bone Medullary cavity Diaphysis Distal epiphysis
bone Medullary cavity Diaphysis Distal epiphysis
bone Medullary cavity Diaphysis Distal epiphysis
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
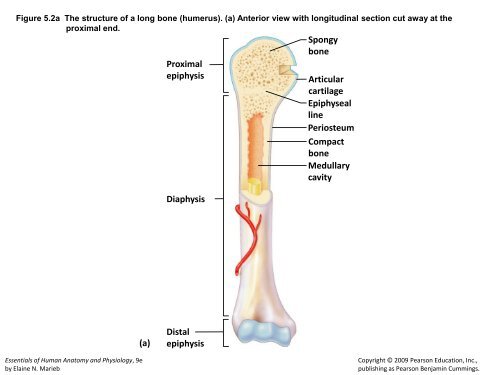
Figure 5.2a The structure of a long <strong>bone</strong> (humerus). (a) Anterior view with longitudinal section cut away at the<br />
proximal end.<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
(a)<br />
Spongy<br />
<strong>bone</strong><br />
Proximal<br />
<strong>epiphysis</strong> Articular<br />
cartilage<br />
Epiphyseal<br />
line<br />
Periosteum<br />
Compact<br />
<strong>bone</strong><br />
<strong>Medullary</strong><br />
<strong>cavity</strong><br />
<strong>Diaphysis</strong><br />
<strong>Distal</strong><br />
<strong>epiphysis</strong><br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.3a Microscopic structure of compact <strong>bone</strong>. (a).<br />
Perforating<br />
fibers<br />
Compact<br />
<strong>bone</strong><br />
Periosteal<br />
blood vessel<br />
Periosteum<br />
(a)<br />
Osteon<br />
(Haversian system)<br />
Lamellae<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Central (Haversian) canal<br />
Perforating (Volkmann’s) canal<br />
Blood vessel<br />
Blood vessel continues<br />
into medullary <strong>cavity</strong><br />
containing marrow<br />
Spongy <strong>bone</strong><br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.3b Microscopic structure of compact <strong>bone</strong>. (b).<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Lamella<br />
Osteocyte<br />
(b)<br />
Lacuna<br />
Canaliculus<br />
Central<br />
(Haversian) canal<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.6a The human skeleton. (a) Anterior view.<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Vertebral<br />
column<br />
Skull<br />
Thoracic cage<br />
(ribs and<br />
sternum)<br />
(a) Anterior view<br />
Sacrum<br />
Cranium<br />
Facial <strong>bone</strong>s<br />
Clavicle<br />
Scapula<br />
Sternum<br />
Rib<br />
Humerus<br />
Vertebra<br />
Radius<br />
Ulna<br />
Carpals<br />
Phalanges<br />
Metacarpals<br />
Femur<br />
Patella<br />
Tibia<br />
Tarsals<br />
Metatarsals<br />
Phalanges<br />
Fibula<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.6b The human skeleton. (b) Posterior view.<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Cranium<br />
Clavicle<br />
Scapula<br />
Rib<br />
Humerus<br />
Vertebra<br />
Radius<br />
Ulna<br />
Carpals<br />
Phalanges<br />
Metacarpals<br />
Femur<br />
Tibia<br />
Fibula<br />
(b) Posterior view<br />
Bones<br />
of<br />
pelvic<br />
girdle<br />
Bones of<br />
pectoral<br />
girdle<br />
Upper<br />
limb<br />
Lower<br />
limb<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.7 Human skull, lateral view.<br />
Coronal suture Frontal <strong>bone</strong><br />
Parietal <strong>bone</strong><br />
Temporal <strong>bone</strong><br />
Lambdoid<br />
suture<br />
Squamous suture<br />
Occipital <strong>bone</strong><br />
Zygomatic process<br />
External acoustic meatus<br />
Mastoid process<br />
Styloid process<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Mandibular ramus<br />
Sphenoid <strong>bone</strong><br />
Ethmoid <strong>bone</strong><br />
Lacrimal <strong>bone</strong><br />
Nasal <strong>bone</strong><br />
Zygomatic <strong>bone</strong><br />
Maxilla<br />
Alveolar<br />
margins<br />
Mandible (body)<br />
Mental foramen<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.9 Human skull, inferior view (mandible removed).<br />
Hard<br />
palate<br />
Zygomatic <strong>bone</strong><br />
Maxilla<br />
(palatine process)<br />
Temporal <strong>bone</strong><br />
(zygomatic process)<br />
Vomer<br />
Mandibular fossa<br />
Styloid process<br />
Palatine <strong>bone</strong><br />
Mastoid process<br />
Temporal <strong>bone</strong><br />
Parietal <strong>bone</strong><br />
Occipital <strong>bone</strong><br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Maxilla<br />
Sphenoid <strong>bone</strong><br />
(greater wing)<br />
Foramen ovale<br />
Carotid canal<br />
Jugular foramen<br />
Occipital condyle<br />
Foramen magnum<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.11 Human skull, anterior view.<br />
Coronal suture<br />
Parietal <strong>bone</strong><br />
Nasal <strong>bone</strong><br />
Sphenoid <strong>bone</strong><br />
Ethmoid <strong>bone</strong><br />
Lacrimal <strong>bone</strong><br />
Zygomatic <strong>bone</strong><br />
Maxilla<br />
Mandible<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Frontal <strong>bone</strong><br />
Superior orbital fissure<br />
