O-Level-Chemistry-Notes
O-Level-Chemistry-Notes
O-Level-Chemistry-Notes
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Copyrights AF/PS/2009/2010 59<br />
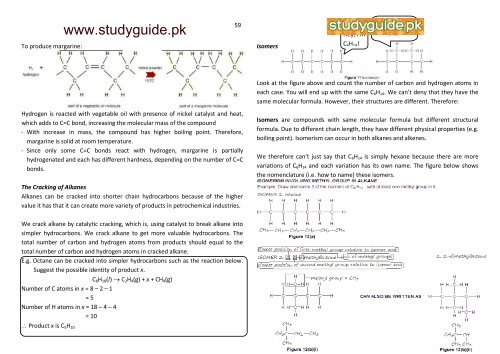
To produce margarine:<br />
Hydrogen is reacted with vegetable oil with presence of nickel catalyst and heat,<br />
which adds to C=C bond, increasing the molecular mass of the compound<br />
- With increase in mass, the compound has higher boiling point. Therefore,<br />
margarine is solid at room temperature.<br />
- Since only some C=C bonds react with hydrogen, margarine is partially<br />
hydrogenated and each has different hardness, depending on the number of C=C<br />
bonds.<br />
The Cracking of Alkanes<br />
Alkanes can be cracked into shorter chain hydrocarbons because of the higher<br />
value it has that it can create more variety of products in petrochemical industries.<br />
We crack alkane by catalytic cracking, which is, using catalyst to break alkane into<br />
simpler hydrocarbons. We crack alkane to get more valuable hydrocarbons. The<br />
total number of carbon and hydrogen atoms from products should equal to the<br />
total number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in cracked alkane.<br />
E.g. Octane can be cracked into simpler hydrocarbons such as the reaction below.<br />
Suggest the possible identity of product x.<br />
C8H18(l) C2H4(g) + x + CH4(g)<br />
Number of C atoms in x = 8 – 2 – 1<br />
= 5<br />
Number of H atoms in x = 18 – 4 – 4<br />
= 10<br />
Product x is C5H10<br />
www.studyguide.pk<br />
Isomers<br />
Hey, I’m<br />
C6H14!<br />
No, you poser!<br />
I’M C6H14!<br />
Look at the figure above and count the number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in<br />
each case. You will end up with the same C6H14. We can’t deny that they have the<br />
same molecular formula. However, their structures are different. Therefore:<br />
Isomers are compounds with same molecular formula but different structural<br />
formula. Due to different chain length, they have different physical properties (e.g.<br />
boiling point). Isomerism can occur in both alkanes and alkenes.<br />
We therefore can’t just say that C6H14 is simply hexane because there are more<br />
variations of C6H14 and each variation has its own name. The figure below shows<br />
the nomenclature (i.e. how to name) these isomers.