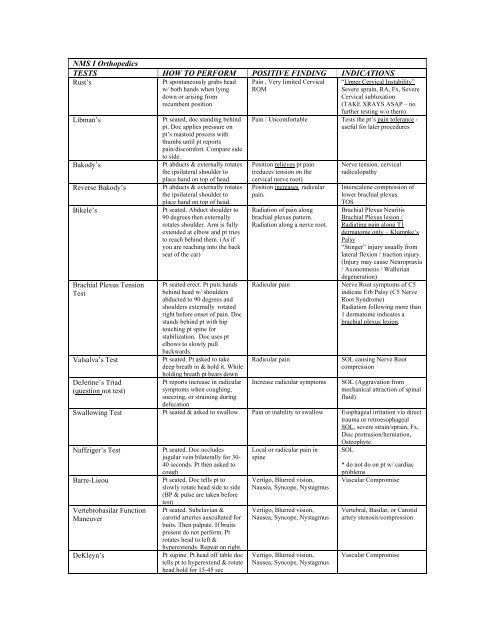
NMS I Orthopedics TESTS HOW TO PERFORM POSITIVE FINDING ...
NMS I Orthopedics TESTS HOW TO PERFORM POSITIVE FINDING ...
NMS I Orthopedics TESTS HOW TO PERFORM POSITIVE FINDING ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>NMS</strong> I <strong>Orthopedics</strong><br />
<strong>TESTS</strong><br />
Rust’s<br />
<strong>HOW</strong> <strong>TO</strong> <strong>PERFORM</strong> <strong>POSITIVE</strong> <strong>FINDING</strong> INDICATIONS<br />
Libman’s<br />
Pt spontaneously grabs head<br />
w/ both hands when lying<br />
down or arising from<br />
recumbent position<br />
Pt seated, doc standing behind<br />
pt. Doc applies pressure on<br />
pt’s mastoid process with<br />
thumbs until pt reports<br />
pain/discomfort. Compare side<br />
to side.<br />
Bakody’s Pt abducts & externally rotates<br />
the ipsilateral shoulder to<br />
place hand on top of head.<br />
Reverse Bakody’s Pt abducts & externally rotates<br />
the ipsilateral shoulder to<br />
place hand on top of head.<br />
Bikele’s Pt seated. Abduct shoulder to<br />
90 degrees then externally<br />
rotates shoulder. Arm is fully<br />
extended at elbow and pt tries<br />
to reach behind them. (As if<br />
you are reaching into the back<br />
seat of the car)<br />
Brachial Plexus Tension<br />
Test<br />
Valsalva’s Test<br />
DeJerine’s Triad<br />
(question not test)<br />
Pt seated erect. Pt puts hands<br />
behind head w/ shoulders<br />
abducted to 90 degrees and<br />
shoulders externally rotated<br />
right before onset of pain. Doc<br />
stands behind pt with hip<br />
touching pt spine for<br />
stabilization. Doc uses pt<br />
elbows to slowly pull<br />
backwards.<br />
Pt seated. Pt asked to take<br />
deep breath in & hold it. While<br />
holding breath pt bears down<br />
Pt reports increase in radicular<br />
symptoms when coughing,<br />
sneezing, or straining during<br />
defecation<br />
Pain , Very limited Cervical<br />
ROM<br />
“Upper Cervical Instability”<br />
Severe sprain, RA, Fx, Severe<br />
Cervical subluxation<br />
(TAKE XRAYS ASAP – no<br />
further testing w/o them)<br />
Pain / Uncomfortable Tests the pt’s pain tolerance -<br />
useful for later procedures<br />
Position relieves pt pain<br />
(reduces tension on the<br />
cervical nerve root)<br />
Position increases radicular<br />
pain.<br />
Radiation of pain along<br />
brachial plexus pattern.<br />
Radiation along a nerve root.<br />
Nerve tension, cervical<br />
radiculopathy<br />
Interscalene compression of<br />
lower brachial plexus.<br />
<strong>TO</strong>S<br />
Brachial Plexus Neuritis<br />
Brachial Plexus lesion /<br />
Radiating pain along T1<br />
dermatome only – Klumpke’s<br />
Palsy<br />
“Stinger” injury usually from<br />
lateral flexion / traction injury.<br />
(Injury may cause Neuropraxia<br />
/ Axonotmesis / Wallerian<br />
degeneration)<br />
Radicular pain Nerve Root symptoms of C5<br />
indicate Erb Palsy (C5 Nerve<br />
Root Syndrome)<br />
Radiation following more than<br />
1 dermatome indicates a<br />
brachial plexus lesion.<br />
Radicular pain SOL causing Nerve Root<br />
compression<br />
Increase radicular symptoms SOL (Aggravation from<br />
mechanical attraction of spinal<br />
fluid)<br />
Swallowing Test Pt seated & asked to swallow. Pain or inability to swallow Esophageal irritation via direct<br />
trauma or retroesophageal<br />
SOL, severe strain/sprain, Fx,<br />
Disc protrusion/herniation,<br />
Osteophyte.<br />
Naffziger’s Test<br />
Pt seated. Doc occludes<br />
jugular vein bilaterally for 30-<br />
40 seconds. Pt then asked to<br />
cough<br />
Barre-Lieou Pt seated. Doc tells pt to<br />
slowly rotate head side to side<br />
(BP & pulse are taken before<br />
Vertebrobasilar Function<br />
Maneuver<br />
DeKleyn’s<br />
test)<br />
Pt seated. Subclavian &<br />
carotid arteries auscultated for<br />
buits. Then palpate. If bruits<br />
present do not perform. Pt<br />
rotates head to left &<br />
hyperextends. Repeat on right.<br />
Pt supine. Pt head off table doc<br />
tells pt to hyperextend & rotate<br />
head hold for 15-45 sec<br />
Local or radicular pain in<br />
spine<br />
Vertigo, Blurred vision,<br />
Nausea, Syncope, Nystagmus<br />
Vertigo, Blurred vision,<br />
Nausea, Syncope, Nystagmus<br />
Vertigo, Blurred vision,<br />
Nausea, Syncope, Nystagmus<br />
SOL<br />
* do not do on pt w/ cardiac<br />
problems<br />
Vascular Compromise<br />