Optic canal<br />
Temporal <strong>bone</strong><br />
Middle nasal concha<br />
of ethmoid <strong>bone</strong><br />
Inferior nasal concha<br />
Vomer<br />
Alveolar margins<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.13a The fetal skull. (a) Superior view.<br />
Frontal <strong>bone</strong><br />
Parietal<br />
<strong>bone</strong><br />
Posterior fontanel<br />
(a)<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Anterior<br />
fontanel<br />
Occipital<br />
<strong>bone</strong><br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.13b The fetal skull. (b) Lateral view.<br />
Parietal <strong>bone</strong><br />
Posterior<br />
fontanel<br />
Occipital<br />
<strong>bone</strong><br />
Mastoid<br />
fontanel<br />
(b)<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Temporal <strong>bone</strong><br />
Anterior fontanel<br />
Sphenoidal<br />
fontanel<br />
Frontal<br />
<strong>bone</strong><br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.14 The vertebral column.<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Anterior Posterior<br />
1st cervical<br />
vertebra (atlas)<br />
2nd cervical<br />
vertebra (axis)<br />
1st thoracic<br />
vertebra<br />
Transverse<br />
process<br />
Spinous<br />
process<br />
Intervertebral<br />
disc<br />
Intervertebral<br />
foramen<br />
1st Lumbar<br />
vertebra<br />
Cervical<br />
curvature<br />
(concave)<br />
7 vertebrae,<br />
C 1 – C 7<br />
Thoracic<br />
curvature<br />
(convex)<br />
12 vertebrae,<br />
T 1 – T 12<br />
Lumbar<br />
curvature<br />
(concave)<br />
5 vertebrae,<br />
L 1 – L 5<br />
Sacral<br />
curvature<br />
(convex)<br />
5 fused<br />
vertebrae<br />
Coccyx<br />
4 fused<br />
vertebrae<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.20a The bony thorax (thoracic cage). (a) Anterior view.<br />
Clavicular notch<br />
True<br />
ribs<br />
(1–7)<br />
False<br />
ribs<br />
(8–12)<br />
(a)<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
L 1<br />
Floating Vertebra<br />
ribs (11, 12)<br />
T1 vertebra<br />
Jugular notch<br />
Manubrium<br />
Sternal angle<br />
Body<br />
Xiphisternal<br />
joint<br />
Xiphoid<br />
process<br />
Intercostal<br />
spaces<br />
Costal cartilage<br />
Sternum<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.21a–b Bones of the shoulder girdle. (a) Articulated right shoulder (pectoral) girdle showing the<br />
relationship to <strong>bone</strong>s of the thorax and sternum, and (b) right clavicle, superior and inferior views.<br />
Scapula<br />
Acromioclavicular<br />
joint<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Clavicle<br />
(a) Articulated right shoulder (pectoral) girdle<br />
showing the relationship to <strong>bone</strong>s of the<br />
thorax and sternum<br />
Posterior<br />
Acromial (lateral)<br />
end<br />
Superior view<br />
Acromial end<br />
Inferior view<br />
Anterior<br />
Sternal (medial)<br />
end<br />
Posterior<br />
Anterior<br />
Sternal end<br />
(b) Right clavicle, superior and inferior views<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.21c Bones of the shoulder girdle. (c) Right scapula, posterior aspect.<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Suprascapular notch<br />
Superior<br />
angle<br />
Spine<br />
Medial<br />
border<br />
(c) Right scapula, posterior aspect<br />
Coracoid process<br />
Lateral border<br />
Acromion<br />
Glenoid <strong>cavity</strong><br />
at lateral angle<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.21d Bones of the shoulder girdle. (d) Right scapula, anterior aspect.<br />
Coracoid<br />
process<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Acromion<br />
Glenoid<br />
<strong>cavity</strong><br />
Suprascapular notch<br />
Superior border<br />
Lateral<br />
(axillary)<br />
border<br />
(d) Right scapula, anterior aspect<br />
Superior<br />
angle<br />
Medial<br />
(vertebral)<br />
border<br />
Inferior angle<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.22a Bones of the right arm and forearm. (a) Humerus, anterior view.<br />
(a)<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Greater<br />
tubercle<br />
Lesser<br />
tubercle<br />
Deltoid<br />
tuberosity<br />
Radial<br />
fossa<br />
Coronoid<br />
fossa<br />
Capitulum<br />
Head of<br />
humerus<br />
Anatomical neck<br />
Intertubercular<br />
sulcus<br />
Medial<br />
epicondyle<br />
Trochlea<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.22b Bones of the right arm and forearm. (b) Humerus, posterior view.<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Head of<br />
humerus<br />
Anatomical<br />
