.<br />
Mukherji, P.N. (ed) 2000. Methodology in social Research, New Delhi: Sage<br />
Publications.<br />
Neumann, W. L. 1991, Social Science Research Methods: Qualitative and Quantitative<br />
Approaches. Needleham Heights, Allyn and Bacon.<br />
Popper, Karl.1959. The Logic of Scientific Discovery. New York: Harper Tarchbooks,<br />
The science Library, Harper and Row.<br />
Sarantakos, soritios.1998. Social Research. London: MacMillan Press Ltd.<br />
SOE <strong>–</strong> 104: RURAL SOCIETY IN INDIA - I<br />
Unit I:Nature of rural Society in India.<br />
a) Peasant society.<br />
b) Concept of village, characteristics of rural society specially in Indian context.<br />
c) Rural recreation, forms of recreation.<br />
d) Folk culture.
Unit II: Planned social change for rural society.<br />
a) Green revolution.<br />
b) Rural reconstruction - objectives and programmes of rural reconstruction.<br />
c) Community development programmes.<br />
d) Panchayat Raj : Panchayat Raj as a democratic decentralization. Structure and<br />
functions: gram Panchayat, Panchayat samiti, Zilla Parishad.<br />
e) 73 rd amendment.<br />
Unit III: Globalization and its impact on agriculture.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Andre Setille, 1974. Six Essays in Comparative Sociology, OUP, New Delhi.<br />
Ashish Nandy, 1999. Ambiguous Journey to the City, New Delhi, OUP.<br />
Berch, Berberogue (ed.). 1992. Class, State and Development in India, Sage, New Delhi.<br />
Beteille Andre. 1974. Studies in Agrarian Social Structure, Oxford University Press,<br />
Delhi.<br />
Desai, A.R. 1977. Rural Sociology in India, Popular Prakashan, Bombay.<br />
Desai, A.R..(Ed.) Peasant Struggles in India, Oxford Uriversity, Bombay, 1979.<br />
Dhanagare, D.N. 1988. Peasant Movements in India, OUP, New Delhi.<br />
Doshi, S.L. and Jain, P.C. Rural Sociology, Rawat Publications, Jaipur and New Delhi,<br />
1999.<br />
Jain, S.C. 1967. “Community development and Panchayati Raj in India” Allied<br />
Publishers, Bombay.<br />
Maheshwari, S.R. 1995. “Rural development in India” Sage publication, New Delhi.<br />
Mencher, J.P., 1983. Social Anthropology of Peasantry Part III, OUP.<br />
Oommen, T.K. : Social Transformation in Rural India, Vikas Publishing House, New<br />
Delhi, 1984.<br />
P. Radhakrisjmam. 1989: Peasant Struggles: Land reforms and Social Change in Malabar<br />
1836 - 1982. Sage Publications : New Delhi.<br />
Roy, C.N. 1994. “Politics or rural development” Rawat Publications, Jaipur.<br />
Sem Njpwamo. 1962. Evolution of Agrarian Relations in India, Peoples Publishing<br />
House, New Delhi.<br />
Sen Sunil. 1979. Agrarian Relations in India 1793 to 1947, People's Publications House,<br />
New Delhi.<br />
Shanin Teodor. 1971. Peasants and Peasants Societies, Modern Sociology Readings,<br />
Penguin.<br />
Sharma, K.L. 1997. Rural Society in India, Rawat Publications, Jaipur and New Delhi.<br />
Sharma, M.P. 1967. “Local self Govt. in India” Kitab-Mahal Allahabad.<br />
Singh Raghavendra Pratap. 1987. Sociology of Rural Development in India, Discovery<br />
Publishing House, Delhi.<br />
Thorner, Daniel and Thorner Alice. 1962. Land and Labour in India, Asia Publications,<br />
Bombay.<br />
Thorner, Daniel and Thorner Alice. 1962. Land and Labour in India, Asia Publications,<br />
Bombay.<br />
Tiwary Jai Kumar. 1994. Rural Trade Information in India, Reliance Publishing House,<br />
New Delhi.
SOE - 105: A03 Political Sociology - I<br />
I. Nature of Political Sociology:<br />
a) Nature and subject matter of political sociology.<br />
b) Development of political sociology.<br />
c) Scope of political sociology.<br />
II. Approaches to Political Sociology:<br />
a) Behavioural approach.<br />
b) System analysis approach.<br />
c) Input Output approach.<br />
III. Political Culture and Socialisation:<br />
a) Political Culture: Meaning and Significance.<br />
b) Political socialisation: Meaning, significance and Agencies.<br />
IV. Elite theories of distribution of power:<br />
a) G. Mosca,<br />
b) C. Wright Mills.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Almond and Powell. 1966. Comparative Polities: The Developmental approach, Boston,<br />
Little Brown and co.<br />
Almond, A Gabriel et. al. 1973. Crises choice and change, Historical Studies of political<br />
Development. Boston.<br />
Barrington Jr. 1958. Political Power and social Theory, Cambridge, Haward University<br />
press.<br />
Bhaskaran, R.1967. Sociology of Politics tradition and politics in India. Asian<br />
publishing house, Bombay.<br />
Biswas, -Diptikumar. Political Sociology, Firma KLM Private, Calcutta.<br />
Bottmore, T.B. 1979. Political Sociology. Hutchinson.<br />
Bottmore, T.B.1966. Elites and Society, London. Penguin Books<br />
Dowse, R. E. and Huges.1971. Political Sociology, New York, Basic Books.<br />
Dubey, S. R. Development of political thought in India.<br />
Elsentadt, S. N (ed).1989. Political Sociology, Vol-I & II, Rawat publications.<br />
Harold, D. Lasswell. 1997. On Political Sociology, The University of Chicago press,<br />
Chicago.<br />
Horowitz, Irving L. 1972. Foundation of Political Sociology, Harper and Row, New York.<br />
Huntington, Samuel P. 1969. Political order in changing societies. Yale University<br />
press. New Haven.<br />
Jangam, R. T. 1980.Text Book of Political Sociology, Oxford and IBH publishing Co.<br />
Mills, C. W. and Hans Gerth.1946. Essays in Sociology.Oxford, New York.<br />
Mills, C.W. The power Elite, Oxford, New York.<br />
Mitra, Subriha K.1992. Power Protest and Participation, Local Elites and the Politics of<br />
Development in India, Routledge.<br />
Mukhopadhaya, Amal Kumar. 1977. Political Sociology. K.B. Bagchi and company,<br />
Pandit, Vijaya laxmi.1984. Elites and Urban politics, Inter-India publication, New<br />
Delhi.<br />
Philips, C. H. (ed). Society and politics in India.
Runciman, W. G. 1965. Social Sciences and Political Theory, Cambridge University press,<br />
London.<br />
Rush, Michael and Philip, Althoff. 1971. An Introduction to Political Sociology,<br />
Thomas Nelson. and Sons Ltd. London.<br />
Thimmaiah,G. 1993. Power politics and social Justice, Sage publication, New Delhi.<br />
Verinder, Grover. 1988. Elections and politics in India, Deep and Deep publications, New<br />
Delhi.<br />
William, Riker.et al. 1973. An Introducation to Positive Political Theory. Englewood,<br />
SOE <strong>–</strong> 106: GENDER AND SOCIETY - I<br />
Unit I:Social construction of gender<br />
a) Gender vs Biology, equality vs Difference<br />
b) Women in the family : Socialization, Nature vs Gender; gender roles, privatepublic<br />
dichotomy, sexual division of labour.<br />
c) Patriarchy as ideology and practice.<br />
Unit II: Theories of Gender Relations<br />
a) Liberal<br />
b) Radical<br />
c) Socialist<br />
Unit III: Gender Based Division of Labour / Work<br />
a) Production vs Reproduction.<br />
b) Household work, invisible work.<br />
c) Women’s work and Technology<br />
d) Development policies, liberalization and globalization and its impact on<br />
women.<br />
Unit IV: Gender and Society in India (Part <strong>–</strong> I)<br />
a) Economy; marginalization of women and sexual division of Labour.<br />
b) Polity: reservations for women.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Agarwal, B. A. 1994. "Field of One's Own: Gender and Land Rights in South Asia,<br />
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.<br />
Altekar, A.S. 1983. The Position of woken in Hindu Civilization, Delhi: Motilal<br />
Banarasidass.<br />
Chanana, Karuna. 1988. Socialization, Women and Education: Exploration in gender<br />
Identity, New Delhi: Orient Longman.<br />
Desai, Ncera and M. Krishnaraj. 1987. Women and Society in India, Delhi : Ajanta.<br />
Dube, Leela et al. (eds.). 1986. Visibility and Power. Essays on Women in Society and<br />
Development, New Delhi : OUP.<br />
Dube, Leela. 1997. Women and Kinship: Comparative Perspectives on Gender in South<br />
and South East Asia. Tokyo: United Nations University press.<br />
Forbes, G. 1998. Women in Modern India. New Delhi, Cambridge University Press.<br />
Gandhi, N. and N. Shah. 1992. The Issues at Stake : Theory and Practice in the<br />
Contemporary Women's Movement in India, New Delhi: Kali for Women.<br />
Ghadially, Rehana (ed.). 1988. Women in Indian Society, New Delhi: Sage.
Government of India. 1974. Towards Equality : report of the Committee on the Status of<br />
Women.<br />
Mies Maria. 1980. Indian Women and Patriarchy: Conflicts and Dilemmas of Students<br />
And Working Women. New Delhi; Concept.<br />
Myers, Kristen Anderson et al. (eds.). 1998. Feminist Foundations: Towards<br />
Transforming Sociology, new Delhi : Sage.<br />
Oakley, Ann. 1972. Sex, Gender and Society, New York : Harper and Row.<br />
Omvedt, Gail. 1975. Caste, Class and Women's Literati on in India, Bulletin of concerned<br />
Asia Scholars, 7, 1975.<br />
Pardeshi, Pratima. 1998. Dr. Ambedkar and the question of Women's Liberation in India,<br />
Pune: WSC, University of Pune.<br />
Sharma, Ursula. 1983. Women, Work and Property in North West India, London;<br />
Tavistock.<br />
Srinivas, M.N. Caste: Its Modern Avatar, New Delhi : Penguin (Leela Dube's Article on<br />
Caste and Women).<br />
Vaid, S & K. 1989. Sangari, Recasting Women : Essays in Colonial History, New Delhi:<br />
Kali for Women.<br />
SOE <strong>–</strong> 109: Sociology of N.G.Os and Development - I<br />
Unit I: Introduction<br />
a) Concept of welfare, development and empowerment<br />
b) Need for welfare and development organizations in capitalist societies<br />
c) Governmental and non-governmental organizations: Nature, structure, roles and<br />
functions<br />
Unit II: Establishing NGOs<br />
a) Registration of NGOs under relevant laws-forms and society’s Act, cooperative<br />
society Act and Chritable Trust Act<br />
b) Registration, process and procedures, constitution, rules and regulations, goals<br />
c) Types of NGOs<br />
Unit III: NGOs Movement in India<br />
a) Past experience and present trends<br />
b) NGOs and government in India: central government, state government and<br />
panchayati Raj levels<br />
c) Role for the NGOs in the new economic policy of the central government<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Chandra, Murli V. (ed). Role of voluntary organizati ons in social development. New<br />
Delhi: Stearling Publishers.<br />
Chaudhuri, D. Paul. 1983. ‘Social welfare administration’, Delhi: Atmaram & Sons.<br />
Garain S. 1998. Organizational effectiveness of NGOs, Jaipur: University Books House.<br />
Garain S. Towards a measure of perceived organizational effectiveness in nongovernmental<br />
organization, Mumbai: Indian Journal of Social Welfare, 54 (2),<br />
251-270.<br />
Government of India- Charitable and Religious Trust Act, 1920.<br />
Government of India- Co-operative Societies Act, 1912.<br />
Government of India-Societies registration Act, 1860.
Jackson, J. 1989. Evaluation of Voluntary Organizations, Delhi: Information and News<br />
Network.<br />
Luthans, Fred. 1990. Organizational behaviour, Boston, Irwin McGraw Hill.<br />
SOE - 110: Sociology of Migration - I<br />
Unit I: Concept of Migration, Sources of Migration data, type of Migration, Census<br />
definition of Migration and limitations.<br />
Unit II: Migration differentials, migration patterns in developed and developing<br />
countries with special reference to India<br />
Unit III: Internal Migration: Determinants of internal migration at the place of origin and<br />
at the place of destination. Consequences of internal migration: Demographic,<br />
economic, social and political at the place of origin and destination.<br />
Consequences of migration at household and individual levels.<br />
Unit IV: International Migration:<br />
Sources of international migration data and problems<br />
Historical and Recent trends of international migration<br />
Types of international migration: Permanent migration, Labour migration, Brain<br />
drain, Refugee migration and Illegal migration.<br />
Causes and consequences of international migration<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Bilsborrow, R.E. 1981. ‘Surveys in internal migration in low income countries: Issues of<br />
survey and sample design’, ILO, Geneva.<br />
Cohen, Robin. 1995. ‘The Cambridge survey of world migration’, Cambridge University<br />
Press, Cambridge.<br />
Hatton, T.J. and Williamson, J.G. 1998. ‘The age of mass migration: Causes and<br />
Economic impact’, Oxford University Press, New York.<br />
Israel, Milton and Wagle, N.K. 1993. ‘Ethnicity, Identity, Migration’, The centre for<br />
South Asian Studies, University of Toronto.<br />
Mishra, B.D. 1995. ‘An introduction to the study of population’, South Asian Publishers<br />
Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi.<br />
Mishra, Omprakash (Ed.) 2004. ‘Forced Migration’, Manak Publications, Delhi.<br />
Mitra, R.G. 2002. ‘Understanding Patterns of Migration from census 2001 data’,<br />
Population stabilization and development, Council of cultural growth and cultural<br />
relations, Cuttack.<br />
Oberai, A.S. and Singh, M.K.M. 1983, ‘Causes and Consequences of internal migration <strong>–</strong><br />
A Study in the Indian Punjab’, Oxford University Press, Delhi.<br />
Pathak, K.B. and Ram, F. 1998. ‘Techniques of Demographic Analysis’, Himalayan<br />
Publishing House, Mumbai.<br />
Rogaly, Ben. 2001. ‘Seasonal migration, Social Change and Migrants Rights <strong>–</strong> Lessons<br />
from West Bengal’, Economic and Political Weekly, Vol. 36 (49).<br />
Shrylock, Henry S., Jacob, S. Siegal and Associates. 1980. ‘The Methods and Materials<br />
of Demography’, Vol. II, US Bureau of the Census, Washington D.C.<br />
United Nations. 1979. ‘Trends and Characteristics of international migration since 1950’,<br />
Demographic Studies No. 64, UN, New York.
