2 B. Body Fluid Compartments and Investigational ... - Data-input.de
2 B. Body Fluid Compartments and Investigational ... - Data-input.de
2 B. Body Fluid Compartments and Investigational ... - Data-input.de
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
a. Anthropometry<br />
The thickness of skin folds of<br />
<strong>de</strong>fined parts of the body is measured<br />
with the help of a callipers<br />
(mostly on the biceps <strong>and</strong> triceps, as<br />
well as sub-scapular <strong>and</strong> supra-iliac). Conclusions<br />
can be ma<strong>de</strong> about body fat from the thickness of<br />
the skin folds.<br />
b. Infra-red interactance<br />
This method uses harmless infra-red light in or<strong>de</strong>r to<br />
measure the percentage of total body fat on the<br />
biceps of the dominant arm with the help of a near<br />
infra-red probe.<br />
Fig. B.3 Infra-red interactance measurement (Futrex)<br />
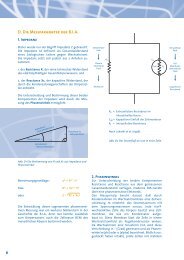
c. Non-phase sensitive BIA measurement<br />
This method measures the total resistance of the<br />
body (impedance Z). By calculating body water, the<br />
compartments for body fat <strong>and</strong> lean body mass can<br />
be obtained. This does not give a <strong>de</strong>termination of<br />
the phase angle <strong>and</strong>, as such, a subdivision of impedance<br />
into water <strong>and</strong> cellular resistance, so that no<br />
judgement can be ma<strong>de</strong> about the body cell mass<br />
BCM or the extra-cellular mass ECM with the nonphase<br />
sensitive BIA.<br />
The compartments measured using the last three<br />
methods are known as body fat (BF) <strong>and</strong> as lean body<br />
mass (LBM), in comparison to the fat-free mass (FFM)<br />
which is obtained in the case of <strong>de</strong>nsitometry. The<br />
difference is that <strong>de</strong>nsitometry measures pure<br />
triglyceri<strong>de</strong>s, whereas body fat also contains 15-18%<br />
water <strong>and</strong> approx. 2% protein.<br />
3. Three-compartment measurement<br />
The 3-compartment mo<strong>de</strong>l arises by subdividing the<br />
lean body mass into the body cell mass BCM <strong>and</strong> the<br />
extra-cellular mass ECM.<br />
The BCM is the sum of all aerobic oxidizing, metabolically<br />
active cells, in other words the muscles,<br />
internal organs <strong>and</strong> the CNS. The interstitial <strong>and</strong><br />
trans-cellular spaces are part of the extra-cellular<br />
mass ECM, as well as the skeleton <strong>and</strong> connective tissue.<br />
Large displacements between the BCM <strong>and</strong> ECM<br />
can arise without changes to the bodyweight <strong>and</strong><br />
lean body mass. Measurements in the 3-compartment<br />
mo<strong>de</strong>l are possible with the following simple<br />
methods:<br />
a. Phase sensitive BIA measurement<br />
The phase sensitive technique of measuring allows<br />
the impedance Z to be differentiated into its two<br />
components resistance R (water resistance) <strong>and</strong><br />
reactance Xc (cell resistance), so that a differentiation<br />
can be ma<strong>de</strong> between body cell mass <strong>and</strong> extracellular<br />
mass.<br />
Fig. B.4 Phase sensitive mono-frequency <strong>de</strong>vice<br />
COMPARTMENTS<br />
3