BG PW Answers _3.pdf
BG PW Answers _3.pdf
BG PW Answers _3.pdf
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
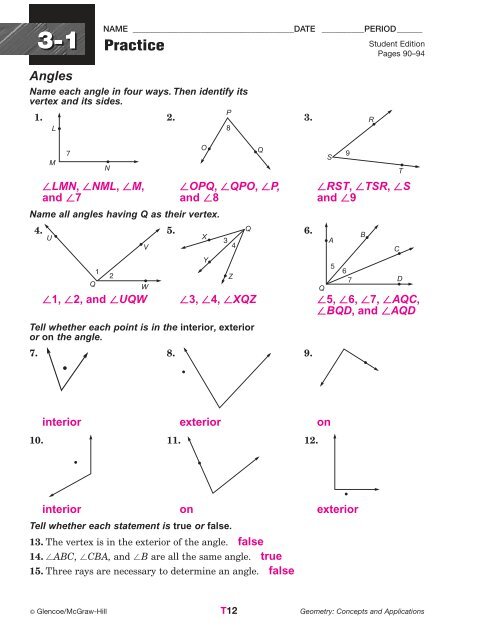
3-1 NAME ______________________________________DATE __________PERIOD______<br />
Practice<br />
Angles<br />
Name each angle in four ways. Then identify its<br />
vertex and its sides.<br />
1. 2. 3.<br />
LMN, NML, M, OPQ, QPO, P, RST, TSR, S<br />
and 7 and 8 and 9<br />
Name all angles having Q as their vertex.<br />
4. 5. 6.<br />
1, 2, and UQW 3, 4, XQZ 5, 6, 7, AQC,<br />
BQD, and AQD<br />
Tell whether each point is in the interior, exterior<br />
or on the angle.<br />
7. 8. 9.<br />
interior exterior on<br />
10. 11. 12.<br />
interior on exterior<br />
Tell whether each statement is true or false.<br />
13. The vertex is in the exterior of the angle. false<br />
14. ABC, CBA, and B are all the same angle. true<br />
15. Three rays are necessary to determine an angle. false<br />
Student Edition<br />
Pages 90–94<br />
© Glencoe/McGraw-Hill T12 Geometry: Concepts and Applications
3-2 Angle Measure<br />
Use a protractor to find the measure of each angle.<br />
Then classify each angle as acute, obtuse, or right.<br />
1. JHI 40; acute<br />
2. KHI 90; right<br />
3. MHI 130; obtuse<br />
4. LHI 110; obtuse<br />
5. LHM 20; acute<br />
6. LHK 20; acute<br />
7. MHJ 90; right<br />
8. MHK 40; acute<br />
9. KHJ 50; acute<br />
10. LHJ 70; acute<br />
NAME ______________________________________DATE __________PERIOD______<br />
Practice<br />
Use a protractor to draw an angle having each measurement.<br />
Then classify each angle as acute, obtuse, or right. See student’s work.<br />
11. 32° acute 12, 178° obtuse<br />
13. 105° obtuse 14. 92° obtuse<br />
15. 80° acute 16. 15° acute<br />
17. 29° acute 18. 150° obtuse<br />
19. 163° obtuse 20. 120° obtuse<br />
Student Edition<br />
Pages 96–101<br />
© Glencoe/McGraw-Hill T13 Geometry: Concepts and Applications
3-3 NAME ______________________________________DATE __________PERIOD______<br />
Practice<br />
The Angle Addition Postulate<br />
Refer to the figure at the right.<br />
1. If mBFC 35 and mAFC 78<br />
find m1. 43<br />
2. If mBFC 20 and mCFD 37<br />
find mBFD. 57<br />
3. If mBFD 60 and FC bisects BFD, find CFD.<br />
30<br />
4. If mAFB 70 and mBFC 15, find mAFC.<br />
85<br />
5. If mDFE 18 and mCFE 45, find CFD.<br />
27<br />
Refer to the figure at the right.<br />
6. If m3 45 and mJLI 20,<br />
find mILK. 65<br />
7. If mGLJ 90, mGLH 30, and<br />
mHLI 30, find mILJ. 30<br />
8. If mHLJ 70 and mGLJ 90, find mGLH. 20<br />
9. If m3 40 and mJLH 60, find mKLH. 100<br />
10. If mGLI 62 and mGLH 40, find mHLI. 22<br />
11. If a right angle is bisected, what type of angles<br />
are formed? acute<br />
12. What type of angles are formed if a 40° angle<br />
is bisected? acute<br />
13. If m1 30, m2 3x, mABC 145, and<br />
m3 5x 5, find x. 15<br />
Student Edition<br />
Pages 104–109<br />
© Glencoe/McGraw-Hill T14 Geometry: Concepts and Applications
3-4 Adjacent Angles and Linear Pairs of Angles<br />
Use the terms adjacent angles, linear pair, or neither<br />
to describe angles 1 and 2 in as many ways as possible.<br />
1. 2. 3.<br />
neither<br />
NAME ______________________________________DATE __________PERIOD______<br />
Practice<br />
adjacent angles; neither<br />
linear pair<br />
4. 5. 6.<br />
neither adjacent<br />