Zachariah, K.C. and Rajan S.I. 2001. ‘Migration Mosaic in Kerala: Trends and<br />
determinants, Demography India, Vol. 30(1).<br />
SOE - 103: Perspectives on Indian Society - I<br />
1. Understanding and Conceptualising Indian Society.<br />
a) Cultural Diversity: Race, Caste, Tribe, Religion, Language.<br />
b) Perspectives in Indian Philosophy,<br />
i) Charvak's materialistic view.<br />
ii) Buddhist views on social equality,<br />
iii) Jain philosophy: equality.<br />
II. History and Development of Indian Sociology.<br />
a) Imperial gazetteer as an instrument of colonial policy.<br />
b) Social Anthropology and Sociology in post independent period.<br />
c) Academic new-colonialism.<br />
d) Americanisation of sociology.<br />
III. Indological / Textual: G. S. Ghurye and Louis Dumont.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Ahuja Ram, 1999, Society in India, Rawat Publication, Jaipur.<br />
Atal, Yogesh. 2004. Indian Sociology: From Where to Where. Jaipur: Rawat<br />
Publications.<br />
Beteille, Andre 1972. Inequality and Social Change. Delhi: Oxford University Press.<br />
Beteille, Andre, 2002. Sociology: Essays on Approach and Method. New Delhi: Oxford<br />
University Press.<br />
Bose, N.K. 1975.The structure of Hindu Society. New Delhi: Orient Longman.<br />
D’Souza, P. R. (ed.). 2000. Contemporary India: Transitions. New Delhi: Sage<br />
Publications.<br />
Dahiwale, S.M. (ed). 2004. Indian Society: Non-Brahmanic Perspectives. Jaipur: Rawat<br />
Publications.<br />
Das, Veena. 2003. The Oxford Companion to Sociology and Social Anthropology. Vol. I<br />
and II, New Delhi:Oxfoerd.<br />
Desai, A. R. 1976. Social Background of Indian Nationalism. Bombay: Popular<br />
Prakashan.<br />
Dhanagare, D. N. 1999. Themes and Perspectives in Indian Sociology. Jaipur: Rawat<br />
Publications<br />
Dumont, Louis, 1970. Homo Hierarchicus. New Delhi: Vikas.<br />
Gardner, Peter in Sylvia Vatuk (ed.). 1969. American studies in the Anthropology of<br />
India. New Delhi.<br />
Ghurye, G. S.1969. Caste and Race in India, Bombay. Popular Prakashan.<br />
Khilnani, Sunil. 1999. The Idea of India. New Delhi: Penguin.<br />
Mukherjee, Ramkrishna. 1979. Sociology of Indian Sociology. Bombay: Allied<br />
Publishers.<br />
Oommen, T.K. and Mukherjee, Partha. Indian Sociology: Reflections and<br />
Introspections. Bombay: Popular.<br />
Panikkar, K. M. 1967. Essential features of Indian Culture. Bombay: Bhartiya Vidya<br />
Bhawan.
Prabhu, P.N. 1954.Hindu Social Organization.Popular book depot.<br />
Pramanik, S. K. 2001.Sociology of G. S. Ghurye. Rawat, New Delhi.<br />
Shama, K. L. 2000. Caste, Class and Tribe. New Delhi: Rawat publication.<br />
Singer, Milton and Cohn, B.S (ed).1975. Structure and Change in Indian society. New<br />
York: Harper and Row.<br />
Singh, K.S. 1992. The people of India: An Introduction, Anthropological survey of India,<br />
Calcutta.<br />
Singh, Yogendra. 2004. Indian Sociology.Jaipur: Rawat.<br />
Singh, Yogendra.1973. Modernization of Indian Tradition. New Delhi: The Thomson<br />
Press Ltd.<br />
Singh, Yogendra.1986. Indian Sociology: Conditioning and Emerging Concerns. New<br />
Delhi: Vistar.<br />
Srinivas. M. N. 2002. Collected Essays. New Delhi: OUP.<br />
The Gazetteer of India. Vol.II, New Delhi: The Government of India Publication.<br />
SOE - 107: Globalization and Society - I<br />
I. The nature and dynamics of globalization<br />
The historical and social context of globalization - world capitalism,<br />
modernization and globalization - distinctive, characteristics of globalization -The<br />
role of information and communication technology - Benefits and disadvantages<br />
of globalization.<br />
II. Agencies of globalization<br />
Political economy of globalization agencies of globalization, Multinational<br />
corporations (MNC's), nation -state, media, market, nongovernmental<br />
organizations (NGO's) International agencies (International Monetary Fund,<br />
World Bank, etc.)<br />
III. Globalization and culture (Part <strong>–</strong> I)<br />
The ethos of globalization (unbridled freedom, individualism, consumerism) -<br />
Diffusion and projection of American value system and cultural patters through<br />
the media - Cultural homogenization, hegemony and dominance.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Appadurai, Arjun, 1997. Modernity at large: Cultural dimensions of<br />
globalization, New Delhi: Oxford University press.<br />
Drezera jean and Amartya Sen, 1996. Indian economic development and social<br />
opportunity, Delhi Oxford University Press.<br />
Escobar, Arturo, 1995. Encountering development: The making and unmaking of the<br />
third world Princeton : Princeton University press.<br />
Ferrante, Joan. 2003. Sociology: A Global Perspective. 5th Edition. Thomson<br />
Hoogvelt, Ankie, 1998. The sociology of development, London: Macmillan.<br />
Hoogvelt, Aukie, 1997, Globalisation and the post-colonial world - The new political<br />
economy of development, London : Macmillan.<br />
Jha, Avinash 2000: Background to Globalization; Centre for Education and<br />
Documentation, Mumbai.
Kiely, Ray and Phil Marfleet (eds.) 1998. Globalization and third world. London :<br />
Routledge.<br />
Lechner, Frank J. and Boli, John (ed) 2000: The Globalization; Backwell, Oxford.<br />
Panikkar, K. N. 1995: Culture and Globalization; Economic and Political weekly, Feb.<br />
18, PP 374-375.<br />
Preston, P.W. 1996. Development theory - An introduction, Oxford Blackwell.<br />
Schuurman, Frans J. (ed) 2002: Globalization and Development Studies; SAGE<br />
Publication, New Delhi.<br />
Waters, Malcolm, 1996. Globalisation, London : Routledge.<br />
SOE <strong>–</strong> 108: <strong>SOCIOLOGY</strong> <strong>OF</strong> AGEING - I<br />
Unit I:The scope and significance of Sociology of Ageing:<br />
a) Trends of increasing ageing population in different societies.<br />
b) Factors responsible for increasing the ageing population<br />
c) Social, economic and political implications of ageing population for developed<br />
and developing societies.<br />
Unit II:Theoretical and Sociological perspectives on ageing:<br />
a) Engagement versus Disengagement theory<br />
b) Integration versus segregation theory.<br />
c) Role theory.<br />
d) Social Exchange theory.<br />
e) Activity theory.<br />
Unit III: Age-Sex Structure and Characteristics:<br />
a) Importance for the study of age-sex structure and characteristics<br />
b) Age structure: Dependency ratio: Youngand Old, Median age of Population, Index of<br />
ageing, Population Pyramid, Determinants of age structure of population<br />
c) Sex Structure: Sex Ratio, Determinants of sex structure<br />
Unit IV:Concepts of age grades and the Aged:<br />
a) Concept of age grades and the aged in tribal, traditional and modern societies<br />
b) Status of aged people in the traditional Indian society<br />
Unit V:Problems of Elderly people:<br />
a) Economic, Psychological, Physical and other Problems<br />
b) Problems of coping with ageing among<br />
i) Retired salaried people<br />
ii) Aged people in unorganized sector<br />
iii) Aged in farming / agriculture<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Alfred de Soza; Walter Femandes (1982) (eds); Ageing in South Asia: Theoretical Issues<br />
and Policy Implications: New Delhi: Indian Social institute.<br />
Bhatla, P. C. (2000) (ed.); Lecture-Series in Geriatrics, New Delhi: National Institute of<br />
Primary Health.<br />
Bhende, A. and T. Kanitkar. 2004. ‘Principles of Population Studies’, Mumbai: Himalaya<br />
Publishing House.<br />
Biswas, S. K. (1987) (ed.): Ageing in Contemporary India Calcutta: India n<br />
Anthropological Society (Occasional Papers)
Choudhary, S. K. (1992) (ed.); Problems of the Aged and of Old Age Homes Bombay:<br />
Akshar Prathi Roop Limited.<br />
Dhillon, P. K. (1992) Psycho-Social Aspects of Ageing in India, New Delhi : Concept<br />
Publishing Company.<br />
Indira, Jai Prakash (1991) (ed.); Quality Ageing: Collected papers, Varanasi Association<br />
of Gerontology.<br />
Kumar S. Vijaya (1991); Family Life and Socio-Economic Problems of the Aged, New<br />
Delhi : Ashish Publishing House.<br />
Kumar, Vinod (1996) (ed.); Ageing Indian Perspective and Global Scenario, New Delhi:<br />
All India Institute of Medical Sciences.<br />
Muthayya B. C; Annesuddin M. (1992); Rural Aged: Existing Conditions, Problems and<br />
Possible Interventions - A Study in Andhra Pradesh, Hyderabad - National<br />
Institute of Rural Development.<br />
Palmore, E. (1993) (ed); Developments and Research on Ageing, Westport: Greenwood<br />
Press.<br />
Rao, K. S. (1994); Ageing, New Delhi: National Book Trust of India.<br />
Sati, P. N. (1987); Needs and the Problems of the Aged; Udaipur: Himanshu Publishers.<br />
Sen, K. Ageing (1994): Debates on Demographic Transition and Social Policy; London:<br />
Zed Books.<br />
Shrylock, Henry S., Jacob, S. Siegal and Associates. 1980. ‘The Methods and Materials<br />
of Demography’, Vol. I & II, US Bureau of the Census, Washington D.C.<br />
Soodae K. S. (1975); Ageing in India: Calcutta : T. K. Mukherjee Minerva Association<br />
(Pvt.) Ltd.<br />
United Nations, Proceedings of the United Nations Round Table on the "Ageing of Asian<br />
Populations", Bangkok <strong>–</strong> 1994.<br />
SOE - 111: Sociology of Mass communication - I<br />
Unit I: Concepts of Communication<br />
a) Communication: Elements of communication. Interpersonal Communication,<br />
Mass Communication, Folk Media and (Popular Culture).<br />
b) Mass Media: Nature and Characteristics.<br />
c) ICT and Information Society<br />
Unit - II Theoretical approaches to communication and development.<br />
a) Functional<br />
b) Marxist<br />
c) Liberal<br />
Unit <strong>–</strong> III Rise and growth of Mass Media in India<br />
a) Newspaper<br />
b) Radio<br />
c) Cinema and T.V.<br />
d) Social impact of mass media<br />
Unit -IV Role of information Communication Technology and Development<br />
a)Internet<br />
b)Mobile<br />
c) Telecommunication
Suggested Readings:<br />
Adult Emery, Agee,Dodd : Introduction to Mass Communication, Mead and Company,<br />
1963.<br />
Ambekar J.B : Communication and Rural Development, Mittal Publication, New Delhi,<br />
1992.<br />
Arvind Singhal and Rogers Everett: India’s Communication Revolution from Bullock<br />
Carts to Cyber Mart, Sage Publications, New Delhi, 2000.<br />
Curran, J. and M. Gurevith ( eds.): Mass Media and Society, Edward Arnold, Sage,<br />
London.<br />
French, D and Michal Richard ( eds ) : Television in Contemporary Asia, Sage, London,<br />
2000.<br />
McQuail, Denis: Mass Communication theory: Sage, New York, 2000.<br />
Melkote Shrinivas : The Information Society, Sage, New Delhi.<br />
Preston, P : Reshaping Communications, Sage, London, 2000.<br />
Relevant Articles from the Journals : Media Asia, Communicator, Social Change,<br />
Univercity News.<br />
Zachariah Aruna : Communication Media and Electronic Revolution, Kanishka, New<br />
Delhi, 1986.<br />
SOE - 112: Contemporary social problems in India - I<br />
Unit I Social Problems: Meaning, Nature and Theoretical approaches<br />
a) Social Problems: Definition and Nature<br />
b) Theoretical approaches to study the social problems: social pathological, social<br />
disorganization, value conflict, deviant behaviour<br />
Unit II Socio-Cultural Problems<br />
a) Poverty<br />
b) Inequality of caste and gender<br />
c) Regional, ethnic and religious disharmonics<br />
d) Family disharmony: i) Domestic violence ii) Dowry iii) Divorce iv)<br />
Intergenerational conflict<br />
Unit III Developmental Problems<br />
a) Population<br />
b) Slums<br />
c) Development induced displacement<br />
d) Ecological degradation and environmental pollution<br />
e) Health problems<br />
f) Terrorism<br />
g) Consumerism<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Ahmad, Siddique. 2005. ‘Criminology’, (5 th Edition), Eastern Book Company, New<br />
Delhi.<br />
Ahuja, Ram. 2002. ‘Social Problems in India’, Rawat Publications, Jaipur.<br />
Bedi, Kiran. 1998. ‘It is always Possible’, Sterling Publications Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi.<br />
Deb, Sibnath. 2007. ‘Contemporary Social Problems in India’, Anmol Publications Pvt.<br />
Ltd., New Delhi.
Horton, Pawl B. and Leslie, Gerald R. 1974. ‘The Sociology of Social Problems’ (fifth<br />
edition), Printice-Hall, New Jersey.<br />
Jogan, Sankar (Ed.). 1992. ‘Social Problems and Welfare in India’, Ashish, New Delhi.<br />
Madan, G.R. 1990. ‘Indian Social Problems’, Vol. I and II, Allied Publishers Limited,<br />
New Delhi.<br />
Mamoria, C.B. 1981. ‘Social Problems and Social Disorganization in India’, Kitab<br />
Mahal, Allahabad.<br />
Mishra, Girish and Pandey, Brajkumar. 1998. ‘White-Collar Crimes’, Gyan, New Delhi.<br />
Mishra, Omprakash (Ed.). 2004. ‘Forced Migration’, Manak Publications, Delhi.<br />
Pavanjape, N.P. 2005. ‘Criminology’, (12 th Edition), Central, Allahabad.<br />
Sarkar, Profulla C. 2008. ‘Understanding Social Problems and Policies’, Serrial<br />
Publications, New Delhi.<br />
Shivananda, J. ‘Contemporary Social Problems’, Alfa Publications, New Delhi.<br />
SOE - 113: Sociology of Education - I<br />
Unit I: Introduction, Growth and Development of Sociology of Education<br />
i) Definition and Scope of Sociology of Education<br />
ii) Development of Sociology of Education<br />
iii) Aim’s of education<br />
iv) Difference between Sociology of education and educational Sociology<br />
Unit II: Society and Education<br />
i) Social function of education<br />
ii) Education as a social system<br />
iii) Socialization process<br />
iv) Education in tribal society<br />
v) Process of social progress and change<br />
Unit III: Sub-Systems of society and education<br />
i) Education system and political system<br />
ii) Education and economic development<br />
iii) Education and totaleterian<br />
iv) Family institution and education<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Aggarwal, J.C. 1985. ‘Theory and Principles of education, Philosophical and<br />
Sociological bases of Education’, Delhi: Vikas Publishing House Pvt. Ltd.<br />
Gore, M.S. 1994. ‘Indian education, structure and process’, New Delhi: Rawat<br />
Publications.<br />
Gore, M.S. at. Al. (eds). 1975. ‘Papers of Sociology of Education in India, NCERT, New<br />
Delhi.<br />
Jeyaraman, N. 1990. ‘Sociology of Education’, Jaipur: Rawat Publications.<br />
Morris, Iror. 1978. ‘The Sociology of Education’, Allan and Unwin.<br />
Musgrave, P.W. 1972. ‘The Sociology of Education’, London, Methuen & Co. Ltd.<br />
Ottaway, A.K.C. 1980. ‘Education and Society <strong>–</strong> n introduction to the Sociology of<br />
Education’, London: Routledge and Kegan Paul.<br />
Shah, B.V. 1998. ‘Sociology of Education’, Jaipur and New Delhi: Rawat Publications.
