Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
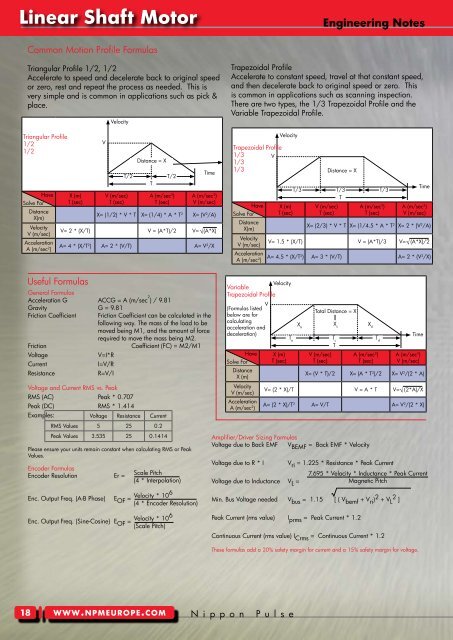
linear shaft motor<br />
Triangular Profile<br />
1/2<br />
1/2<br />
Solve For<br />
Distance<br />
X(m)<br />
Velocity<br />
V (m/sec)<br />
Acceleration<br />
A (m/sec 2 )<br />
General Formulas<br />
Acceleration G ACCG = A (m/sec 2<br />
) / 9.81<br />
Gravity G = 9.81<br />
Friction Coefficient Friction Coefficient can be calculated in the<br />
following way. The mass of the load to be<br />
moved being M1, and the amount of force<br />
required to move the mass being M2.<br />
Friction Coefficient (FC) = M2/M1<br />
18<br />
Common Motion Profile Formulas<br />
Triangular Profile 1/2, 1/2<br />
Accelerate to speed and decelerate back to original speed<br />
or zero, rest and repeat the process as needed. This is<br />
very simple and is common in applications such as pick &<br />
place.<br />
Have<br />
Useful Formulas<br />
Voltage V=I*R<br />
Current I=V/R<br />
Resistance R=V/I<br />
Voltage and Current RMS vs. Peak<br />
RMS (AC) Peak * 0.707<br />
Peak (DC) RMS * 1.414<br />
Examples:<br />
X (m)<br />
T (sec)<br />
Encoder Formulas<br />
Encoder Resolution Er =<br />
Enc. Output Freq. (A-B Phase) E OF =<br />
Enc. Output Freq. (Sine-Cosine) E OF =<br />
V<br />
Velocity<br />
V (m/sec)<br />
T (sec)<br />
Distance = X<br />
T/2 T/2<br />
T<br />
A (m/sec 2 )<br />
T (sec)<br />
Scale Pitch<br />
(4 * Interpolation)<br />
www.npmeurope.com<br />
Velocity * 10 6<br />
(4 * Encoder Resolution)<br />
Velocity * 10 6<br />
(Scale Pitch)<br />
A (m/sec 2 )<br />
V (m/sec)<br />
X= (1/2) * V * T X= (1/4) * A * T 2 X= (V 2 /A)<br />
V= 2 * (X/T) V = (A*T)/2 V= √(A*X)<br />
A= 4 * (X/T 2 ) A= 2 * (V/T) A= V 2 /X<br />
Voltage Resistance Current<br />
RMS Values 5 25 0.2<br />
Peak Values 3.535 25 0.1414<br />
Please ensure your units remain constant when calculating RMS or Peak<br />
Values.<br />
Time<br />
Trapezoidal Profile<br />
1/3<br />
V<br />
1/3<br />
1/3<br />
Solve For<br />
Have<br />
Distance<br />
X(m)<br />
Velocity<br />
V (m/sec)<br />
Velocity<br />
X (m)<br />
T (sec)<br />
Amplifier/Driver Sizing Formulas<br />
Voltage due to Back EMF V BEMF = Back EMF * Velocity<br />
Voltage due to R * I V ri = 1.225 * Resistance * Peak Current<br />
Voltage due to Inductance V L =<br />
Min. Bus Voltage needed V bus = 1.15 [ ( V bemf + V ri ) 2 + V L 2 ]<br />
Peak Current (rms value) I prms = Peak Current * 1.2<br />
Continuous Current (rms value) I Crms = Continuous Current * 1.2<br />
These formulas add a 20% safety margin for current and a 15% safety margin for voltage.<br />
N i p p o n P u l s e<br />
engineering notes<br />
Trapezoidal Profile<br />
Accelerate to constant speed, travel at that constant speed,<br />
and then decelerate back to original speed or zero. This<br />
is common in applications such as scanning inspection.<br />
There are two types, the 1/3 Trapezoidal Profile and the<br />
Variable Trapezoidal Profile.<br />
T/3 T/3 T/3<br />
T<br />
V (m/sec)<br />
T (sec)<br />
Distance = X<br />
A (m/sec 2 )<br />
T (sec)<br />
Time<br />
A (m/sec 2 )<br />
V (m/sec)<br />
X= (2/3) * V * T X= (1/4.5 * A * T 2 X= 2 * (V 2 /A)<br />
V= 1.5 * (X/T) V = (A*T)/3 V= √ (A*X)/2<br />
Acceleration<br />
A (m/sec 2 ) A= 4.5 * (X/T2 ) A= 3 * (V/T) A= 2 * (V 2 /X)<br />
Velocity<br />
Variable<br />
Trapezoidal Profile<br />
V<br />
(Formulas listed<br />
below are for<br />
calculating<br />
acceleration and<br />
deceleration)<br />
Solve For<br />
Have<br />
Distance<br />
X (m)<br />
Velocity<br />
V (m/sec)<br />
Acceleration<br />
A (m/sec 2 )<br />
X (m)<br />
T (sec)<br />
X a<br />
Total Distance = X<br />
T a T c T d<br />
T<br />
V (m/sec)<br />
T (sec)<br />
X c<br />
A (m/sec 2 )<br />
T (sec)<br />
Time<br />
A (m/sec 2 )<br />
V (m/sec)<br />
X= (V * T)/2 X= (A * T 2 )/2 X= V 2 /(2 * A)<br />
V= (2 * X)/T V = A * T V= √ (2*A)/X<br />
A= (2 * X)/T 2 A= V/T A= V 2 /(2 * X)<br />
7.695 * Velocity * Inductance * Peak Current<br />
Magnetic Pitch<br />
X d