In the figure at the right GB and GF are opposite<br />
rays and GA and GD are opposite rays.<br />
7. Which angle forms a linear pair with AGC?<br />
CGD<br />
8. Do FGE and EGC form a linear pair? Justify your answer.<br />
No; they do not contain sides that are opposite rays.<br />
9. Name two angles that are adjacent angles.<br />
Sample answer: DGE and EGF<br />
10. Name three angles that are adjacent to EGD.<br />
Sample answer: DGC, DGB, EGA<br />
11. Which angle forms a linear pair with <strong>BG</strong>C?<br />
CGF<br />
12. Name two adjacent angles that form a linear pair.<br />
Sample answer: AGB and AGF<br />
Student Edition<br />
Pages 110–114<br />
adjacent<br />
angles;<br />
linear pair<br />
© Glencoe/McGraw-Hill T15 Geometry: Concepts and Applications
3-5 NAME ______________________________________DATE __________PERIOD______<br />
Practice<br />
Complementary and Supplementary Angles<br />
Refer to the figures at the right.<br />
1. Name an angle supplementary<br />
to CBD. DBE<br />
2. Name a pair of adjacent<br />
supplementary angles.<br />
Sample answer: CBA, ABE<br />
3. Name an angle complementary<br />
to CBF. F<strong>BG</strong><br />
4. Name two angles that are complementary.<br />
Sample answer: XQZ, ZQS<br />
5. Find the measure of an angle that is<br />
supplementary to XQZ. 140<br />
6. Find the measure of the complement<br />
of VQY. 50<br />
7. Name two angles that are supplementary.<br />
Sample answer ZQX, XQV<br />
8. Name an angle complementary to MON. MOL<br />
9. Name an angle supplementary to POQ. POL<br />
10. Find the measure of NOP. 70<br />
Exercises 1–3<br />
Exercises 4–7<br />
Student Edition<br />
Pages 116–121<br />
Exercises 8–10<br />
© Glencoe/McGraw-Hill T16 Geometry: Concepts and Applications
3-6 Congruent Angles<br />
Find the value of x in each figure.<br />
1. 2. 3.<br />
55 110 47<br />
4. 5. 6.<br />
52<br />
NAME ______________________________________DATE __________PERIOD______<br />
Practice<br />
43 25<br />
7. What is the measure of an angle that is<br />
supplementary to HIJ if HIJ KLM? 126<br />
8. If 2 is complementary to 3, 1 is<br />
complementary to 2, and m1 35,<br />
what are m2 and m3? 55, 35<br />
9. What is the value of x if PQR and SQT<br />
are vertical angles and mPQR 47 and<br />
mSQT 3x 2? 15<br />
10. Find the measure of an angle that is supplementary<br />
to B if the measure of B is 58. 122<br />
Student Edition<br />
Pages 122–127<br />
© Glencoe/McGraw-Hill T17 Geometry: Concepts and Applications
3-7 Perpendicular Lines<br />
AG ⊥ CE,AC<br />
⊥ BF and point B is the midpoint of AC.<br />
Determine whether the following is true or false.<br />
1. 1 CBD true<br />
2. 1 is a right angle. true<br />
3. 2 and 3 are complementary<br />
angles. false<br />
4. mGDF mFDE 90 true<br />
5. 1 5 true<br />
6. AC is the only line perpendicular<br />
to BF at B. true<br />
7. 3 is an acute angle. false<br />
8. 1 2 false<br />
9. 2 6 true<br />
Practice<br />
10. AG is perpendicular to DE . true<br />
11. Name four right angles. Sample answer: 1, 5, CBD, EDG<br />
12. Name a pair of supplementary angles. Sample answer: 2 and 3<br />
13. If m3 120, find m2. 60<br />
14. Which angle is complementary to FDE? GDF<br />
15. If m6 45, find m2. 45<br />
NAME ______________________________________DATE __________PERIOD______<br />
Student Edition<br />
Pages 128–133<br />
© Glencoe/McGraw-Hill T18 Geometry: Concepts and Applications