M. A. II <strong>SEMESTER</strong><br />
SOC-201: Theoretical Perspectives in Sociology<br />
Unit I Structuralism and post structuralism<br />
a) Human Nature and Cultural Diversity- C. Levi-Strauss.<br />
b) Structuralism and Post-Structuralism- M. Foucault.<br />
Unit II. Neo-Functionalism and Neo-Marxism<br />
a) J. Alexander.<br />
b) J. Habermass.<br />
c) L. Althusser.<br />
Unit III Phenomenology and Ethnomethodology<br />
a) Alfred Schutz.<br />
b) Peter Berger and T.G. Luckmann.<br />
c) Harold Garfinkel and Goffman.<br />
Unit IV. Structuration and Post-Modernism<br />
a) Anthony Giddens.<br />
b) J. Derrida<br />
c) Michel Foucault,<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Giddens, Anthony. 1983. Central Problem in Social Theory: Action. Structure and<br />
contradiction in Social Analysis, London: MacMillan.<br />
Kaiper, Adam rind Jessica Kuper. (Eds ).(2nd Edition).1996. The Social Science<br />
encyclopedia. London and New York : Routledge.<br />
Ritzer, George and Goodman, D. 2004. Sociological Theory (6rd Edition) New York:<br />
McGraw-Hill.<br />
Schutz, Alfred.1962. The Problem of Social Reality Vol.I.The Hague, Martinus Mijhoff.<br />
Shama, Ram Nath and Shama, Rajendra K. 1988. Contemporary Sociological Theories,<br />
(1st Edition), Bombay: Media Promoters & Publishers,<br />
Sturrock, Johan (Ed.). 1979. Structuralism and since: From Levi Strauss to Derrida,<br />
Oxford, Oxford University Press.<br />
Turner, Jonathan H. 1995.The Structure of Sociological Theory (4th Edition), Jaipur and<br />
Mew Delhi: Rawat Publication.<br />
Zeitlin, Irving M. 1998. Rethinking Sociology; A Critique of contemporary Theory,<br />
(Indian Edition). Jaipur and New Delhi: Rawat Publication.<br />
SOC <strong>–</strong> 202: Methodology of Social Research<br />
I. Quantitative Methods and Survey Research:<br />
a) Survey techniques and limitation.<br />
b) Operationalization and research design: functions, Characteristics, phases,<br />
difference in designing quantitative and qualitative research. Design for different<br />
types of research.<br />
c) Sampling: Purposes, principles, advantages, types: probability and non -<br />
probability.<br />
d) Questionnaire construction and Interview schedule: format, sequence, types of<br />
questions, pit-falls in question construction, steps, pre-testing, advantages,<br />
limitations.
e) Reliability and validity: Test related correlation, split-half correlation, verage<br />
interterm correlation, validity: concurrent, predictive, construct.<br />
II. Statistics in Social Research:<br />
a) Measures of central tendency: mean, median, mode.<br />
b) Measures of dispersion: Standard/ Quartile Deviation.<br />
c) Measures of association: Yules Q, Phi Coefficient Q. Contingency coefficient<br />
(c). Crammers V, Gamma (G), Rho correlation (rs), Karl Pea rson's correlation<br />
coefficient (r).<br />
III. Qualitative Research Techniques:<br />
a) Participant observation, ethnography, interview guide.<br />
b) Case study method: characteristics, purpose, sources, planning, advantages, and<br />
criticism, developing theories from case studies.<br />
c) Content analysis: characteristics, steps, process, sources of data, difference with<br />
historical method, strength, and limitations.<br />
d) Encounters and experiences in field work.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Agresti Alan and Finly Barbara. 1986.Statistical Methods for the Social Sciences,<br />
Dellen Publishing Company, New Jersey.<br />
Ahuja, Ram. 2001. Research Methods, Rawat Publications, Jaipur.<br />
Bose, Pradip Kumar. 1985. Research Methodology: A Trend Report ICSSR, New Delhi.<br />
Bryman, Alan.1988. Quantity and Quality in Social Research. Unwin Hyman, Lonlon.<br />
Denzin, N. K. & Lincoln, Y. S. 2000. Handbook of Qualitative Research (2nd edition). .<br />
Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.<br />
Kidder, Louse H. 1987.Research Method s in Social Relations. Holt, Rinehart and<br />
Kothari, C.R. 1985. Research Methodology-Methods and Techniques. New Delhi:<br />
Wishwa Prakashan,<br />
Patrick, McNeill and Steve, Chapman. 1990. Research Methods, Routledge, New<br />
York.<br />
Sharma, K. R. 2004. Research Methodology. New Delhi: National Publishing House.<br />
Shipman, Martin, 1988.The Limitations of Social Research, Logman. Londan,.<br />
Sjoberg, Gideon and Roger, Nett, 2002. Methodology for Social Research, Rawat<br />
Srinivas, M.N .and Mada n T.N. (Eds.). 1975. Encounter and Experience: Personal<br />
Vaus, D. A. de .1991. Surveys in Social Research (3rd ed), Allen & Unwin.<br />
Wilkinson, T. S. and Bhandarkar, P. L. Methodology and Techniques of Social<br />
Research. Bpmbay: Himalaya Publishing House.<br />
Winston, New York. McNeill,<br />
SOE <strong>–</strong> 204: RURAL SOCIETY IN INDIA - II<br />
Unit I: Rural social institutions and their changing nature.<br />
a) Family<br />
b) Caste<br />
c) Marriage<br />
d) Religion<br />
e) Education
f) Economy - Balutedari system, land reforms in India.<br />
g) Rural leadership, factionism.<br />
Unit II: Rural social problems.<br />
a) Rural poverty<br />
b) Castism<br />
c) Landless labour.<br />
Unit III: Water and Agriculture, irrigation management practices.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Andre Setille, 1974. Six Essays in Comparative Sociology, OUP, New Delhi (Relevant<br />
chapters).<br />
Ashish Nandy, 1999. Ambiguous Journey to the City, New Delhi, OUP.<br />
Berch, Berberogue (ed.) 1992: Class, State and Development in India, Sage, New Delhi.<br />
Beteille Andre. 1974. Studies in Agrarian Social Structure, Oxford University Press,<br />
Delhi.<br />
Desai, A.R. 1977. Rural Sociology in India, Popular Prakashan, Bombay.<br />
Desai, A.R..(Ed.) Peasant Struggles in India, Oxford Uriversity, Bombay, 1979.<br />
Dhanagare, D.N. 1988. Peasant Movements in India, OUP, New Delhi.<br />
Doshi, S.L. and Jain, P.C. Rural Sociology, Rawat Publications, Jaipur and New Delhi,<br />
1999.<br />
Jain, S.C. 1967. “Community development and Panchayati Raj in India” Allied<br />
Publishers, Bombay.<br />
Maheshwari, S.R. 1995. “Rural development in India” Sage publication, New Delhi.<br />
Mencher, J.P., 1983. Social Anthropology of Peasantry Part III, OUP.<br />
Oommen, T.K. : Social Transformation in Rural India, Vikas Publishing House, New<br />
Delhi, 1984.<br />
P. Radhakrisjmam. 1989: Peasant Struggles : Land reforms and Social Change in<br />
Malabar 1836 - 1982. Sage Publications : New Dcihi.<br />
Roy, C.N. 1994. “Politics or rural development” Rawat Publications, Jaipur.<br />
Sem Njpwamo. 1962. Evolution of Agrarian Relations in India, Peoples Publishing<br />
House, New Delhi.<br />
Sen Sunil. 1979. Agrarian Relations in India 1793 to 1947, People's Publications House,<br />
New Delhi.<br />
Shanin Teodor. 1971. Peasants and Peasants Societies, Modern Sociology Readings,<br />
Penguin.<br />
Sharma, K.L. 1997. Rural Society in India, Rawat Publications, Jaipur and New Delhi.<br />
Sharma, M.P. 1967. “Local self Govt. in India” Kitab-Mahal Allahabad.<br />
Thorner, Daniel and Thorner Alice 1962 Land and Labour in India, Asia Publications,<br />
Bombay.<br />
Thorner, Daniel and Thorner Alice. 1962. Land and Labour in India, Asia Publications,<br />
Bombay.<br />
Tiwary Jai Kumar. 1994. Rural Trade Information in India, Reliance Publishing House,<br />
New Delhi.
SOE - 205: Political Sociology Part - II<br />
I. Political Participation:<br />
a) Pressure groups and Interest groups.<br />
b) Voting behaviour<br />
c) Political role of intellectuals.<br />
II. Political process and parties in India.<br />
a) Role of Caste, religion, regionalism and language in Indian polities.<br />
b) Political parties: Characteristics, social composition of parties, mass<br />
participation, functions of political parties.<br />
III. Political Bureaucracy:<br />
a) Characteristics.<br />
b) Types.<br />
c) Significance.<br />
IV. Public opinion.<br />
a) Role of mass media.<br />
b) Politicization of social life.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Almond and Powell. Comparative Polities.<br />
Almond, A Gabriel et. al. 1973. Crises choice and change, Historical Studies of political<br />
Development. Boston.<br />
Bhambri, C.P. 1971. Bureaucracy and Politics in India, Vikas Publications, Bombay.<br />
Bhaskaran, R.1967. Sociology of Politics tradition and politics in India. Asian<br />
publishing house, Bombay.<br />
Biswas, -Diptikumar. Political Sociology, Firma KLM Private, Calcutta.<br />
Blau, P. 1956. Bureaucracy in Modern Society, Random House, New York.<br />
Calcutta.<br />
Damle Y. B. 1982. Caste, Religion and Politics in India, Oxford and IBM publishing<br />
company, New Delhi.<br />
Dowse, R. E. and Huges.1971. Political Sociology, New York, Basic Books.<br />
Dubey, S. R. Development of political thought in India.<br />
Elsentadt, S. N (ed).1989. Political Sociology, Vol-I & II, Rawat publications.<br />
Harold, D. Lasswell. 1997. On Political Sociology, The University of Chicago press,<br />
Chicago.<br />
Huntington, Samuel P. 1969. Political order in changing societies. Yale University<br />
press. New Haven.<br />
Jangam, R. T. 1980.Text Book of Political Sociology, Oxford and IBH publishing Co.<br />
Kashyap, S. 1971. Indian Political parties, The institute of Constitutional and<br />
Parliamentary studies. Published by Research, Delhi.<br />
Key, V. O. 1964. Politics, parties and pressure groups, Cropwell. New York.<br />
Kothari, Rajani (ed). 1973. Caste in Indian Politics. Orient Longmans Ltd.<br />
Kothari, Rajani. 1970. Politics in India, Orient Longman, New Delhi.<br />
Merton, R. K (ed). 1952. Reader in Bureaucracy, Glenca the free press.<br />
Mills, C. W. and Hans Gerth.1946. Essays in Sociology.Oxford, New York.<br />
Mukhopadhaya, Amal Kumar. 1977. Political Sociology. K.B. Bagchi and company,<br />
Delhi.
Nehru, Jawaharlal.1951. The discovery of India, Meridian Books, London.<br />
Philips, C. H. (ed). Society and politics in India.<br />
Robert, Michels. 1949. Political parties, Glencko free press.<br />
Verinder, Grover. 1988. Elections and politics in India, Deep and Deep publications, New<br />
Delhi.<br />
SOE <strong>–</strong> 206: GENDER AND SOCIETY - II<br />
Unit I: Gender and Society in India<br />
a) Religion and Culture : women as repositories of cultural practices and<br />
traditions, marriage, dowry and property.<br />
b) Personal Laws and civil Code: Hindu code bill, Syrian Christian law, Muslim<br />
personal law, Customary law and Tribal women.<br />
Unit II: Status, Position and changing nature of tribal, Dalit, rural and urban<br />
women in India.<br />
a) Health<br />
b) Education<br />
c) Family Status<br />
d) Political Participation<br />
e) Land rights.<br />
Unit III: Gender and Major issues<br />
a) Gender and Violence<br />
b) Gender and Development<br />
c) Women empowerment.<br />
Unit IV: Women's organization and Movement in India.<br />
a) Women's organizations: A historical sketch.<br />
b) Women's movement in India: Special Reference to Maharashtra.<br />
c) Views on women’s empowerment: Mahatma Phule, Rajarshi Shahu and<br />
Tarabai Shinde.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Agarwal, B. A. 1994. "Field of One's Own : Gender and Land Rights in South Asia,<br />
Cambridge : Cambridge University Press.<br />
Altekar, A.S. 1983. The Position of woken in Hindu Civilization, Delhi: Motilal<br />
Banarasidass.<br />
Chanana, Karuna. 1988. Socialization, Women and Education : Exploration in gender<br />
Identity, New Delhi: Orient Longman.<br />
Desai, Ncera and M. Krishnaraj. 1987. Women and Society in India, Delhi : Ajanta.<br />
Dube, Leela et al. (eds.). 1986. Visibility and Power. Essays on Women in Society and<br />
Development, New Delhi : OUP.<br />
Dube, Leela. 1997. Women and Kinship: Comparative Perspectives on Gender in South<br />
and South East Asia. Tokyo: United Nations University press.<br />
Forbes, G. 1998. Women in Modern India. New Delhi, Cambridge University Press.<br />
Gandhi, N. and N. Shah. 1992. The Issues at Stake : Theory and Practice in the<br />
Contemporary Women's Movement in India, New Delhi: Kali for Women.<br />
Ghadially, Rehana (ed.). 1988. Women in Indian Society, New Delhi: Sage.
Government of India. 1974. Towards Equality : report of the Committee on the Status of<br />
Women.<br />
Mies Maria. 1980. Indian Women and Patriarchy: Conflicts and Dilemmas of Students<br />
And Working Women. New Delhi; Concept.<br />
Myers, Kristen Anderson et al. (eds.). 1998. Feminist Found ations: Towards<br />
Transforming Sociology, new Delhi : Sage.<br />
Oakley, Ann. 1972. Sex, Gender and Society, New York : Harper and Row.<br />
Omvedt, Gail. 1975. Caste, Class and Women's Literati on in India, Bulletin of concerned<br />
Asia Scholars, 7, 1975.<br />
Pardeshi, Pratima. 1998. Dr. Ambedkar and the question of Women's Liberation in India,<br />
Pune: WSC, University of Pune.<br />
Sharma, Ursula. 1983. Women, Work and Property in North West India, London;<br />
Tavistock.<br />
Srinivas, M.N. Caste : Its Modern Avatar, New Delhi : Penguin (Leela Dube's Article on<br />
Caste and Women).<br />
Vaid, S & K. 1989. Sangari, Recasting Women : Essays in Colonial History, New Delhi:<br />
Kali for Women.<br />
SOE <strong>–</strong> 209: Sociology of N.G.Os and Development - II<br />
Unit I: Introduction: Social Development<br />
a) Concept and definition of social development<br />
b) Current debates on development<br />
c)) Approaches to development<br />
d) Development indicators, inter-country comparison<br />
Unit II: Social development in India<br />
a) The historical and social context of development in the pre-independence phase<br />
b) The post independent phase: government measures and five year plans<br />
c) Demographic transition<br />
Unit III: Rural development<br />
a) Agrarian and land reforms<br />
b) Green revolution<br />
c) Industricalization and urban development<br />
d) Other issues- Labour relations, gender issues, education, health, environment<br />
issues (land, water, forest)<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Bagchi, A.K. 1982. Political economy of underdevelopment, Cambridge: Cambridge<br />
University Press.<br />
Desai, V. 1988. Rural development (Vol. 1) Mumbai: Himalaya Publishing House.<br />
Government of India, Five Year Plan documents, New Delhi.<br />
Jacob, K.K. 1992. Social Development Perspectives.<br />
Joshi, P.C. 1976. Land Reforms.<br />
Singh, R.R. (Ed.). 1995. Whither Social Development, New Delhi: ASSWI.<br />
Singh, Y. 1972. Modernization of Indian Tradition, Delhi: Thomas Press.
