Frühjahrssymposium 2013 in Berlin - JungChemikerForum Berlin
Frühjahrssymposium 2013 in Berlin - JungChemikerForum Berlin
Frühjahrssymposium 2013 in Berlin - JungChemikerForum Berlin
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Synthesis and study of antioxidant properties of fullerene C60<br />
derivatives.<br />
Robert Czochara, Michał Symonowicz, Grzegorz Litw<strong>in</strong>ienko<br />
Faculty of Chemistry – University of Warsaw – Pasteura 1 – Warsaw – POL<br />
rczochara@chem.uw.edu.pl<br />
Oxidative damage of organic materials is caused by free radicals and Reactive Oxygen<br />
Species (ROS). Antioxidants can <strong>in</strong>hibit oxidation reaction by removal of free<br />
radicals. Activity of antioxidants depends on structure and chemical nature, thus,<br />
nanoparticles are new promis<strong>in</strong>g objects for free radical research. Fullerenes [1] can<br />
f<strong>in</strong>d many potential applications <strong>in</strong> science, <strong>in</strong>dustry and medic<strong>in</strong>e. [2,3] Carbon core<br />
makes fullerene an <strong>in</strong>terest<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>itial structure <strong>in</strong> the development of novel radicalscaveng<strong>in</strong>g<br />
compounds with specific functionalities. Recently, it has been shown that<br />
fullerenes and their derivatives can trap several radicals per molecule [4] and can potentially<br />
be used as a protective substance aga<strong>in</strong>st ROS.<br />
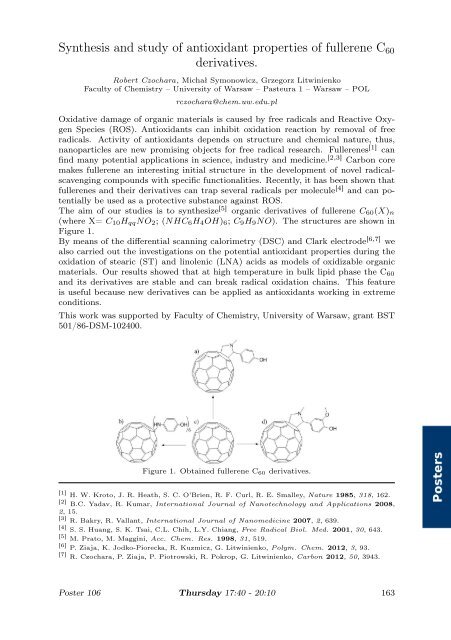
The aim of our studies is to synthesize [5] organic derivatives of fullerene C60(X)n<br />
(where X= C10HqqNO2; (NHC6H4OH)6; C9H9NO). The structures are shown <strong>in</strong><br />
Figure 1.<br />
By means of the differential scann<strong>in</strong>g calorimetry (DSC) and Clark electrode [6,7] we<br />
also carried out the <strong>in</strong>vestigations on the potential antioxidant properties dur<strong>in</strong>g the<br />
oxidation of stearic (ST) and l<strong>in</strong>olenic (LNA) acids as models of oxidizable organic<br />
materials. Our results showed that at high temperature <strong>in</strong> bulk lipid phase the C60<br />
and its derivatives are stable and can break radical oxidation cha<strong>in</strong>s. This feature<br />
is useful because new derivatives can be applied as antioxidants work<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> extreme<br />
conditions.<br />
This work was supported by Faculty of Chemistry, University of Warsaw, grant BST<br />
501/86-DSM-102400.<br />
Figure 1. Obta<strong>in</strong>ed fullerene C60 derivatives.<br />
[1]<br />
H. W. Kroto, J. R. Heath, S. C. O’Brien, R. F. Curl, R. E. Smalley, Nature 1985, 318, 162.<br />
[2]<br />
B.C. Yadav, R. Kumar, International Journal of Nanotechnology and Applications 2008,<br />
2, 15.<br />
[3]<br />
R. Bakry, R. Vallant, International Journal of Nanomedic<strong>in</strong>e 2007, 2, 639.<br />
[4]<br />
S. S. Huang, S. K. Tsai, C.L. Chih, L.Y. Chiang, Free Radical Biol. Med. 2001, 30, 643.<br />
[5]<br />
M. Prato, M. Magg<strong>in</strong>i, Acc. Chem. Res. 1998, 31, 519.<br />
[6]<br />
P. Ziaja, K. Jodko-Piorecka, R. Kuzmicz, G. Litw<strong>in</strong>ienko, Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 93.<br />
[7]<br />
R. Czochara, P. Ziaja, P. Piotrowski, R. Pokrop, G. Litw<strong>in</strong>ienko, Carbon 2012, 50, 3943.<br />
Poster 106 Thursday 17:40 - 20:10 163