neck<br />
Radial<br />
groove<br />
Deltoid<br />
tuberosity<br />
Medial<br />
epicondyle<br />
(b) Trochlea<br />
Olecranon fossa<br />
Lateral epicondyle<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.22c Bones of the right arm and forearm. (c) Anterior view of the <strong>bone</strong>s of the forearm: the radius and the ulna.<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Head<br />
Neck<br />
Radial<br />
tuberosity<br />
Radius<br />
Styloid process<br />
of radius<br />
(c)<br />
Trochlear notch<br />
Olecranon process<br />
Coronoid process<br />
Proximal radioulnar<br />
joint<br />
Ulna<br />
Interosseous<br />
membrane<br />
Styloid process of ulna<br />
<strong>Distal</strong> radioulnar joint<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.23 Bones of the right hand, anterior view.<br />
Phalanges<br />
(fingers)<br />
Metacarpals<br />
(palm)<br />
Carpals<br />
(wrist)<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
<strong>Distal</strong><br />
Pisiform<br />
Triquetrum<br />
Lunate<br />
Ulna<br />
Middle<br />
Proximal<br />
Hamate<br />
5<br />
4 3 2<br />
Radius<br />
1<br />
Trapezium<br />
Trapezoid<br />
Scaphoid<br />
Capitate<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.24a The bony pelvis. (a) Articulated male pelvis.<br />
Coxal<br />
<strong>bone</strong><br />
(or hip<br />
<strong>bone</strong>)<br />
llium<br />
Pubic<br />
<strong>bone</strong><br />
Ischium<br />
(a)<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Sacrum<br />
Coccyx<br />
Pubic arch<br />
Pelvic brim<br />
Ischial spine<br />
Acetabulum<br />
Iliac crest<br />
Sacroiliac<br />
joint<br />
Pubic symphysis<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.24b The bony pelvis. (b) Right coxal <strong>bone</strong>, showing the point of fusion of the ilium, ischium, and pubic <strong>bone</strong>s.<br />
Posterior<br />
superior<br />
iIiac spine<br />
Posterior<br />
inferior<br />
iliac spine<br />
Greater sciatic<br />
notch<br />
Ischial body<br />
Ischial spine<br />
Ischial<br />
tuberosity<br />
Ischium<br />
Ischial ramus<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
(b)<br />
Ala<br />
Ilium<br />
Iliac crest<br />
Anterior superior<br />
iliac spine<br />
Anterior inferior<br />
iliac spine<br />
Acetabulum<br />
Body of pubis<br />
Pubis<br />
Inferior ramus<br />
of pubis<br />
Obturator<br />
foramen<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.24c The bony pelvis. (c) Comparison of the male (left) and female (right) pelves.<br />
(c)<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
False pelvis False pelvis<br />
Inlet of<br />
true<br />
pelvis<br />
Pelvic brim<br />
Pubic arch<br />
(less than 90º)<br />
Pelvic<br />
brim<br />
Inlet of<br />
true<br />
pelvis<br />
Pubic arch<br />
(more than 90º)<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.25a Bones of the right thigh and leg. (a) Femur (thigh <strong>bone</strong>), anterior view.<br />
Neck<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Intertrochanteric<br />
line<br />
Lateral condyle<br />
(a)<br />
Head<br />
Lesser trochanter<br />
Patellar surface<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.25b Bones of the right thigh and leg. (b) Femur, posterior view.<br />
Head<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Lesser trochanter<br />
Gluteal tuberosity<br />
Intercondylar fossa<br />
Medial condyle<br />
(b)<br />
Greater trochanter<br />
Intertrochanteric<br />
crest<br />
Lateral condyle<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.25c Bones of the right thigh and leg. (c) Tibia and Fibula of the leg, anterior view.<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Intercondylar eminence<br />
Lateral condyle<br />
Head<br />
Proximal tibiofibular<br />
joint<br />
<strong>Distal</strong> tibiofibular<br />
joint<br />
Lateral malleolus<br />
(c)<br />
Fibula<br />
Medial condyle<br />
Tibial tuberosity<br />
Interosseous<br />
membrane<br />
Anterior border<br />
Tibia<br />
Medial malleolus<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Figure 5.26 Bones of the right foot, superior view.<br />
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9e<br />
by Elaine N. Marieb<br />
Tarsals:<br />
Medial<br />
cuneiform<br />
Intermediate<br />
cuneiform<br />
Navicular<br />
Talus<br />
Phalanges:<br />
<strong>Distal</strong><br />
Middle<br />
Proximal<br />
Metatarsals<br />
Tarsals:<br />
Lateral<br />
cuneiform<br />
Cuboid<br />
Calcaneus<br />
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.,<br />
publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.