SOE <strong>–</strong> 210: Sociology of Migration - II<br />
Unit I: Theories of Migration: Push-Pull hypothesis, Ravenstein’s Law of Migration,<br />
Everett Lee’s Theory of migration, Wolpert’s decision making aspect of<br />
migration, Todaro’s model of rural-urban migration<br />
Unit II: Measures of migration and problems of base population in estimation of<br />
migration rates<br />
Unit III: Direct methods of estimating migration:<br />
Estimation of life time and inter-censal migration from place of birth data,<br />
duration of residence data, place of last residence data and residence at a fixed<br />
prior date data<br />
Unit IV: Indirect measures of Net internal migration<br />
Unit V: Methods of estimating international migration<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Cohen, Robin. 1995. ‘The Cambridge survey of world migration’, Cambridge University<br />
Press, Cambridge.<br />
Cohen, Robin. 1996. ‘Theories of Migration, The international Library of Studies on<br />
migration’, Edward Elgar, Cheltenham.<br />
Mishra, B.D. 1995. ‘An introduction to the study of population’, South Asian Publishers<br />
Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi.<br />
Pathak, K.B. and Ram, F. 1998. ‘Techniques of Demographic Analysis’, Himalayan<br />
Publishing House, Mumbai.<br />
Shrylock, Henry S., Jacob, S. Siegal and Associates. 1980. ‘The Methods and Materials<br />
of Demography’, Vol. II, US Bureau of the Census, Washington D.C.<br />
Todaro, Michael P. 1976. ‘Internal migration in developing countries’, International<br />
Labour Organization, Geneva.<br />
United Nations. 1970. ‘Methods of measuring internal migration’, Manual VI, New York.<br />
SOE - 203: Perspectives on Indian Society <strong>–</strong> II<br />
I. Structural-Functionalism: M. N. Srinivas and S.C. Dube.<br />
II. Marxism: D. P. Mukherji, A. R. Desai and Ramakrishna Mukherjee.<br />
III. Subaltern perspective: B. R. Ambedkar and David Hardiman.<br />
IV. Current Debates in Indian Sociology: Contextualisation and Indigenisation.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Ambedkar, B.R. 1946. Who were Sudras? Bombay: Thacker and Co. Ltd.<br />
Ambedkar, B.R. 1948. Untouchables. New Delhi: Amrit Book Co.<br />
Ambedkar, B.R. 1957. Buddha and his Dhamma. Bombay: Siddhartha College.<br />
Desai, A. R (ed).1969. Introduction to Rural Sociology in India, Oxford, Bombay.<br />
Desai, A. R. 1948. Social Background of Indian Nationalism. Oxford, Bombay.
Desai, A. R. 1980. "Relevance of the Marxist Approach to the study of Indian Society" in<br />
Sociological Bulletin.<br />
Desai, A.R.1978. Peasant Struggles in India, Oxford. Bombay.<br />
Dube, S. C. 1955.The Indian village, Routlege, London.<br />
Guha, Ranjit (ed). 1982. Subaltern studies: Writings on south Asian History and society.<br />
Delhi:Oxford,<br />
Hardiman, David. 1987. The Coming of the Devi. Bombay: Oxford.<br />
Hardiman, David. 1996. Feeding the Bania: Peasants and Usurers in Western India.<br />
London: Oxford.<br />
Momin, A. R. 1996. The Legacy of G.S. Ghurye. Bombay: Popular Prakashan.<br />
Mukerji, D. P. 1958. Diversities. New Delhi: Peoples publishing.<br />
Mukherjee, Ramkrishna. 1958. Six villages of Bengal, Popular, Bombay.<br />
Mukherjee, Ramkrishna. 1975. The Dynamics of A Rural Society, Academic-verlag,<br />
Berlin.<br />
Mukherjee, Ramkrishna. 1979. Sociology of Indian Sociology. Bombay: Allied<br />
Publishers.<br />
Sharma, Surendra. 1985. Sociology in India: A perspectives from sociology of<br />
Knowledge. Jaipur: Rawat.<br />
Singhi, N. K. 1996. Theory and Ideology in Indian Sociology. Jaipur: Rawat publication.<br />
Srinivas, M. N.1960. India's villages. Bombay: Asia Publishing house.<br />
Srinivas, M.N. Caste in modern India. New Delhi: Asia Publishing house.<br />
SOE - 207: Globalization and Society - II<br />
I. Globalization and culture (Part <strong>–</strong> II)<br />
Globalization and the resurgence of ethnic consciousness: global tourism,<br />
diasporic communities, transnational ethnic and religious movements, religious<br />
fundamentalism.<br />
II. Social consequences of globalization<br />
Inequality within and among nation states - differential perception of<br />
globalization among nations and their populations - Socio-economic impact of<br />
globalization - impact on individual and group identities.<br />
III. Globalization and the Indian experience:<br />
Globalization and public policy - Debate on globalization - impact of<br />
globalization: Indian education, Indian agriculture Trends and Prospects.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Appadurai, Arjun, 1997. Modernity at large: Cultural dimensions of<br />
globalization, New Delhi: Oxford University press.<br />
Drezera jean and Amartya Sen, 1996. Indian economic development and social<br />
opportunity, Delhi Oxford University Press.<br />
Escobar, Arturo, 1995. Encountering development: The making and unmaking of the<br />
third world Princeton : Princeton University press.<br />
Hoogvelt, Ankie, 1998. The sociology of development, London: Macmillan.<br />
Hoogvelt, Aukie, 1997, Globalisation and the post-colonial world - The new political<br />
economy of development, London : Macmillan.
Kiely, Ray and Phil Marfleet (eds.) 1998. Globalization and third world. London :<br />
Routledge.<br />
Preston, P.W. 1996. Development theory - An introduction, Oxford Blackwell.<br />
Waters, Malcolm, 1996. Globalisation, London : Routledge.<br />
SOE - 208: <strong>SOCIOLOGY</strong> <strong>OF</strong> AGEING -II<br />
Unit I: Family and Aged:<br />
a) Family and aged in urban and rural settings<br />
b)Supports of family for aged; physical, financial, social, psychological and<br />
emotional<br />
Unit II: Government policies and Aged:<br />
a) Policies of the Government with regard to aged salaried people from<br />
Government and non-government; farming sectors and unorganized daily-wage<br />
earners sectors<br />
b)Support systems needed for elderly at family community and state levels<br />
Unit III: Social security measures:<br />
a) Superannuation benefits/ pensions/medical reimbursement etc.<br />
b)Other financial assistances and concessions<br />
c) Provisions for leisure time activities i.e. Day-core Centres<br />
d)Opportunities for participation in working other services<br />
e) Medical facilities - hospitalization etc.<br />
f) Other social security measures<br />
Unit IV: Old age Homes:<br />
a) Concept, nature and structure<br />
b)"Matoshri Old age Home Schemes" of Maharashtra Government<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Alfred de Soza; Walter Femandes (1982) (eds); Ageing in South Asia: Theoretical Issues<br />
and Policy Implications: New Delhi: Indian Social institute.<br />
Bhatla, P. C. (2000) (ed.); Lecture -Series in Geriatrics, New Delhi ; National Institute of<br />
Primary Health.<br />
Bhende, A. and T. Kanitkar. 2004. ‘Principles of Population Studies’, Mumbai: Himalaya<br />
Publishing House.<br />
Biswas, S. K. (1987) (ed.): Ageing in Contemporary India Calcutta : Indian<br />
Anthropological Society (Occasional Papers)<br />
Choudhary, S. K. (1992) (ed.); Problems of the Aged and of Old Age Homes Bombay:<br />
Akshar Prathi Roop Limited.<br />
Indira Jai Prakash (1991) (ed.); Quality Ageing: Collected papers, Varanasi Association<br />
of Gerontology.<br />
Joshi, Pratap - Old Age Care and Welfare Administration - Kanishka Publishers, New<br />
Delhi, 2000.<br />
Kumar, Vinod (1996) (ed.); Ageing Indian Perspective and Global Scenario, New Delhi:<br />
All India Institute of Medical Sciences.
Muthayya, B. C; Annesuddin M. (1992); Rural Aged: Existing Conditions, Problems and<br />
Possible Interventions - A Study in Andhra Pradesh, Hyderabad - National<br />
Institute of Rural Development.<br />
Rao, K. S. (1994); Ageing, New Delhi: National Book Trust of India.<br />
Sati, P. N. (1987); Needs and the Problems of the Aged; Udaipur: Himanshu Publishers.<br />
Sen, K. Ageing (1994): Debates on Demographic Transition and Social Policy; London:<br />
Zed Books.<br />
Shrylock, Henry S., Jacob, S. Siegal and Associates. 1980. ‘The Methods and Materials<br />
of Demography’, Vol. I & II, US Bureau of the Census, Washington D.C.<br />
Soodae, K. S. (1975); Ageing in India: Calcutta: T. K. Mukherjee Minerva Association<br />
(Pvt.) Ltd.<br />
United Nations, Proceedings of the United Nations Round Table on the "Ageing of Asian<br />
Populations", Bangkok <strong>–</strong> 1994.<br />
SOE - 211: Sociology of Mass communication - II<br />
Unit I: Study of Culture<br />
a) Popular Culture, Mass Culture, Folk Culture.<br />
b) Role of mass media in Popular Culture.<br />
c) Relationship between Popular Culture and leisure and recreation.<br />
d) Relationship between Popular Culture.<br />
Unit II: Impact of ICT<br />
a) Popular Culture<br />
b) Television<br />
c) Commercialisation of leisure<br />
d) Popular Music and its social reach<br />
Unit III: Globalisation and folk Culture<br />
a) Local, regional and national Cultures<br />
b) Control of MNC’s over global information flow and entertainment.<br />
Unit IV: Social Issues of Marketing<br />
a) Use and abuse of Media.<br />
b) Advertisement and its social economic effects.<br />
c) Effects of Globalisation: Positive and negative.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Anne Gray, Research practice for cultural studies sage ,London, 2005.<br />
Don Robotham, Culture, Society and Economy Bringing production Back in, Sage,<br />
London 2005.<br />
Elizabeth Long (ed), From Sociology to Cultural studies, Blackwells, 1997.<br />
French D and Michael Richard, 2000 eds : Television in Contemporary Asia (London :<br />
Sage).<br />
Gunaratne, S. 2000, eds : Handbook of the media in Asia (London : Sage)<br />
John Nguyet Erni and Ackbar Abbas, inter nationalising Cultural studies, Blackwell,<br />
London, 2005.<br />
Manuel, P. 1998 Cassette Culture : Popular music and Technology in North India.<br />
Mitra. A. 1993 : Television and Popular Culture in India (Delhi : Sage).<br />
Singhal.A and E.M. Rogers, 2000 : India’s Communication Revolution (Delhi : Sage).
SOE - 212: Contemporary social problems in India - II<br />
Unit I: Disorganizational Problems<br />
a) Crime and delinquency<br />
b) White-Collar crime and changing profile of crime and criminals<br />
c) Corruption<br />
d) Suicide<br />
Unit II: Social Vices<br />
a) Alcoholism and Drug Addiction<br />
b) Gambling and Smoking<br />
c) Prostitution<br />
d) Beggary<br />
e) Sex Offences: Rape, Incest, Adultery, Eve-teasing<br />
Unit III: Problems of Nation Building Secularism, Pluralism and Nation Building<br />
Unit IV: Social Welfare Services and Five-Year Plans<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Ahuja, Ram. 2002. ‘Social Problems in India’, Rawat Publications, Jaipur.<br />
Bedi, Kiran. 1998. ‘It is always Possible’, Sterling Publications Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi.<br />
Deb, Sibnath. 2007. ‘Contemporary Social Problems in India’, Anmol Publications Pvt.<br />
Ltd., New Delhi.<br />
Jain, Prabha Shasi and Singh, Mamta. 2001. ‘Violence against Women’, Radha, New<br />
Delhi.<br />
Jogan, Sankar (Ed.). 1992. ‘Social Problems and Welfare in India’, Ashish, New Delhi.<br />
Madan, G.R. 1990. ‘Indian Social Problems’, Vol. I and II, Allied Publishers Limited,<br />
New Delhi.<br />
Mamoria, C.B. 1981. ‘Social Problems and Social Disorganization in India’, Kitab<br />
Mahal, Allahabad.<br />
Sarkar, Profulla C. 2008. ‘Understanding Social Problems and Policies’, Serrial<br />
Publications, New Delhi.<br />
Shivananda, J. ‘Contemporary Social Problems’, Alfa Publications, New Delhi.<br />
Weinberg, M.S.; Rubington Earl and Sue Kiefer Hammersmith. 1981. ‘The Solution of<br />
Social Problems-Five Perspectives (2 nd edition), Oxford University Press, New<br />
York.<br />
SOE - 213: Education and society - II<br />
Unit I: Theoretical approaches in Sociology of Education<br />
i) Marxian Perspective<br />
ii) Liberal Perspective<br />
iii) Interactionist Perspective<br />
iv) Emile Durkheim’s Perspective<br />
v) Talcott Parsons’ Perspective<br />
Unit II: Social Stratification and Education<br />
i) Need of social stratification<br />
ii) Definition of social stratification<br />
iii) Caste and Class system of stratification in Indian society
iv) Impact of educational system on stratification in independent India<br />
v) Education for liberalization, privatization and globalization<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Chitnis, Suma and P.G. Altbach. 1993. ‘Higher education reform in India: Experience<br />
and Perspectives, Sage Publications, New Delhi.<br />
Durkheim, Emile: Education and Sociology<br />
Gore, M.S. 1994. ‘Indian education, structure and process’, New Delhi: Rawat<br />
Publications.<br />
Gore, M.S. at. Al. (eds). 1975. ‘Papers of Sociology of Education in India, NCERT, New<br />
Delhi.<br />
Morris, Iror. 1978. ‘The Sociology of Education’, Allan and Unwin.<br />
Musgrave, P.W. 1972. ‘The Sociology of Education’, London, Methuen & Co. Ltd.<br />
Ottaway, A.K.C. 1980. ‘Education and Society <strong>–</strong> n introduction to the Sociology of<br />
Education’, London: Routledge and Kegan Paul.<br />
Roger, Ginod. 1990. ‘Problems of Sociology in Education’, New Delhi: Sterling<br />
Publishers Pvt. Ltd.<br />
Ruhela, S.P. 1971. ‘Sociological dimension of Indian Education’, Raj Prakashan, New<br />
Delhi.<br />
Saxena, sakuntala. 1975. ‘Sociological Perspectives in Indian Education, Ashafa<br />
Publications, New Delhi.<br />
Singh, Amrik and Philip G. Altabacli (eds): The Higher learning in India<br />
Sukla, Suresh Chandra and Krishna Kumar (eds). 1985. ‘Sociological Perspective in<br />
Education’, Delhi: Chanakya Publications.
M.A. III <strong>SEMESTER</strong><br />
SOC <strong>–</strong> 301: Classical Sociological Tradition - I<br />
Unit I: Origins of sociological theory<br />
Historical, socio-economical and intellectual forces.<br />
a) Historical and socio-economic forces<br />
French revolution. Industrial Revolution and Emergence of capitalism and<br />
their impact on economy and society.<br />
d) The Enlightenment and its impact<br />
Unit II: Karl Marx (1818 - 1883 A.D.)<br />
a) Karl Marx: Intellectual Background and historical context.<br />
b) Marxian Dialectical materialism as a perspective of change: its principal<br />
and laws.<br />
c) Historical materialism: Material conditions of life as the primary and<br />
objective reality - Basic structure and superstructure -economic determinism -<br />
Transformation of human society through different stages from primitive to<br />
socialism.<br />
d) Marx's analysis of Capitalism: Emergence and development of industrial<br />
capitalism - Surplus Value - Alienation<br />
e) Classes and Class struggle: Notion of Class: Emergence of Classes - Class<br />
consciousness - Class conflict - Proletariat Revolution - Classless Society.<br />
f) Karl Marx’s views on the state: the state in relation to classes -future of the state<br />
after proletariat revolution.<br />
g) Theory of Ideology: Ideology as a part of Superstructure and its role.<br />
Unit III: Emile Durkheim<br />
a) Emile Durkheim: Intellectual Background and major works<br />
b) Contribution to the Methodology of Sociology, Sociology as a science -<br />
Concept of Social Fact - Methodological Rules.<br />
c) Division of Labour: Mechanical and Organic Solidarity -Explanation of<br />
increasing division of labour in terms of its causes and function - Pathological<br />
forms of division of labour.<br />
d) Theory of Suicide: - Types of suicide and its distinctive sociological<br />
interpretation of Suicide.<br />
e) Theory of Religion:- Durkheim's definition of 'Religion' -Analysis of<br />
Totemism as the most elementary religion and its sociological interpretation.<br />
Religious Rituals, their types and social functions.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Aron. Raymond: Main Currents in Sociological Thought, Vol. I and II, 1965-67<br />
Coser, Lewis, A.: Masters of Sociological Thought Harrcourt Base, New York, 1977.<br />
Dahrendort, Ralp: Class and class conflict in an Industrial Society -Standard University<br />
Press, 1959.<br />
Durkheim: Simmel Memorial Issue - American Journal of Sociology, May, 1958.
