Learning Theories - Cognitive Learning Theories CHAPTER
Learning Theories - Cognitive Learning Theories CHAPTER
Learning Theories - Cognitive Learning Theories CHAPTER
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>CHAPTER</strong> 5 l LEARNING THEORIES - COGNITIVE LEARNING THEORIES<br />
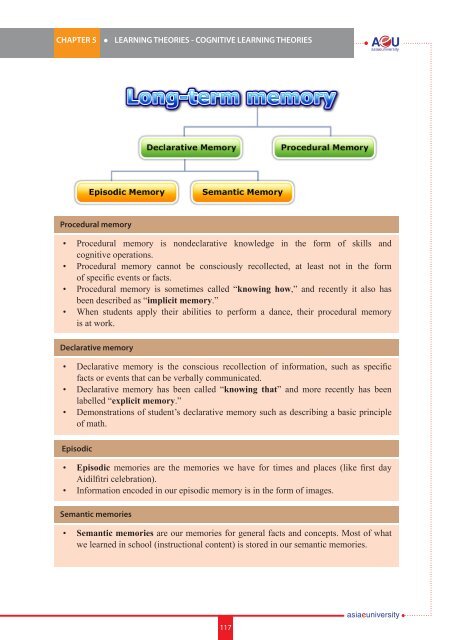
Procedural memory<br />
• Procedural memory is nondeclarative knowledge in the form of skills and<br />
cognitive operations.<br />
• Procedural memory cannot be consciously recollected, at least not in the form<br />
of specific events or facts.<br />
• Procedural memory is sometimes called “knowing how,” and recently it also has<br />
been described as “implicit memory.”<br />
• When students apply their abilities to perform a dance, their procedural memory<br />
is at work.<br />
declarative memory<br />
• Declarative memory is the conscious recollection of information, such as specific<br />
facts or events that can be verbally communicated.<br />
• Declarative memory has been called “knowing that” and more recently has been<br />
labelled “explicit memory.”<br />
• Demonstrations of student’s declarative memory such as describing a basic principle<br />
of math.<br />
Episodic<br />
• Episodic memories are the memories we have for times and places (like first day<br />
Aidilfitri celebration).<br />
• Information encoded in our episodic memory is in the form of images.<br />
Semantic memories<br />
• Semantic memories are our memories for general facts and concepts. Most of what<br />
we learned in school (instructional content) is stored in our semantic memories.<br />
117<br />
i.<br />
117