- Page 1 and 2: MOOD DISORDERS Edited by Neşe Koca
- Page 3: free online editions of InTech Book
- Page 6 and 7: VI Contents Chapter 8 Mood Disorder
- Page 9 and 10: Chapter 1 Murine Models for Develop
- Page 11 and 12: Murine Models for Developping an In
- Page 13 and 14: Murine Models for Developping an In
- Page 15: Murine Models for Developping an In
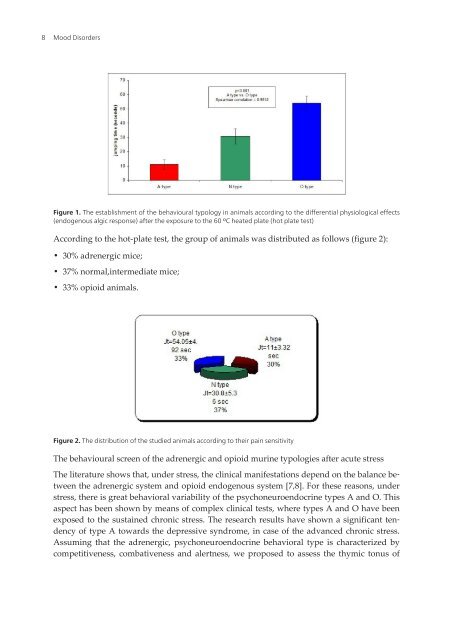
- Page 19 and 20: Murine Models for Developping an In
- Page 21 and 22: Murine Models for Developping an In
- Page 23 and 24: Murine Models for Developping an In
- Page 25 and 26: Murine Models for Developping an In
- Page 27 and 28: Murine Models for Developping an In
- Page 29 and 30: Murine Models for Developping an In
- Page 31 and 32: Chapter 2 Depression and Glucose Me
- Page 33 and 34: 2.2. Clinical symptoms Depression i
- Page 35 and 36: al., 2011, in a group of more than
- Page 37 and 38: Depression and Glucose Metabolism (
- Page 39 and 40: psychosocial factors which associat
- Page 41 and 42: Depression and Glucose Metabolism (
- Page 43 and 44: ≤ 0.01 for all parameters). Reduc
- Page 45 and 46: Scale Groups SSRI´s/SNRI´s N Mean
- Page 47 and 48: studies and almost disappears in mo
- Page 49 and 50: Depression and Glucose Metabolism (
- Page 51 and 52: Depression and Glucose Metabolism (
- Page 53 and 54: Depression and Glucose Metabolism (
- Page 55 and 56: Depression: Classification, Culture
- Page 57 and 58: Depression: Classification, Culture
- Page 59 and 60: Depression: Classification, Culture
- Page 61 and 62: Regier (2004, p. 25) describes the
- Page 63 and 64: sation takes hold and a degree of c
- Page 65 and 66: clear that lesser forms of unhappin
- Page 67:
[20] MedlinePlus (2012) http://www.
- Page 70 and 71:
62 Mood Disorders Although there is
- Page 72 and 73:
64 Mood Disorders Emotional symptom
- Page 74 and 75:
66 Mood Disorders These symptoms ca
- Page 76 and 77:
68 Mood Disorders creasingly delega
- Page 78 and 79:
70 Mood Disorders chapter; therefor
- Page 80 and 81:
72 Mood Disorders 7.2.1. Reinforcem
- Page 82 and 83:
74 Mood Disorders fect on the patie
- Page 84 and 85:
76 Mood Disorders Some patients may
- Page 86 and 87:
78 Mood Disorders will get up at 8
- Page 88 and 89:
80 Mood Disorders peutic setting un
- Page 90 and 91:
82 Mood Disorders detailed in this
- Page 92 and 93:
84 Mood Disorders 8.3. Cognitive te
- Page 94 and 95:
86 Mood Disorders and correctly und
- Page 96 and 97:
88 Mood Disorders Therapist: “Ima
- Page 98 and 99:
90 Mood Disorders 1. Analysis of be
- Page 100 and 101:
92 Mood Disorders [7] Wittchen, H.-
- Page 102 and 103:
94 Mood Disorders [36] Hollon, S.D.
- Page 104 and 105:
96 Mood Disorders [68] Yorbik, O.,
- Page 106 and 107:
98 Mood Disorders [103] Lindsley, D
- Page 109 and 110:
Mitochondrial Functions in Mood Dis
- Page 111 and 112:
Genetic defects or stress can cause
- Page 113 and 114:
Figure 2. Representation of process
- Page 115 and 116:
ain. Normally the H 2O 2 is then in
- Page 117 and 118:
ADP level State 1 Low State 2 High
- Page 119 and 120:
2.3.2. Uncoupling proteins Uncoupli
- Page 121 and 122:
Complex IV inhibitors KCN and sodiu
- Page 123 and 124:
pathogenesis of axonal degeneration
- Page 125 and 126:
3.3. Inflammatory and neurodegenera
- Page 127 and 128:
plete data exist on the effect of p
- Page 129 and 130:
4.3. Effects of mood stabilizers on
- Page 131 and 132:
Antidepressant Biological model Aff
- Page 133 and 134:
Mood stabilizer Biological model Af
- Page 135 and 136:
Mitochondrial Functions in Mood Dis
- Page 137 and 138:
Mitochondrial Functions in Mood Dis
- Page 139 and 140:
Mitochondrial Functions in Mood Dis
- Page 141 and 142:
Mitochondrial Functions in Mood Dis
- Page 143 and 144:
Mitochondrial Functions in Mood Dis
- Page 145 and 146:
Mitochondrial Functions in Mood Dis
- Page 147 and 148:
Mitochondrial Functions in Mood Dis
- Page 149 and 150:
Mitochondrial Functions in Mood Dis
- Page 151 and 152:
Mitochondrial Functions in Mood Dis
- Page 153 and 154:
Long-Term Adaptive Changes Induced
- Page 155 and 156:
Long-Term Adaptive Changes Induced
- Page 157 and 158:
5-HT 1B/1D (-) SERT 5-HT 1A (-) [5-
- Page 159 and 160:
Long-Term Adaptive Changes Induced
- Page 161 and 162:
postsynaptic 5-HT 1A receptors in t
- Page 163 and 164:
Long-Term Adaptive Changes Induced
- Page 165 and 166:
3.3. Neurotrophins modulation by 5-
- Page 167 and 168:
BDNF levels before treatment, and a
- Page 169 and 170:
References Long-Term Adaptive Chang
- Page 171 and 172:
Long-Term Adaptive Changes Induced
- Page 173 and 174:
Long-Term Adaptive Changes Induced
- Page 175 and 176:
Long-Term Adaptive Changes Induced
- Page 177 and 178:
Long-Term Adaptive Changes Induced
- Page 179 and 180:
Long-Term Adaptive Changes Induced
- Page 181 and 182:
Long-Term Adaptive Changes Induced
- Page 183 and 184:
Long-Term Adaptive Changes Induced
- Page 185 and 186:
Long-Term Adaptive Changes Induced
- Page 187 and 188:
Long-Term Adaptive Changes Induced
- Page 189 and 190:
Biological Markers and Genetic Fact
- Page 191 and 192:
Collectively, serotonin receptor, T
- Page 193 and 194:
Biological Markers and Genetic Fact
- Page 195 and 196:
imaging and genetics have been emer
- Page 197 and 198:
Biological Markers and Genetic Fact
- Page 199 and 200:
Biological Markers and Genetic Fact
- Page 201 and 202:
Biological Markers and Genetic Fact
- Page 203:
Biological Markers and Genetic Fact
- Page 206 and 207:
198 Mood Disorders pressed. Already
- Page 208 and 209:
200 Mood Disorders cy may takes its
- Page 210 and 211:
202 Mood Disorders of the developin
- Page 212 and 213:
204 Mood Disorders 2.2.1. Touch and
- Page 214 and 215:
206 Mood Disorders found by Jung et
- Page 216 and 217:
208 Mood Disorders mize the risk of
- Page 218 and 219:
210 Mood Disorders [20] Misri S, Ko
- Page 220 and 221:
212 Mood Disorders [49] Melley M, C
- Page 222 and 223:
214 Mood Disorders [78] Rahman A, I
- Page 224 and 225:
216 Mood Disorders [106] Taylor A,
- Page 226 and 227:
218 Mood Disorders [134] Esquivel-S
- Page 229 and 230:
Cognitive Functions in Euthymic Bip
- Page 231 and 232:
Cognitive Functions in Euthymic Bip
- Page 233 and 234:
Cognitive Functions in Euthymic Bip
- Page 235 and 236:
4. Discussion 4.1. Cognitive functi
- Page 237 and 238:
poor functional outcome. Executive
- Page 239 and 240:
Cognitive Functions in Euthymic Bip
- Page 241 and 242:
References Cognitive Functions in E
- Page 243 and 244:
Cognitive Functions in Euthymic Bip
- Page 245 and 246:
Cognitive Functions in Euthymic Bip
- Page 247:
Cognitive Functions in Euthymic Bip
- Page 250 and 251:
242 Mood Disorders Figure 1. 2. Fat
- Page 252 and 253:
244 Mood Disorders 3.1. The role of
- Page 254 and 255:
246 Mood Disorders dylserine is syn
- Page 256 and 257:
248 Mood Disorders and 42 (Aβ 42)
- Page 258 and 259:
250 Mood Disorders about omega-3 fa
- Page 260 and 261:
252 Mood Disorders First, DHA compe
- Page 262 and 263:
254 Mood Disorders tained from the
- Page 264 and 265:
256 Mood Disorders [11] Salem, N.,
- Page 266 and 267:
258 Mood Disorders bind to retinoid
- Page 268 and 269:
260 Mood Disorders [67] Yao, J. K.,
- Page 271 and 272:
Chapter 11 Neuronal Insulin Recepto
- Page 273 and 274:
Neuronal Insulin Receptor Signaling
- Page 275 and 276:
Neuronal Insulin Receptor Signaling
- Page 277 and 278:
Neuronal Insulin Receptor Signaling
- Page 279 and 280:
Neuronal Insulin Receptor Signaling
- Page 281 and 282:
Neuronal Insulin Receptor Signaling
- Page 283 and 284:
Neuronal Insulin Receptor Signaling
- Page 285 and 286:
involved in the various cognitive a
- Page 287 and 288:
Neuronal Insulin Receptor Signaling
- Page 289 and 290:
Neuronal Insulin Receptor Signaling
- Page 291 and 292:
Neuronal Insulin Receptor Signaling
- Page 293 and 294:
Neuronal Insulin Receptor Signaling
- Page 295:
Neuronal Insulin Receptor Signaling