Fletcher, Ronald: The Making of Sociology, Vol. 1 and II, Michael Joseph Ltd., London,<br />
1971.<br />
Giddens, Anthony: Capitalism and Modern Social Theory - An analysis of the writings of<br />
Marx, Durkheim and Weber, Cambridge University Press, 1971.<br />
Hughes, John A., Martin, Peter J. and Sharrock, W.W.: Understanding Classical<br />
Sociology: Marx, Durkheim and Webber, Sage, London, 1995.<br />
Lefebre Henri: The Sociology of Marx<br />
Morrison, Ken: Marx, Durkheim and Weber - Formations of Modem Sociology Thought,<br />
Sage, New Delhi, 1995.<br />
Nisbet: The Sociological Tradition, Heinemann Educational Books Ltd., London, 1966.<br />
Parsons, Talcott: The Structure of Social Action, Vol. I and II, McGraw Hill, New York,<br />
1937-1949.<br />
Popper Karl: Open Society and its Enemies Routledge, London, 1945.<br />
Rex John: Key problems in Sociological theory.<br />
Tom Bottommore: Marxist Sociology.<br />
Yakhot, O. Spirin, A.: The Basic Principles of Dialetical and Historical Materialism,<br />
Progress Publishers, Moscow, 1971.<br />
Zeithin, Irving M.: Ideology and the Development of Sociological Theory, Prentice -<br />
Hall, New Delhi, 1969.<br />
SOC - 302: Sociology of change and Development - I<br />
Unit I: Meaning and Forms of Social Change<br />
A) Evolution, progress, transformation<br />
B) Theories: Linear and Cyclical<br />
C) Factors: Demographic, Economic, Religious, Bio-Tech, Info-tech and Media.<br />
Unit II: Concept of Development, Theories of Development and Under-Development<br />
A) Concepts: Economic Growth, Social Development, Sustainable Development,<br />
Human Development, Alternate Development<br />
B) Centre-Periphery Theory<br />
C) World-Systems Theory<br />
Unit III: Paths of Development<br />
A) Capitalist Path of Development,<br />
B) Socialist Path of Development,<br />
C) Mixed Economy as a Path of Development<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Abraham, M.F. Modern Sociological Theory: An Introduction, New Delhi, OUP, 1990.<br />
Amin, Samir, Unequal Development, New Delhi, OUP, 1979.<br />
Appadurai, Arjun, Modernity at large: Cultural Dimensions of Globalization, New Delhi,<br />
OUP, 1997.<br />
Dereze, Jean and Amartya Sen, India : Economic Development and Social Opportunity,<br />
New Delhi, OUP, 1996.<br />
Desai, A.R. 1985. India's Path of Development: A Marxist Approach, Bombay: Popular<br />
Prakashan (Chapter 2).<br />
Desai, A.R. State and Society, Popular Prakashan, Mumbai, 1975.
Giddens Anthony, Global Problems and Ecological Crisis in introduction to sociology<br />
Ilnd Edi. New York: W.W. Norton & Co., 1996.<br />
Giddens, Anthony, The consequences of Modernity, Cambridge: Polity press, 1990.<br />
Haq, Mahbub Ul, Reflections on Human Development, New Delhi, OUP, 1991.<br />
Harrison, D. The Sociology of Modernization and Development, New Delhi, Sage, 1989.<br />
Moore, Wilbert and Robert Cook, Social Change, New Delhi: Printice Hall (India), 1967.<br />
Sharma, S.L. "Criteria of Social Development", Journal of Social Action, Jan-Mar, 1980.<br />
Sharma, S.L. "Salience of Ethnicity in Modernization : Evidence from India",<br />
Sociological Bulletin, Vol. 39, Nos. 1 & 2, pp. 33-51, 1994.<br />
Sharma, S.L. Development: Socio-cultural Dimension, Jaipur, Rawat (Chapter 1), 1986.<br />
Sharma, S.L. perspectives on sustainable development in South Asia, The case of India in<br />
Samad (Ed. ) Perspectives on sustainable Development in Asia. Kuala Lumpur,<br />
ADIPA, 1994.<br />
Sharma, S.L. Social Action Groups as Harbingers of silent Revolution, Economic and<br />
Political Weekly, Vol. 27, No. 47,1992.<br />
Shrma, S.L. Empowerment without Antagonism: A case for Reformulation of Women's<br />
Empowerment Approach. Sociological Bulletin, Vol. 49, No. 1,2000.<br />
Srinivas, M.N. Social Change in Modern India, Berkley : University of Berkley, 1966.<br />
Symposium on Implications of Globalization, Sociological Bulletin, Vol. 44 (Articles by<br />
Mathew, Panmi & Pathy), 1995.<br />
Wallersteir, Imnanual, The Modern World System, New York : OUP, 1974.<br />
Waters, Malcoln, Globalization, New York : Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1995.<br />
World Commission on Environment and Development, Our Common Future (Brundland<br />
Report), New Delhi, OUP, 1987.<br />
SOE - 303: SOCIAL DEMOGRAPHY - I<br />
Unit I: Introduction to social demography: definition, scope and<br />
significance of social demography.<br />
Unit II: Sources and nature of demographic data: Population censuses, Vital<br />
Registration system, Population Registers, Sample Surveys, Administrative<br />
Records, Parish Registers and Archival Records<br />
Unit III: Theories of population:<br />
a) Malthus theory of population.<br />
b) Natural law theory of population, 1) Double day 2) Herbert Spencer.<br />
c) Social theory of population: 1) Karl Marx 2) Arson Dumont<br />
d) Theory of demographic transition, theory of Optimum population<br />
Unit IV: Demographic variables of population change:<br />
a) Fertility: Concepts, basic measures of fertility, factors affecting fertility, cause<br />
for higher fertility, fertility trends in India since 1901.<br />
b) Mortality: Concepts, broad measures of mortality, expectation of life at birth,<br />
infant mortality, cause of infant mortality, maternal mortality, cause of maternal<br />
mortality, levels and trends in mortality in India<br />
c) Migration: Concepts, types of migration, causes of migration, legal restrictions<br />
on international migration, future of international migration.
Suggested Readings:<br />
Abuzzar M.<strong>–</strong> Socio-economic Aspects of population structures, Rawat Publication, Jaipur, 1988.<br />
Agarwal, S.N.<strong>–</strong> India’s population problem, IInd Ed., Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi, 1977.<br />
Appleman, P. An Essay on the piinciple of population, W.W. Norton, and Company,<br />
N.Y. 1976.<br />
Barclay, G.W. - Techniques of population Analysis, John Wiley and Sons, New York,<br />
1958.<br />
Bhattacharjee, P.T. and Shastri, G.N, - Population in India : A study of Inter-state<br />
variations, New Delhi, 1976.<br />
Bhende, A.A. and Tara Kanitkar - Principles of population studies, Himalaya Publishing<br />
House, Bombay, 1992.<br />
Bogue Donald, J. - Principles of Demography, John Wiley and Sons, New fork, 1969.<br />
Brown, L.R. - World Population Trends : Sign of Hope, Sign of stress, population Report<br />
series, Woild Watch paper No. 16., 1977.<br />
Carr Saunders, A.M. - World population : past Growth and preseni Trends, Clarendon,<br />
Oxford, 1936.<br />
Census of India- 1951, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991,2001.<br />
Chandrashekhar, S. 1) Asia's population problem, 2) India's population. Allied publishers,<br />
Bombay, 1967.<br />
Coontz, S.E. - Population Theories and their Economic Interpretation. McMillian,<br />
London, 1957.<br />
Dandekar Kumudini - ^Demographic survey of six Rural Communities, Asia Publishing<br />
House, Bombay, 1959.<br />
Davis Kingsley - Population of India and Pakistan, Princeton, 1961.<br />
Doubleday, T. - The True Law of Population, George Pierce, London., 1847.<br />
Govt, of India, Demographic year Book, Ministry; of Health and Family Welfare, New<br />
Delhi.<br />
Gyan Chand - Population in perspective, Orient Longman, New Delhi, 1972<br />
Hauser, P.M. and Duncan, D. - The study of Population, University of Chicago Press,<br />
Chicago, 1959,<br />
Joshi, B.H. - Changing Demographic structure of India, Raj Publishing House, Jaipur,<br />
2000.<br />
Mamoria, C.B. - India's population problem, Chat P. House, Allahabad 1981.<br />
Mitra Ashok - India's Population: Aspect on Quality and Control, Vol 1 and II, Abhinav<br />
Prakashan, New Delhi, 1978.<br />
Pande, G.C. Principles of Demography, Anmol publication, New Delhi, 1990.<br />
Pathak, L.P. - Population studies, Rawat Publication, Jaipur, 1998.<br />
Peterson William - Population, MacmilHan, New York, 1969.<br />
Raj, Hans. 1981. ‘Fundamentals of Demography’, Surjeet Publications, Delhi.<br />
Ranade, P.S. - Population Dynamics in India, Ashish Publishing House, New Delhi, 1990.<br />
Satish Tiwari - Indian Population : Today and Tomorrow, Rajat Publication, Delhi,<br />
1999.<br />
Saxena, G.B. Indian Population, Govt, of India, 1989.<br />
Sharma, R.K. Demography and Population problems, Atlantic publishers and<br />
Dif.lributors, Darya Ganj, Delhi, 1997.
Shrylock, Henry S., Jacob, S. Siegal and Associates. 1980. ‘The Methods and Materials<br />
of Demography’, Vol. I & II, US Bureau of the Census, Washington D.C.<br />
Sinha, V.C. and Zachariah, E. 1984. ‘Elements of Demography’, Allied publishers Pvt.<br />
Ltd. New Delhi.<br />
Srivastava, S.C. - Studies in demography, Jai Prakash Nath And Comp. Meenit. 1989.<br />
Thomlinson Ralph - Population Dynamics, Random House. New York, 1965.<br />
Thompson, W.S. - Population Problem, Tata McGraw Hills, New Delhi, 1972.<br />
United Nations - 1) Demographic year Book, 2) Population charts, 3)<br />
Population Bulletions, New York.<br />
SOE - 305: Social Movements in India - I<br />
Unit I. Definition and features of social movements.<br />
Unit II. Theories of social movements:<br />
a) Structural <strong>–</strong> functional;<br />
b) Marxist;<br />
c) Resource Mobilization Theory;<br />
d) Interactionist;<br />
e) New Social Movements;<br />
f) Sociology of Action.<br />
Unit III. Social Movements and social change:<br />
a) Reform, Rebellion, Revival;<br />
b) Millerian;<br />
c) Revolution, Insurrection;<br />
d) Schisms and splits;<br />
e) Counter Movements.<br />
Unit IV. The social basis of Social Movements:<br />
a) Class, caste, gender and ethnicity;<br />
b) Role of leadership;<br />
c) Mode of institutions;<br />
d) Role of ideology;<br />
e) Role of Mass Media.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Baoks.1972. The sociology of social movements. London. Macmillan.<br />
Das, Veena. (ed). 2003. Oxford India companion to Sociology and Social Anthropology.<br />
New Delhi: Oxford University Press.<br />
Gouldner, A.W. (ed.), 1950. Studies in Leadership. New York.Harper and Brothers.<br />
Oomen T. K. 1972. Charism, Stability and change: A Analysis of Bhoodan Gramdan<br />
Movement. New Delhi: Thomas press,<br />
Oomen T. K. 1990. Protest and Change: Studies in social movements. New Delhi: Sage<br />
Publications,<br />
Rao, M.S. A. 1979. Social Movements and social Transformation Delhi: Macmillan.<br />
Sage Publications,<br />
Shah, Nandita. 1992. The issues at stake. Theory and Practice in the contemporary<br />
movements in India, Kali for Women, New Delhi.
Shiva, Vandana. 1991; Ecology and Politics of survival New Delhi: Sage publications.<br />
Singh, Rajendra. 2000. Social Movements, Old and new— A post modernist critique<br />
New Delhi:<br />
SOE <strong>–</strong> 307: Sociology of Information Society - I<br />
I. Conceptual understanding:<br />
Historical change, Industrial Informationalism, Technology Society and<br />
Capitalisation.<br />
II. IT revolution Enterprise:<br />
Culture, Institutions and organizations of the information economy, Transition from<br />
Industrialism to Informationalism.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Ambekar J.B. Communication andd Rural Development, Mittal, New Delhi, 1992.<br />
Arvind Singhal and Rogers Everett: India's Communication Revolution from Bullock<br />
Carts to Cyber Mart, Sage Publications, New Delhi.<br />
Barrie Axford and Richard Huggin (ed) New Media and Politics, Sage, New Delhi,<br />
2001.<br />
Beyer, Peter, Religion and Globalisation Sage, London, 1994.<br />
Bhatnagar, Subhash, Information and Communication: Technology in Development, Sage<br />
Publications, New Delhi, 2000.<br />
Common Steven, Post Modernist Culture, Blackwell, New York, 1989.<br />
December and Randall, The World Wide Web, Unleashed, MacmiUan Computer<br />
Publishing, 1994.<br />
Goel S.K., Communication Media and Informational Technology, Commonwealth<br />
Publishers, New Delhi, 1999.<br />
Jacobs, Ronald N., Race, Media and the Crisis of Civil Society (From Wattsto Rodney<br />
King), Cambridge University Press.<br />
Joann Yates and John Van, Mannen, Information Technology and Organizational<br />
Transformation, Sage New Delhi, 2001.<br />
Lee Chin - Chuan, Media Imperialism, Sage, California, 1979.<br />
Manuel, Castells, The Rise of Network Society, Blakwell, Publishers, 1996.<br />
Mark Taylor and Esa Saariner, Imagologies, Routledge, London, 1994.<br />
Melkote Shrinivas, The Information Society, Sage London, 2001.<br />
Michael H, The Metaphysies of Virtual Society, OUP, London, 1993.<br />
Mosco, Vincent, The Political Economy of Communication, Sage, London, (Ruthenkjal<br />
Renewal), 1996.<br />
Preston, P. Reshaping Communications - Technology Information and Social Change,<br />
Sage, New Delhi, 2001.<br />
Shrivastava, K.M., Media Towards the 21 st Century Sterling Publishers, New Delhi, 1009.<br />
Zachariah Aruna: Communication Media and Electronic Revolution, Kanishka<br />
Publiclation, New Delhi, 1996.<br />
Zrkocrzy, P. and N. Heap Information Technology, Pitman, New York, 1995.
SOE - 308: Urban Society in India - I<br />
Unit I. Basic concepts: Urban, urbanism, sub-urbanization, Ecology,<br />
urban culture, urbanization, factors responsible for rapid urbanization.<br />
Unit II. Classical Sociological Traditions:<br />
a) Emile Durkheim- Division of labour, the moral basis of the community.<br />
b) Marx and Engels- The town, the country and the capitalist mode of production.<br />
c) Max Weber- The city and the growth of rationality.<br />
d) Tonnies- The dichotomy model.<br />
Unit III. The Urban as an ecological community:<br />
a) The traditional ecological approach of Park, Burgess and McKenzie.<br />
b) Spatial models inspired by this school-Concentric Zone model, Sector model,<br />
multi-nuclear model.<br />
c) Critiques of this apporach- Nihan, Walter Firey.<br />
d) Neo-ecological school and its critique.<br />
Unit IV. The Urban as a cultural form:<br />
a) Simmel-the metropolis and mental life<br />
b) Wirth- urbanism as a way of life<br />
c) Redfield- the rural- urban continuum<br />
d) Abu-Lughod Janet- ruralisation of the city<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Abrahmson, Mare. 1976. Urban Sociology. Englewood Cliff, Prentice Hall.<br />
Anderson, Nels. 1968. Urban Sociology. New Delhi: Asia Publishing House.<br />
Bergel, EX. 1955.Urban Sociology, New York: Mc-Graw Hill Book Company.<br />
Bhattacharya, B. 1979. Urban Development in India, Shree Publishing House, Delhi.<br />
Colling workth, J. A. 1972. Problems of and Urban Society Vol-II, George Allen & Unwin<br />
Ltd.<br />
D’souza, Alfred. (Ed). 1983. Urban growth & Urban Planning. New Delhi: Indian Social<br />
Institute.<br />
Elsentadt, S. N. and Shachar. 1987. Society, Culture and Urbanization. New Delhi: Sage<br />
Publications.<br />
Gore, M. S. 1968.Urbanization and family change. Bombay: Popular Prakashan.<br />
Kopardekar, H. O. 1986. Social Aspects of Urban Development. Mumbai: Popular<br />
Prakashan.<br />
Pickvance, C. G., (ed), 1976. Urban Sociology: Critical Essays. Methuen, London.<br />
Prasad, D. Ravindra. 1989. Urban renewal: The Indian experience. New Delhi: Sterling<br />
Publishers PVT Ltd.<br />
Quinn, J. A. Urban Sociology. New Delhi: S. Chand & Co.<br />
Rao, M. S.A., Bhat and Kadekar, L. N. (Ed) 1991. A reader in Urban Sociology. Orient<br />
Longman.<br />
Rarachandran, R. 1990. Urbanization and urban system in India. Delhi: Oxford.<br />
Ronnan, Paddison. 2001. Handbook of Urban studies. New Delhi: Sage.<br />
Saberwal, Satish. (ed). 1978. Process and Institution in Urban India. New Delhi: Vikas<br />
Publishing House.<br />
Sandor, Halebsky. 1973. The sociology of city. New York: Charles Scribner’s sons.
