Brinjal - Efresh India
Brinjal - Efresh India
Brinjal - Efresh India
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
eFresh – Empowering <strong>India</strong>n Agriculture<br />
<strong>Brinjal</strong><br />
(Solanum melongena L.)<br />
This is a typical <strong>India</strong>n vegetable grown in many parts of the country, almost<br />
throughout the year. There are many varieties of <strong>Brinjal</strong>. Of them, white <strong>Brinjal</strong> has<br />
some medicinal properties. <strong>Brinjal</strong> is a warm season fruit vegetable, highly susceptible<br />
to frost. Optimum temperature for growth and fruit set is 16-22 degrees Celsius. The<br />
long fruited varieties set fruit at higher temperature and show tolerance to frost.<br />
A wild type of <strong>Brinjal</strong> with deeply variegated leaves – solanum sisimbrifolium (Lam) is<br />
considered to be the ancestral species of the present day cultivated <strong>Brinjal</strong>. It is highly<br />
cross pollinated due to hetero style nature of the flower. There are four types of<br />
flowers in <strong>Brinjal</strong> a).long styled b).medium styled c). short styled and d). pseudo<br />
styled. Only long styled and medium styled flowers set fruit.
eFresh – Empowering <strong>India</strong>n Agriculture<br />
In <strong>Brinjal</strong> flowers generally open in the morning. Anther dehiscence occurs 15 to 20<br />
minutes after the flowers open. Receptivity ranges from a day prior to 4 days after<br />
opening. Pollen is most fertile immediately after the anther dehiscence. Opening of<br />
anthers is mostly by a pore or slit at apex. The somatic chromosome number is 2n=24.<br />
The fruit shape in <strong>Brinjal</strong> is governed by 3 genes. Round shape is partially dominant<br />
over long shape. Similarly the cluster character is partially dominant over solitary<br />
nature. It is governed by a single gene. Large fruit size is dominant over small and<br />
purple fruit color is dominant over green.<br />
Major problems in <strong>Brinjal</strong> production are fruit & shoot borer and bacterial wilt. White<br />
Long <strong>Brinjal</strong>, Thorn pendy, H407 are resistant to fruit borer. Breeding for bacterial wilt<br />
resistance in <strong>Brinjal</strong> resulted in the selection of Sm48, 56 and 71.<br />
Varieties<br />
There are many varieties and hybrids in <strong>Brinjal</strong>. They are classified based on shape,<br />
color, calyx character, thorny nature etc. There are regional preferences for these<br />
characters. Among straight varieties Pusa Purple Long, P.Purple Cluster, P.Kranti,<br />
P.Purple Round developed at IARI and Arka Sheel, A.Shirish, A.Kusumakar,<br />
A.Navaneeth of IIHR, Punjab Barsati of PAU, Azad Kranti, Pant Samrat from U.P. are<br />
popular. A large number of hybrids were developed by private and public research<br />
organizations and are now in the market.<br />
Cultivation details<br />
<strong>Brinjal</strong> seed is sown on a raised nursery bed and the seedlings after 4-5 weeks are<br />
transplanted in a well prepared field at 75X60, 60X60 or 60X45 cm. spacing depending<br />
on the growth habit of the variety or hybrid cultivated. About 200 gm. Of seed is<br />
required to raise the nursery in about 40 Sq.m. for transplanting in an acre. When<br />
hybrid seeds are used about 60-80 gm. are utilized for transplanting in one acre.<br />
The main field for production is prepared by plowing 3-4 times, leveling the land and<br />
making ridges & furrows to facilitate flow irrigation and drainage. Before the final<br />
plowing 3-4 tons of well decomposed farm yard manure and 200 kg of Single Super<br />
Phosphate is applied per acre and incorporated into the soil before making the ridges.
eFresh – Empowering <strong>India</strong>n Agriculture<br />
Seedlings are taken out from the nursery in the morning and kept in shade and<br />
transplanted in the evening on the sides of the ridges and irrigated immediately. The<br />
roots of the seedlings before transplanting are dipped in solution containing PSB and<br />
the tops in the solution containing a pesticide and a fungicide. The seedlings are<br />
transplanted without bending the tap root.<br />
Irrigation & Manuring :<br />
Irrigations are given every week to maintain soil moisture levels at 60% depletion.<br />
Weeding, hoeing and other cultural operation are carried out to keep the field free<br />
from weeds and to facilitate root aeration.<br />
Depending on the soil type and the cultivar, fertilizer doses are decided. Normally 40<br />
kg N, 40 kg P and 25 kg K are applied per acre. Complete P in the form of SSP and half<br />
of K in the form of MOP is applied before transplanting. N is applied in 3 split doses<br />
starting from 5 th week at monthly intervals. Balance K is applied in the 2&3<br />
applications of N. <strong>Brinjal</strong> normally does not require application of micro nutrients,<br />
unless the soils and irrigation waters are defective.<br />
During flowering and fruiting weekly sprays of 2, 4-D @ 2ppm is given for improving<br />
fruit set and yield.<br />
In fields with persistent weeds, pre planting application of Treflon @ 400-500 gm per<br />
acre reduces the problem.<br />
Harvesting and Yield<br />
<strong>Brinjal</strong> is harvested before it attained full maturity, as it is edible from the time it is<br />
quarter grown, until it reached ripening. <strong>Brinjal</strong> with green calyx is preferred by the<br />
consumers.<br />
Storage<br />
After harvest, <strong>Brinjal</strong> can remain in good condition for 3-4 days at room temperatures<br />
and up to 4 weeks in cold storage at 8-10 degree C. and 90% R.H. <strong>Brinjal</strong> packed in<br />
plastic crates stand well in transport.
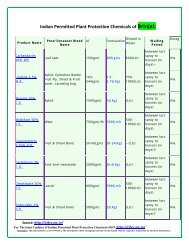
Crop Protection<br />
eFresh – Empowering <strong>India</strong>n Agriculture<br />
Many pests and diseases affect <strong>Brinjal</strong> right from nursery stage till the produce is<br />
harvested. Damping off of seedlings in the nursery is common. Phomopsis blight, leaf<br />
spots, wilt, little leaf and mosaic are major diseases. Among the pests, fruit & shoot<br />
borer takes a heavy toll followed by damage caused by Epilachna beetles, jassids, red<br />
spider mites, mealy bugs etc.