Sarrienn, Eliel. 1943. The city it's growth. Calcutta: Scientific Book Agencies.<br />
Saunder, Peter. 1981. Social theory and urban question. Hutchionson. London.<br />
Sujata, Patel and Kushal, Deb (ed) 2006.Urban Studies. Oxford.<br />
Wilson, R. A. and Scbulza, D. A. 1978. Urban Sociology. Prentice Hail, Englewood.<br />
SOE-309: Sociology of Disaster Management - I<br />
Unit I: Disaster and Development: Content and Definition; Disaster and level of<br />
development; Vulnerability and disaster preparedness, education and awareness.<br />
Unit II: Classification/Types of Disaster: Disaster, risk, hazard; Natural-famine, drought,<br />
floods/Storms, cyclones, and earthquakes. Manmade -Riots, biological warfare.<br />
Industrial, militancy insurgency, eviction.<br />
Unit III: Issues Involved: Policy Issues, Politics of Aid, Gender.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Birnabaum, F., Coplon, J., “Crisis Intervention after a Natural Disaster”, Social Case<br />
Work, Vol. 54, No.9, 545-551.<br />
Blaufard, H. and Levine, J. 1972. “Crisis Intervention in an Earthquake”. Social Work,<br />
Vol. 17, No. 4, 16-19.<br />
Chen, L. 1973, “Disaster in Bangladesh: Health Crisis in a Developing nation, New<br />
York: Oxford University Press.<br />
Fritz, C.E. 1968. “Disaster”, Sills, D. (ed.) International Encyclopedia of Social Science.<br />
Vol. 4. U.S.A., The Macmillan Company and the Free Press. 202-208.<br />
Hoff, A. 1978. “People in Crisis”, Understanding and Helping, California: Addison<br />
Wesley Publishing Company.<br />
SOE - 304: Criminology - I<br />
1. Criminology: Concept of crime, criminal criminality, deviance, delinquency,<br />
jurisprudence, evidence, relationship of sociology with criminology, Victimology,<br />
penology and social work. Conceptual approaches to crime: legal, behavioural<br />
and sociological.<br />
2. Perspectives on crime causation: Different theories of crime - classical, positivist,<br />
psychological, Marxian, geographical theories, sociological theories.<br />
3. Types of crime: Economic, crime against property, professional crime, crime<br />
against moral turpitude, white-collar crime. Changing profile of crime and<br />
criminals. Organized crimes, crime against women, Domestic violence and<br />
children, sexual harassment, cyber crimes.<br />
4. Juvenile delinquency: Concept extent in India, causes and consequences of<br />
juvenile delinquency, measures to solve the problem of juvenile delinquency,<br />
correctional institutions for Juvenile Delinquents, The Juvenile Justice (Care and<br />
Protection of Children) Act, 2000.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Bedi Kiran, 1998, It is Always Possible, New Delhi, Sterling Publications, Pvt Ltd..<br />
Bequai, August 1978. Computer Crime, Toronty: Lesington Books,
Buckland, John, 1992. Combating Computer Crime: Prevention, Detection and<br />
Investigation, New Delhi: McGraw Hill.<br />
Contemporary Issues, London : Sage Publications.<br />
Control and Prevention, Bombay: Sysman Computers Pvt. Ltd.<br />
Criminology, Jalandhar : ABC Publications.<br />
Drapkin Ismail and Viano, Emilio, 1975. Victimology: A New Focus, London, Lesington<br />
Press.<br />
Gill, S.S. 1998. The Pathology of Corruption. New Delhi Harper Collin's Publishers<br />
(India.)<br />
Goel, Rakesh M. and Manohar S. Powar, 1994, Computer Crime : Concept.<br />
Gote-Gavhane Shubhangi, 1997. Female Criminality and Sociological Theories,<br />
Aurangabad (Maharashtra) India, South Asian Social Research Publication.<br />
Haiiman, Taryl, A. 1950. The Economics of crime New York: St. Martins's Press.<br />
Inciarti James, A. and Pottieger Anne E. 1978; Violent Crime: Historical and<br />
Kaldate, Sudha, 1982. Society, Delinquent and Juvenile Court, New Delhi, Ajanta<br />
Publications.<br />
Lilly, J. Robert Francis T. Wallen and Richard Ball A., 1955. Criminological Theory,<br />
Context and Consequences, New Delhi: Sage Publications.<br />
Makkar, S.P. Singh and Paul C. Friday, 1993. Global Perspectives in<br />
Ministry of Home Affairs, 1998. Crime In India Report, New Delhi, Government<br />
of India.<br />
Ministry of Home Affairs, Report of the All India Committee on Jail Reforms, 1980-<br />
83, New Delhi: Government of India.<br />
Pace, Denay, F. 1991. Concept of Vice, Narcotics and Organized Crime, London Prentice<br />
<strong>–</strong> Hall.<br />
Rayan, Patrick J. and George Rush, 1997. Understanding Organized Crime in global<br />
Perspective, London: Sage Publications.<br />
Reid, Suetitus, 1976. Crime and Criminology, Illnayse: Deydan Press,<br />
Revid, Jorathan, 1995. Economic Crime, London, Kejan Paul.<br />
Shankardas, Rani Dhavan, 2000. Punishment and the Prison: Indian and International<br />
Perspective, New Delhi: Sage Publications.<br />
Sutherland, Edwin H. and Donald R. Cressey, 1968. Principles of Criminology Bombay :<br />
The Times of India Press.<br />
Walklete Sandra, 1998. Understanding Criminology Philadelphia, Open<br />
University Press.<br />
Weinberg, Dand and Kip Schlegal, 1990. White Collar Crime Reconsidered, Boston :<br />
Northeastern University Press.<br />
Williams, Frank P. and Marilyn D. Meshare, 1998. Criminological Theory, New Jersey:<br />
Prentice Hall.<br />
Williamsen, Herald, E. 1990. The Correction Profession, New Delhi, Sage Publication.<br />
SOE <strong>–</strong> 306: Environment and Society - I<br />
1) Sociology and Environment:<br />
a) Emergence of Environmental Sociology:<br />
i) Early interest in Ecological issues<br />
ii) Environmental Sociology: Meaning, Nature and Scope
) Contributions of Selected Social Scientists:<br />
i) Radhakarnal Mukherjee<br />
ii) Ramchandra Guha<br />
iii)Dunlap and Carton.<br />
2) Environment and Society: A brief Introduction to Theoretical Approaches:<br />
a) Deep ecology<br />
b) Social constructionism<br />
c) Realism<br />
d) Eco-feminism<br />
e) Gandhian approach<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Agarwal S. K.: Environmental Issues and Themes APH Publishing Corporation, New<br />
Delhi, 1997.<br />
Calvert, Peter and Susan Calvert, The South, The North and the Environment, Pinter,<br />
London and New York, 1999.<br />
Carton Williams, Jr. and Dunlap Riley (Ed.) American Sociologist, 13, pp. 41-49; (1980):<br />
American Behavioural Scientist, 24(1) pp.15-47; (1979) : 1980 Annual Review of<br />
Sociology, (5) pp. 243-273-(1994): American Sociologist, 25(i) pp. 5-30.<br />
Centre for Science and Environment: The State of India's Environment. A Citizen's<br />
Report. 1982.<br />
Gadgil, Madhav and Ramachandra Guha: Ecology and Equity: The Use and Abuse of<br />
Nature in Contemporary India, New Delhi, OUR, 1996.<br />
Giddens, Anthony, The Consequences of Modernity, Cambridge, Polity Press. 1990.<br />
Giddens, Anthony: Introduction to Sociology, (4th Ed.), New York: W.W. Norton and<br />
Co., 1996.<br />
Limmermom M. E. and other (Ed.): Environmental Phi losophy from Animal Rights to<br />
Radical Ecology, Prentice Hall, Englewood Clifts, New Jersey 1993.<br />
Mattel Luke: Ecology and Society: An Introduction, Polity Press, 1994.<br />
Michael Reddift: Development and Environmental Crisis, Meheun Co, Ltd., New York,<br />
1984.<br />
Munshi, Indra: "Environment in Sociological Theory", in Sociological Bulletin, Vol. 49,<br />
No. 2<br />
Pravin Sheth: Environmentalism, Politics, Ecology and Development, Rawat New Delhi<br />
1997.<br />
Riley E. Dunlap: "The Evolution of Environmental Sociologv 7 " in The International<br />
Handbook of Environmental Sociology, Michael Reddift and Graham Woodgate<br />
(Eds.) Edward Elgar, Cheltanham, V. K. 1997.<br />
Wallerstein, Immanuel: The Modern World System, New York. OUP, 1974.<br />
World Bank : World Development Reuort. 1995.<br />
World Commission on Environment and Development Our Common Future, 1987.
SOE - 310: Health and Society - I<br />
Unit I: Basic Concepts<br />
i) Its Aim and Scope of Sociology of Health<br />
ii) Health and its relation to social institutions<br />
iii) Concept of Health: Illness, Sickness, diseases, death<br />
Unit II: Family and its relation with health care<br />
i) Approaches to health care in nuclear and extended family<br />
ii) Pattern of child rearing<br />
iii) Significance of family in context of illness<br />
iv) Family relationship <strong>–</strong> emotion and anxiety<br />
v) The sick role and patients role<br />
Unit III: Measurement of health and illness<br />
i) Sources of data on illness and measurements of health and illness<br />
ii) Diet and nutrition<br />
iii) Causes of death<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Cockerham-Williamc. 1997. ‘Reading in Medical Sociology’, New Jersey, Printice-Hall.<br />
D. Banerjee. 1985. ‘Health and Family Planning Services in India: An epidemiological,<br />
socio-cultural and political analysis and a perspective, New Delhi: Lok Paksha.<br />
Dasgupta, R. 1993. ‘Nutritional Planning in India’, Hyderabad: NIN.<br />
Elman, C. 1984. ‘Culture, health, illness, wright’, Bristol.<br />
Guilmoto C. and I. Rajan (ed). 2005. ‘Fertility Transition in south India, sage<br />
Publications, New Delhi.<br />
Gwatkin, D.L. and M. Gulliot. 2000. ‘The burden of disease among the global poor:<br />
Current situation, future trends and implications for strategy, Human development<br />
network, health, nutrition and Population’, The IBRD, World Bank, Washington<br />
D.C.<br />
Hyder, A.A.; Rotllant, G. and Morrow R.H. 1998. ‘Measuring the burden of disease:<br />
Healthy life years, American Journal of Public Health, Vol. 88 (2), pp. 196-202.<br />
Imrana, Quadeer. 2000. ‘Health care system in transition III, Journal of Public Health<br />
Medicine, Vol. 22, No. 1, pp. 25-32.<br />
Jejeebhoy, Shirin. 2003. ‘Action that protect: Promoting sexual and reproductive health<br />
and choice among young people in India’, Population Council, New Delhi.<br />
Ministry of Health and family Welafre. 1997. ‘Reproductive and Child Health<br />
Programme’, Mannual for India and Karnataka, Government of India.<br />
Murray, C.J. 1994. ‘Quantifying the burden of disease: The technical basis for Disability<br />
Adjusted Life Years’, Bulletin of the WHO, Vol. 72 (3), pp. 429-445.<br />
Murray, C.J. and A.D. Lopez. 1994. ‘Quantifying disabilities: Data, Methods and results’,<br />
Bulletin of the WHO, Vol. 72 (3), pp. 481-494.<br />
Nayar, K.R. 1998. ‘Ecology and Health System approach, New Delhi: APH Publishing<br />
Corporation.<br />
Park, J.E. and Park, K. 1989. ‘Text Book of Preventive and Social Medicine (12 th<br />
Edition), M/s Banarasidas Bhanot Publisher, Jabalpur.<br />
World Bank. 1993. ‘World Development Report 1993: Investigating in Health’, Oxford<br />
University Press, New York.
World Health Organization. 1999. ‘The world Health report 1999: making a difference,<br />
WHO, Geneva, Switzerland, WHO.<br />
SOE - 311: Tribal Sociology - I<br />
Unit I: Tribal Society: Definition, Nature, approaches and classifications<br />
a) Definition and Characteristics of Tribes<br />
b) Approaches to the study of Tribes: Sociological and Anthropological<br />
c) Racial and Linguistic classification<br />
Unit II: Problems of Tribes<br />
a) Land alienation, poverty and indebtedness<br />
b) Health and nutrition<br />
c) Displacement and rehabilitation<br />
Unit III: Tribes in Transition<br />
a) The concept of Tribanization<br />
b) Impact of industrialization and urbanization<br />
c) Media and Tribal Society<br />
d) Issues of Tribal identity and Tribal movements<br />
Unit IV: Tribal policy in India, forest <strong>–</strong> Tribe interaction deforestation and its impact on<br />
tribal population, Role of state and NGOs to protect and promote the tribals<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Bailey, F.G.1960.Caste and Nation, OUP, Bombay,<br />
Behera D.K. and Georg Pfeffer Contemporary Society: Tribal studies, Vol-I to VIII New<br />
Delhi: concept Publishing company.<br />
Bose, A.; Nangbri, T & Kumar, N. (eds) 1990. Tribal demography and development in<br />
North-East India, Delhi: B.R.<br />
Furer-Hymendrof, C.V., 1982.Tribes of India: The struggle for survival, Delhi oxford<br />
university press.<br />
Hutton J.H. Caste in India: its nature functions and origin. Cambridge: University press.<br />
Keesing R.M., Cultural Anthropology: A contemporary perspective, New York: Holt,<br />
Rinehard and Winston.<br />
Mehta, P.L. Constitutional protection to scheduled tribes in India in retrospect and<br />
prospect, Delhi: H.K.<br />
Raha, Manish Kumar1997. Tribal India: Problem of Development. New Delhi,<br />
Salunke S.B.‘Gond’: Savandan Prakashan, Aurangabad.<br />
Sharma K.L., Caste, Class and Social Movements<br />
Singh, K.S. 1982. Tribal movements in India Vol. I & II, New Delhi: Manohar<br />
Prakashan,
SOE - 312: Social Psychology - I<br />
Unit I: Introduction to social psychology<br />
a) Definition<br />
b) Nature and scope of social psychology<br />
c) Relationship with other Social sciences<br />
Unit II: Behaviour and Attitude<br />
a) Interrelation between behaviour and attitude<br />
b) Formation of attitude<br />
c) Theories of attitude change<br />
Unit III: Growth and Development<br />
a) Role of heredity and environment<br />
b) Culture and personality<br />
c) Theories of personality<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Baron, Robert. A. and Byrne, Donn Social Psychology, 7th edition, Prentice Hall of India<br />
Pvt. Ltd.<br />
Harari, Herbert and McDavid Jhon, W, 1986, Social Psychology, CBS Publisers &<br />
Distributors, Delhi.<br />
Kimball Young: Handbook of social psychology<br />
Krutch and Crutchfield: Social Psychology<br />
Myers, David G.(1988) Social Psychology, 2nd Edition, McGraw Hill Book Company.
M.A. IV <strong>SEMESTER</strong><br />
SOC <strong>–</strong> 401: CLASSICAL SOCIOLOGICAL TRADITION - II<br />
Unit I: Max Weber<br />
a) Max Weber: Intellectual background and his major works<br />
b) Contribution to the Methodology of Social Sciences Distinctive nature of<br />
Social Realities - Sociology as an interpretative science - concepts of ‘Verstehen’<br />
and ‘Ideal Types’<br />
c) Theory of Social Action: Concept of Social Action - Types of Social<br />
Action - Interpretive understanding of Social Action.<br />
d) Views on capitalism: Analysis of Modern Capitalism Protestant Ethic and<br />
Emergence of Capitalism Role of ideas and values in Social Change.<br />
e) Theory of Authority; Power and Authority - Types of Authority: base of<br />
their legitimacy, their distinctive features. Method of administration and modes of<br />
inheritance.<br />
f) Concept of Bureaucracy: Capitalism, growing rationalism and emergence<br />
of modern bureaucracy- Weberian Model of Bureaucracy - Relationship between<br />
political leaders and bureaucracy.<br />
Unit II: Vilfredo Pareto<br />
a) Vilfredo Pareto ; Intellectual Background<br />
b) Contribution to Methodology: Logico-experimental Method.<br />
c) Logical and non-logical action; classification - explanation of non-logical<br />
action in terms of his theory of Residues and Derivations Classification of<br />
Residues and Derivations.<br />
d) Theory of Elites: Elites and Masses - Types of Elites -Circulation of elites.<br />
Role of Elites.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Aron. Raymond; Main Currents in Sociological Thought, Vol. I and II, 1965-67<br />
Bendix, Richard: Max Weber, An Intellectual Potrait (for Weber double days), 1960.<br />
Coser, Lewis, A.: Masters of Sociological Thought Harrcourt Base, New York, 1977.<br />
Fletcher, Ronald: The Making of Sociology, Vol. 1 and II, Michael Joseph Ltd., London,<br />
1971.<br />
Gerth, M. and Millis, C.W. from Max Weber and Essays in Sociology.<br />
Giddens, Anthony: Capitalism and Modern Social Theory - An analysis of the writings of<br />
Marx, Durkheim and Weber, Cambridge University Press, 1971.<br />
Hughes, John A., Martin, Peter J. and Sharrock, W.W.: Understanding Classical<br />
Sociology: Marx, Durkheim and Webber, Sage, London, 1995.<br />
Morrison, Ken: Marx, Durkheim and Weber - Formations of Modem Sociology Thought,<br />
Sage, New Delhi, 1995.<br />
Nisbet: The Sociological Tradition, Heinemann Educational Books Ltd., London, 1966.<br />
Parsons, Talcott: The Structure of Social Action, Vol. I and II, McGraw Hill, New York,<br />
1937-1949.<br />
Popper Karl: Open Society and its Enemies Routledge, London, 1945.<br />
Rex John: Key problems in Sociological theory.
Zeithin, Irving M.: Ideology and the Development of Sociological Theory, Prentice -<br />
Hall, New Delhi, 1969.<br />
SOC - 402: Sociology of change and Development - II<br />
Unit I: Social Change in Contemporary India<br />
A) Processes of Change: Westernization and Modernization<br />
B) Social Processes of Change: Sanskritization and Secularization;<br />
C) Religious conversions<br />
Unit II: Indian Experience of Development:<br />
A) Sociological appraisal of Five Year Plans<br />
B) Social consequences of economic reforms<br />
C) Socio-cultural repercussions of Globalization<br />
D) Social implications of Info-Tech revolution<br />
Unit III: Development of Marathwada region<br />
A) Regional dimension of Development<br />
B) Developmental projects<br />
i) Irrigation projects ii) Industrial Development<br />
C) Impact of Various Movements on Development<br />
i) Hyderabad Mukti Sangram ii) Marathwada Vikas Andolan<br />
iii) Renaming Movement of Marathwada University<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Amin, Samir, Unequal Development, New Delhi, OUP, 1979.<br />
Appadurai, Arjun, Modernity at large: Cultural Dimensions of Globalization, New Delhi,<br />
OUP, 1997.<br />
Dereze, Jean and Amartya Abraham, M.F. Modern Sociological Theory: An<br />
Introduction, New Delhi, OUP, 1990.<br />
Dereze, Jean and Amartya Sen, India: Economic Development and Social Opportunity,<br />
New Delhi, OUP, 1996.<br />
Desai, A.R. 1985. India's Path of Development: A Marxist Approach, Bombay: Popular<br />
Prakashan (Chapter 2).<br />
Desai, A.R. State and Society, Popular Prakashan, Mumbai, 1975.<br />
Giddens Anthony, Global Problems and Ecological Crisis in introduction to sociology<br />
Ilnd Edi. New York: W.W. Norton & Co., 1996.<br />
Giddens, Anthony, The consequences of Modernity, Cambridge: Polity press, 1990.<br />
Haq, Mahbub Ul, Reflections on Human Development, New Delhi, OUP, 1991.<br />
Harrison, D. The Sociology of Modernization and Development, New Delhi, Sage, 1989.<br />
Moore, Wilbert and Robert Cook, Social Change, New Delhi: Pretice Hall (India), 1967.<br />
Sharma, S.L. "Criteria of Social Development", Journal of Social Action, Jan-Mar, 1980.<br />
Sharma, S.L. "Salience of Ethnicity in Modernization : Evidence from India",<br />
Sociological Bulletin, Vol. 39, Nos. 1 & 2, pp. 33-51, 1994.<br />
Sharma, S.L. Development: Socio-cultural Dimension, Jaipur, Rawat (Chapter 1), 1986.
Sharma, S.L. Perspectives on sustainable development in South Asia, The case of India in<br />
Samad (Ed.) Perspectives on sustainable Development in Asia. Kuala Lumpur,<br />
ADIPA, 1994.<br />
Sharma, S.L. Social Action Groups as Harbingers of silent Revolution, Economic and<br />
Political Weekly, Vol. 27, No. 47,1992.<br />
Sharma, S.L. Empowerment without Antagonism: A case for Reformulation of Women's<br />
Empowerment Approach. Sociological Bulletin, Vol. 49, No. 1,2000.<br />
Srinivas, M.N. Social Change in Modern India, Berkley : University of Berkley, 1966.<br />
Symposium on Implications of Globalization, Sociological Bulletin, Vol. 44 (Articles by<br />
Mathew, Panmi & Pathy), 1995.<br />
Wallersteir, Imnanual, The Modern World System, New York: OUP, 1974.<br />
Waters, Malcolm, Globalization, New York: Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1995.<br />
World Commission on Environment and Development, Our Common Future (Brundland<br />
Report), New Delhi, OUP, 1987.<br />
SOE - 403: SOCIAL DEMOGRAPHY - II<br />
Unit I:Social variables of population growth:<br />
a) Marriage patterns and population growth, influence of re-marriage, divorce and widowhood,<br />
new trends in marriage.<br />
b) Family, Family patterns and population growth, their impact on population growth.<br />
c) Education, its role in population growth.<br />
Unit II: Population projection: Meaning, Importance of population Projection, Methods of population<br />
projection.<br />
Unit III: Population, Environment and Economic Development: Population and environmental<br />
pollution, impact of both on each other, Effect of population growth on economic development and<br />
consequences of economic development on population growth.<br />
Unit IV: Population policy: Meaning, need of population policy, population policy of India and China,<br />
population education, Socio-cultural factors affecting population growth, measures taken for<br />
population control.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Abuzzar M.<strong>–</strong> Socio-economic Aspects of population structures, Rawat Publication, Jaipur, 1988.<br />
Adams, E. and Shekhar, P. Projection of Population and Age Sex Structure, Vol. III, W. Demographic<br />
Conf. Belgrade, 1956.<br />
Agarwal, S.N.<strong>–</strong> India’s population problem, IInd Ed., Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi, 1977.<br />
Agarwal, U.D. Population projections and their accuracy, B.R. Publishing Corporation,<br />
Tri nagar, Delhi, 1961.<br />
Appleman, P. An Essay on the Principle of population, W.W. Norton, and Company,<br />
N.Y. 1976.<br />
Arsene Dumount - Depopulation Et Civilization, Paris, 1890.<br />
Barclay, G.W. - Techniques of population Analysis, John Wiley and Sons, New York,<br />
1958.<br />
Bhattacharjee, P.T. and Shastri, G.N, - Population in India: A study of Inter-state<br />
variations, New Delhi, 1976.
Bhende, A.A. and Tara Kanitkar - Principles of population studies, Himalaya Publishing<br />
House, Bombay, 1992.<br />
Bogue Donald, J. - Principles of Demography, John Wiley and Sons, New fork, 1969.<br />
Bose Ashish 1) Studies in Demography, 2) Urbanization in India, Academic Books Ltd.,<br />
New Delhi, 1930.<br />
Brown, L.R. - World Population Trends: Sign of Hope, Sign of stress, population Report<br />
series, Woild Watch paper No. 16., 1977.<br />
Carr Saunders, A.M. - World population: past Growth and preseni Trends, Clarendon,<br />
Oxford, 1936.<br />
Chandrashekhar, S. 1) Asia's population problem, 2) India's population. Allied publishers,<br />
Bombay, 1967.<br />
Govt, of India, Demographic year Book, Ministry; of Health and Family Welfare, New<br />
Delhi.<br />
Hauser, P.M. and Duncan, D. - The study of Population, University of Chicago Press,<br />
Chicago, 1959,<br />
Kohli, S. - Family Planning in India, Tata McGraw, New Delhi, 1977.<br />
Mamoria, C.B. - India's population problem, Chat P. House, Allahabad 1981.<br />
Mitra Ashok - India's Population: Aspect on Quality and Control, Vol 1 and II, Abhinav<br />
Prakashan, New Delhi, 1978.<br />
Nitti, F.S. - Population and Social System, London, 1984.<br />
Raj, Hans. 1981. ‘Fundamentals of Demography’, Surjeet Publications, Delhi.<br />
Ranade, P.S. - Population Dynamics in India, Ashish Publishing House, New Delhi, 1990.<br />
Sharma, R.K. - Demography and Population problems, Atlantic publishers and<br />
Dif.lributors, Darya Ganj, Delhi, 1997.<br />
Shrylock, Henry S., Jacob, S. Siegal and Associates. 1980. ‘The Methods and Materials<br />
of Demography’, Vol. I & II, US Bureau of the Census, Washington D.C.<br />
Sinha, V.C. and Zachariah, E. 1984. ‘Elements of Demography’, Allied publishers Pvt.<br />
Ltd. New Delhi.<br />
Srivastava, S.C. - Studies in demography, Jai Prakash Nath And Comp. Meenit. 1989.<br />
United Nations - 1) Demographic year Book, 2) Population charts, 3)<br />
Population Bulletions, New York.<br />
Willcox, W.F. - International Migration, Vol. I and II, National Bureau of Economic<br />
Research, New York.<br />
SOE - 405: Social Movements in India<br />
Unit I. Social Movements in India:<br />
a) Peasant movement in Maharashtra;<br />
b) Labour and Trade Union;<br />
c) Tribal movements.<br />
Unit II. New Social Movements:<br />
a) Dalit Movements;<br />
b) Gender and social movements;<br />
c) Ecological Movements;<br />
d) Ethnic Movements.<br />
Unit III. Social Movements in the social setting:
a) Social Movements and the State;<br />
b) Social Movements and the Civil Society.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Ahuja, Ram.1999. Society in India. Jaipur: Rawat Publication.<br />
Colonial India New Delhi.. Sage.<br />
Dasgupta, Biplab. 1974. The Naxalite Movement Bombay. Allied Publishers.<br />
Desai, A. R. 1966. Social Background of Indian Nationalism. Bombay: Popular<br />
Prakashan.<br />
Desai, A. R.. (ed). 1979; Peasant Struggles in India. Delhi: Oxford University Press<br />
Dhanagare, D. N, 1983; Peasant Movements in India-1920-1950. New Delhi: Oxford<br />
University Press<br />
Gore, M. S. 1983. The social context of an ideology: Ambedkar's political and social<br />
thoughts. New Delhi: sage publications<br />
Hardiman, David. 1987. The Coming of the Devi. Bombay: Oxford.<br />
Omvedt, Gail. 1994; Dalits and the Democratic Revolution : Dr. Ambedkar the Dalit<br />
Movement in<br />
Rao M. S. A. (ed.) 1974. Social Movements in India, Vol. 1 and 2; Manohar<br />
Publications, New Delhi.<br />
Selliot Eleanor.1995. From Untouchable to dalit Essays on the Ambedkar Movements.<br />
New Delhi: Monohar.<br />
Shah, Ghanashyam (ed), 2001. Dalit Identity and Politics New Delhi. Sage Publications.<br />
Shah, Ghanshyam. 1990. Social Movements in India. New Delhi: Sage Publications.<br />
Shah, Ghanshyam. 2002. Social Movements and the Indian State. New Delhi: Sage<br />
Publications,<br />
Singh K. S. 1982. Tribal Movements in India; Vol. I and II. Delhi: Manohar.<br />
Singh, K.S. 1982. Tribal Movements in India: New Delhi: Manohar.<br />
SOE <strong>–</strong> 407: Sociology of Information Society - II<br />
I. Transformation of work and employment:<br />
The service economy and the information society, The new occupational structures,<br />
the work process in the informational paradigm.<br />
II. Informational Technology and the Restructuring of capital-labour;<br />
Relationships, social dualism / fragmented societies.<br />
III. Computer mediated communication, institutional control, social networks<br />
and virtual communities.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Ambekar J.B. Communication and Rural Development, Mittal, New Delhi, 1992.<br />
Arvind Singhal and Rogers Everett: India's Communication Revolution from Bullock<br />
Carts to Cyber Mart, Sage Publications, New Delhi.<br />
Barrie Axford and Richard Huggin (ed) New Media and Politics, Sage, New Delhi,<br />
2001.<br />
Beyer, Peter, Religion and Globalisation Sage, London, 1994.<br />
Bhatnagar, Subhash, Information and Communication: Technology in Development, Sage<br />
Publications, New Delhi, 2000.
Common Steven, Post Modernist Culture, Blackwell, New York, 1989.<br />
December and Randall, The World Wide Web, Unleashed, MacmiUan Computer<br />
Publishing, 1994.<br />
Goel S.K., Communication Media and Informational Technology, Commonwealth<br />
Publishers, New Delhi, 1999.<br />
Jacobs, Ronald N., Race, Media and the Crisis of Civil Society (From Wattsto Rodney<br />
King), Cambridge University Press.<br />
Joann Yates and John Van, Mannen, Information Technology and Organizational<br />
Transformation, Sage New Delhi, 2001.<br />
Lee Chin - Chuan, Media Imperialism, Sage, California, 1979.<br />
Manuel, Castells, The Rise of Network Society, Blakwell, Publishers, 1996.<br />
Mark Taylor and Esa Saariner, Imagologies, Routledge, London, 1994.<br />
Melkote Shrinivas, The Information Society, Sage London, 2001.<br />
Michael H, The Metaphysies of Virtual Society, OUP, London, 1993.<br />
Mosco, Vincent, The Political Economy of Communication, Sage, London, (Ruthenkjal<br />
Renewal), 1996.<br />
P. Preston, Reshaping Communications - Technology Information and Social Change,<br />
Sage, New Delhi, 2001.<br />
P. Zrkocrzy, N. Heap Information Technology, Pitman, New York, 1995.<br />
Shrivastava, K.M., Media Towards the 21 st Century Sterling Publishers, New Delhi, 1009.<br />
Zachariah Aruna: Communication Media and Electronic Revolution, Kanishka<br />
Publiclation, New Delhi, 1996.<br />
SOE - 408: Urban Society in India<br />
Unit I. Urbanization in India: Emerging trends in urbanisation, Factors of urbanisation,<br />
sociological dimensions of urbanisation, Social consequences of urbanisation.<br />
Unit II. Classification of cities: The nature of pre-industrial and post industrial cities,<br />
functional classification of cities, Different approaches to the study of urban<br />
centers.<br />
Unit III. Urban problems: causes and solution, housing, alcoholism, drug addiction,<br />
prostitution, Aids, slums and environmental pollution.<br />
Unit IV. Urban planning: Meaning and definition of urban planning, importance of<br />
planning, factors affecting planning, master plan, urban administration.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Ahuja, Ram. 1997. Social Problems in India. Jaipur: Rawat Publications.<br />
Bose, Ashis. 1973. Studies in India's Urbanization. New Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill<br />
Publishing Co.<br />
Dahiwale, S. M. 1997.Rural poverty and slums. Jaipur: Rawat Publications.<br />
Desai A. R. and Pillai S. D. 1970. Slums and Urbanization. Bombay: Popular Prakashan.<br />
Diddee, Jaymala and Rangaswamy, Vimla. 1993. Urbanization- Trends, Perspectives<br />
challenges. Jaipur: Rawat Publication.<br />
D'Souza, Alfred. 1978. The Indian City, Poverty; Ecology and Urban Development. New<br />
Delhi: Manohar.
Gill, Rajesh. 1994. Slum as urban villages. Jaipur: Rawat Publicarions.<br />
Hanumappa, H. G. 1981.Urbanization trends in India. New Delhi: Ashish Publishing<br />
House.<br />
K. Sivaramkrishnan, A Kundu and B. N. Singh, 2005.Handbook of Urbanization in<br />
India. Delhi.<br />
Kosambi, Meera. 1994, Urbanisation and Urban Development in India. ICSSR.New<br />
Delhi.<br />
Nayar P. K. B. 1982. Sociology in India: Retrospect and Prospect. Delhi: B.R.Publishing<br />
Corporation<br />
Pramanik, S. K. 2001. Sociology of G. S. Ghurye. Rawat. New Delhi.<br />
Rao, M. S. A. (ed.).1974. Urban Sociology in India. New Delhi: Orient Longman.<br />
SOE - 409: Sociology of Disaster Management - II<br />
Unit I: Impact of Disaster: Physical, economical, spatial and psycho-social.<br />
Unit II: Disaster Management: Pre-disaster Prevention, Preparation, education,<br />
preparedness, Actual disaster, short term plan, long term plan, stress and trauma,<br />
search, relief, recovery, restoration, resource mobilization; Post-Disaster,<br />
Rehabilitation. Negative effects of migration<br />
Unit III: Intervening Parties: Government Organization, voluntary organization, local<br />
groups, community participation, volunteers, and Social workers.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Dhirendra, Sharma, 1983. India’s Nuclear Estate, New Delhi: Lancers<br />
Jatinder, K. Bajaj The Bhopal Tragedy: The Responsibility of the Scientific Community<br />
Nandy, Ashis. Science, Authoritarianism and Culture.<br />
Nandy, Ashis. 1985.The Bomb, The Illustrated weekly of India<br />
Sen, Amartya 1981.Poverty and Famines New Delhi: OUP<br />
SOE <strong>–</strong> 404: Criminology <strong>–</strong> II<br />
I. Female criminality: Concept, extent in India, theories of female criminality, causes and<br />
consequences of female criminality, female victims, family court, correctional<br />
institutions and rehabilitation of female offenders and female victims.<br />
II. Theories of punishment: Retributive, deterrent, reformative, futility and cost of<br />
punishment, role of Police in crime investigation, role of forensic science in crime<br />
investigation, bail, charge-sheet, custody, trial. Correction and its forms: meaning<br />
and significance of correction; forms of correction - person based, community<br />
based.<br />
III. Correctional programmes in prisons: History of prison reforms in India, national<br />
policy on prisons, commissions and committees, on jail reforms and criminal<br />
Justice system, scientific classification of prisoners, modernization of prison<br />
industry and involvement of private sector, correctional programmes -<br />
educational, vocational, psychiatric, meditation, recreation etc. Kiran Bedi's New<br />
Delhi Model of correction.<br />
IV. Problems of correctional administration: Antiquated jail manual and prison act,<br />
overcrowding, custodial mindset, lack of inter-agency coordination among police,
prosecution, Judiciary and prison, human rights and prison management<br />
limitations and prospects of correction. Alternatives to imprisonment: Probation,<br />
parole, open prisons, after-care and rehabilitation, victimological perspective;<br />
victims's responsibility in crime, compensation to victims.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Bedi Kiran, 1998, It is Always Possible, New Delhi, Sterling Publications, Pvt Ltd..<br />
Bequai, August 1978. Computer Crime, Toronty: Lesington Books,<br />
Buckland, John, 1992. Combating Computer Crime: Prevention, Detection and<br />
Investigation, New Delhi: McGraw Hill.<br />
Contemporary Issues, London : Sage Publications.<br />
Control and Prevention, Bombay: Sysman Computers Pvt. Ltd.<br />
Criminology, Jalandhar : ABC Publications.<br />
Drapkin Ismail and Viano, Emilio, 1975. Victimology: A New Focus, London, Lesington<br />
Press.<br />
Gill, S.S. 1998. The Pathology of Corruption. New Delhi Harper Collin's Publishers<br />
(India.)<br />
Goel, Rakesh M. and Manohar S. Powar, 1994, Computer Crime : Concept.<br />
Gote-Gavhane Shubhangi, 1997. Female Criminality and Sociological Theories,<br />
Aurangabad (Maharashtra) India, South Asian Social Research Publication.<br />
Haiiman, Taryl, A. 1950. The Economics of crime New York: St. Martins's Press.<br />
Inciarti James, A. and Pottieger Anne E. 1978; Violent Crime: Historical and<br />
Kaldate, Sudha, 1982. Society, Delinquent and Juvenile Court, New Delhi, Ajanta<br />
Publications.<br />
Lilly, J. Robert Francis T. Wallen and Richard Ball A., 1955. Criminological Theory,<br />
Context and Consequences, New Delhi: Sage Publications.<br />
Makkar, S.P. Singh and Paul C. Friday, 1993. Global Perspectives in<br />
Ministry of Home Affairs, 1998. Crime In India Report, New Delhi, Government<br />
of India.<br />
Ministry of Home Affairs, Report of the All India Committee on Jail Reforms, 1980-<br />
83, New Delhi: Government of India.<br />
Pace, Denay, F. 1991. Concept of Vice, Narcotics and Organized Crime, London Prentice<br />
<strong>–</strong> Hall.<br />
Rayan, Patrick J. and George Rush, 1997. Understanding Organized Crime in global<br />
Perspective, London: Sage Publications.<br />
Reid, Suetitus, 1976. Crime and Criminology, Illnayse: Deydan Press,<br />
Revid, Jorathan, 1995. Economic Crime, London, Kejan Paul.<br />
Shankardas, Rani Dhavan, 2000. Punishment and the Prison: Indian and International<br />
Perspective, New Delhi: Sage Publications.<br />
Sutherland, Edwin H. and Donald R. Cressey, 1968. Principles of Criminology Bombay :<br />
The Times of India Press.<br />
Walklete Sandra, 1998. Understanding Criminology Philadelphia, Open<br />
University Press.<br />
Weinberg, Dand and Kip Schlegal, 1990. White Collar Crime Reconsidered, Boston :<br />
Northeastern University Press.
Williams, Frank P. and Marilyn D. Meshare, 1998. Criminological Theory, New Jersey:<br />
Prentice Hall.<br />
Williamsen, Herald, E. 1990. The Correction Profession, New Delhi, Sage Publication.<br />
SOE <strong>–</strong> 406: Environment and Society - II<br />
I. Resources, Populations, Development and Environmental problems:<br />
a) State of Natural Resources: water, forests, land, and its degradation.<br />
b) Population growth, poverty, consumption patterns and<br />
environmental problems.<br />
c) Industrialization, urbanization and environmental problems.<br />
d) Globalisation and Environmental problems.<br />
II. Towards Environmental Protection/Conservation.<br />
a) Constitutional provisions and major environmental laws in India.<br />
b) Major environmental movements in India: A brief review<br />
c) Sustainable Development: An alternative path of development<br />
d) Major international events, their outcome and the politics of the<br />
environment.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Agarwal S. K. Environmental Issues and Themes APH Publishing Corporation, New<br />
Delhi, 1997.<br />
Gadgil, Madhav and Ramachandra Guha: Ecology and Equity: The Use and Abuse of<br />
Nature in Contemporary India, New Delhi, OUR, 1996.<br />
Giddens, Anthony, The Consequences of Modernity, Cambridge, Polity Press. 1990.<br />
Giddens, Anthony: Introduction to Sociology, (4th Ed.), New York: W.W. Norton and<br />
Co., 1996.<br />
Limmermom M. E. and other (Ed.): Environmental Phi losophy from Animal Rights to<br />
Radical Ecology, Prentice Hall, Englewood Clifts, New Jersey 1993.<br />
Mattel Luke: Ecology and Society: An Introduction, Polity Press, 1994.<br />
Michael Reddift: Development and Environmental Crisis, Meheun Co, Ltd., New York,<br />
1984.<br />
Pravin Seth: Environmentalism, Politics, Ecology and Development, Rawat New Delhi<br />
1997.<br />
Rao P. K. Sustainable Development-Economics and Policy, Blackwell, 2001.<br />
Riley E. Dunlap. ‘The Evolution of Environmental Sociology’ in The International<br />
Handbook of Environmental Sociology, Michael Reddift and Graham Woodgate<br />
(Eds.) Edward Elgar, Cheltanham, V. K. 1997.<br />
Satapathy, Nityanand. Sustainable Development: An Alternative Paradigm, Karnavati<br />
publications, Ahmedabad, 1998.<br />
Satyanarayana B. (Ed.) Social Sciences and Planning for Sustainable Development,<br />
Himalaya, Mumbai.1998.<br />
Sharma S. L. ‘Perspectives on Sustainable Development in South Asia’, in Samad (Ed.):<br />
Perspectives on Sustainable Development in Asia, Kuala Lampur: ADIPA.<br />
Wallerstein, Immanuel: The Modern World System, New York, OUP, 1974.<br />
World Bank: World Development Report. 1995.
World Commission on Environment and Development Our Common Future, 1987.<br />
SOE - 410: Health and Society - II<br />
Unit I: Reproductive health behaviour <strong>–</strong> Men and women<br />
Need and Problems<br />
Unit II: Reproductive Track Infection/Sexually Track Infections and Human<br />
Immunodeficiency Virus/Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (HIV/AIDS)<br />
Maternal Health<br />
Abortions: Spontaneous and Induced<br />
Reproductive morbidity <strong>–</strong> obstetric, gynaecological and contraceptive<br />
Unit III: Policies and Programmatic action<br />
National Health Policy<br />
Health Transition in India<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Bever, M. 2000. ‘Making abortions safe: A matter of good public health policy and<br />
practice’, Bulltin WHO, Vol 78 (5), pp. 590-592.<br />
Bhat, P.N.M. 2002. ‘Levels and Differentials in Maternal Mortality in Rural India: New<br />
Estimates from Sisterhood method’, NCAER working paper series No. 87,<br />
NCAER, New Delhi.<br />
Elman, C. 1984. ‘Culture, health, illness, wright’, Bristol.<br />
Guilmoto C. and I. Rajan (ed). 2005. ‘Fertility Transition in south India, sage<br />
Publications, New Delhi.<br />
Imrana, Quadeer. 2000. ‘Health care system in transition III, Journal of Public Health<br />
Medicine, Vol. 22, No. 1, pp. 25-32.<br />
Jejeebhoy, Shirin. 2003. ‘Action that protect: Promoting sexual and reproductive health<br />
and choice among young people in India’, Population Council, New Delhi.<br />
Kuttan, Mahadevan and Others (ed). 2000. Reproductive health of humankind in Asia<br />
and Africa: a Global Perspective, B.R. ublishing Corporation, Delhi.<br />
Ministry of Health and family Welafre. 1997. ‘Reproductive and Child Health<br />
Programme’, Mannual for India and Karnataka, Government of India.<br />
Park, J.E. and Park, K. 1989. ‘Text Book of Preventive and Social Medicine (12 th<br />
Edition), M/s Banarasidas Bhanot Publisher, Jabalpur.<br />
Ramasubban, Radhika and Jejeebhoy, Shirin (ed). 2000. ‘Women’s reproductive health in<br />
India’ New Delhi: Rawat Publications.<br />
World Bank. 1993. ‘World Development Report 1993: Investigating in Health’, Oxford<br />
University Press, New York.<br />
World Health Organization. 1999. ‘The world Health report 1999: making a difference,<br />
WHO, Geneva, Switzerland, WHO.<br />
World Health Organization. 2003. ‘Towards Adulthood: Exploring the sexual and<br />
reproductive health of adolescents in South Asia’, WHO.<br />
Unit I: Approaches to Tribal Development:<br />
SOE - 411: Tribal Sociology - II
a) Assimilationist and integrationist<br />
b) Indian constitution-safeguards and provisions for scheduled tribes<br />
c) History of Tribal Development in India with special reference to Maharashtra<br />
Unit II: Planning and Development.<br />
Scheduled Tribes in five years plans. Strategies of tribal development: special<br />
multi purpose sub-plans, interacted tribal development.<br />
Unit III: The so-called mega development and their impact on tribal communities,<br />
sustainable tribal development, Ashram schools: Educational institutionalization<br />
of the tribal children.<br />
Unit IV: Sustainable Tribal Development, Neheru’s perspectives on tribal development.<br />
The role of social workers in tribal development.<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Furer-Hymendrof, C.V., 1982. Tribes of India: The struggle for survival, Delhi oxford<br />
university press.<br />
Hadaon A.C. 1924. Races of Mankind, Cambridge University press, London<br />
Harasukar, Laxmi: 2005.The tribes and their development, Current, Agra,<br />
Mehta, P.L. Constitutional protection to scheduled tribes in India in retrospect and<br />
prospect, Delhi: H.K.<br />
Murdock G.P. 1961. Our primitive contemporaries Macmillan, New Delhi<br />
Oommen T.K. 1986.Insiders and Outsiders in India, Primordial collectivism and cultural<br />
Puralism in Nation Building-in-international sociology-international sociological<br />
Association Vol-I<br />
Singh, K.S. 1972.Tribal situation in India, Indian Institute of Advanced Studies, Simla,<br />
Vidhyarthi, L.P. Roy B.K.P. 1976. The Tribal culture of India, concept publishing co.<br />
New Delhi<br />
SOE - 412: Social Psychology - II<br />
Unit I: Social Perception<br />
a) Human motivation<br />
b) Perceptual processes <strong>–</strong> Prejudice, stereotypes, empathy<br />
Unit II: Leader and leadership<br />
a) Characteristics of leaders<br />
b) Types of leaders<br />
c) Functions of leadership<br />
Unit III: Public opinion and propaganda<br />
a) Dynamics of public opinion<br />
b) Measurement of public opinion<br />
c) Propaganda <strong>–</strong> Suggestion and education<br />
d) Techniques of propaganda<br />
Suggested Readings:<br />
Distributors, Delhi.<br />
Gurin, Veroff and Feld, 1960, American’s views their Mental Health, Basic Book, New<br />
York
Harari, Herbert and McDavid Jhon, W, 1986, Social Psychology, CBS Publisers &<br />
Maccoby, E.E.New Comp., T.E. and Harty, E/K/(Eds), 1958, Reading in Social<br />
Merton, R.K. 19 52, Bureautcratic structure and personality, Reader in Bureacracy,<br />
Glenco III Free Press.<br />
Psychology, Holt, New York.<br />
Publications, great Britain.<br />
Tannenbaun, Arnold S. 1966, Social Psychology of the Work organization, Tavistock