Vertebral, Basilar, or Carotid<br />
artery stenosis/compression<br />
Vascular Compromise
Distraction Test<br />
Foraminal Compression<br />
Jackson’s Compression<br />
Test<br />
Maximum Cervical<br />
Compression<br />
Spurlings Test<br />
Pt seated. w/ hands on glabella<br />
and EOP slightly traction pt’s<br />
head upward.<br />
Active C ROM performed<br />
first.<br />
Pt seated doc places<br />
downward pressure on pt<br />
head/neck. Head is rotated to<br />
each side with similar<br />
compression.<br />
Pt seated. Head is laterally<br />
flexed toward shoulder. Doc<br />
exerts downward compression.<br />
(Bilaterally tested)<br />
Pt seated Pt actively rotates<br />
head & hyperextends neck to<br />
side of complaint. Repeats on<br />
opposite side<br />
Pt seated. Pt head is laterally<br />
flexed to side of complaint.<br />
Doc applies compression to<br />
head/neck. Neck then<br />
extended/rotated and<br />
compressed. Doc then applies<br />
a vertical blow to top of head<br />
Lhermitte’s Test Pt seated in neutral position.<br />
Head/neck passively flexed to<br />
pt chest<br />
O'Donahue’s<br />
Passive and active resisted<br />
ROM or any joint.<br />
Kernig’s Sign<br />
Pt supine doc flexes pt hip &<br />
knee 90 degrees doc then tries<br />
to extend leg<br />
Brudzinski’s Sign Supine pt flexes head/neck<br />
Shoulder Depressor Test<br />
toward xiphoid process/chest<br />
Pt seated. Doc depresses pt<br />
shoulder on affected side &<br />
laterally flexes neck away<br />
from shoulder.<br />
Soto Hall Test Pt supine. Doc supports pt<br />
head w/ one hand & knifeedge<br />
contact on sternum w/<br />
opposite hand. Pt actively<br />
flexes head/neck to chest . Doc<br />
follows w/ passive head/neck<br />
flexion to chest<br />
Allen’s Test Pt seated. Affected elbow is<br />
flexed & arm supinated. Doc<br />
occludes radial and ulnar<br />
arteries. Pt pumps hand<br />
open/close. Then opens hand<br />
and doc will release 1 artery so<br />
blood flow can resume.<br />
Repeated on other artery.<br />
Performed bilaterally.<br />
1. Local pain increases<br />
2. Peripheral pain decreases<br />
3. Local pain decreases<br />
1. Radicular pain<br />
2. Local Neck pain<br />
1. Muscle, ligament, or joint<br />
capsule damage<br />
2. IVF encroachment, cervical<br />
radiculopathy<br />
3. Facet impingement<br />
1. Foraminal (cervical Nerve<br />
Root) encroachment,<br />
radiculopathy<br />
2. Sprain/strain<br />
Radicular pain IVF encroachment<br />
(radiculopathy)<br />
Facet irritation (local pain)<br />
Radicular Pain IVF encroachment<br />
*Tight stretching pain on<br />
convex side – muscle strain<br />
Radicular Pain Foraminal / Nerve Root<br />
encroachment<br />
Sharp radiating pain down<br />
spine & upper/lower<br />
extremities.<br />
Facet involvement – local pain<br />
Bilateral arm/leg pain –<br />
Cervical<br />
myelopathy.radiculopathy<br />
Unilateral arm/leg pain<br />
following a dermatome –<br />
Nerve Root traction .<br />
Pt. may have MS, Stenosis,<br />
Tumor, Disc herniation<br />
Pain Pain w/ active – strain<br />
Pain w/ passive – sprain<br />
Pain in spine or involuntary<br />
flexion of the opposite<br />
knee/hip<br />
Involuntary hip and knee<br />
flexion<br />
Radicular pain<br />
produced/aggravated<br />
*test can be used on any joint<br />
in body*<br />
Pain with fever – meningitis<br />
Pain & fever – meningitis<br />
Dural sleeve adhesion of<br />
spinal Nerve Root, adjacent<br />
joint capsule, brachial plexus<br />
traction.<br />
* common hyperextension<br />
injury especially in young.<br />
Pain Local pain w/ active – muscle<br />
sprain.<br />
Local pain w/ passive –<br />
ligament strain.<br />
Fracture<br />
Facet Involvement<br />
Circulation should return in 5<br />
seconds or less.<br />
Vascular Compromise<br />
<strong>TO</strong>S
Adson’s Test<br />
Modified Adson’s Test<br />
Pt seated. Doc palpates the<br />
radial artery. Pt rotates head to<br />
affected side. Pt extends neck<br />
as far as possible. Pt holds<br />
breath for 10 sec.<br />
Same as above but rotate head<br />
toward unaffected side.<br />
Halstead’s Test Pt seated. Doc palpates radial<br />
pulse of affected arm. Doc<br />
applies downward traction on<br />
arm while pt hyperextends<br />
neck. (If negative do test with<br />
pt rotating head to opposite<br />
side<br />
Allen's Maneuver Test Pt seated. Doc flexes pt’s<br />
elbow to 90, palpates the<br />
radial pulse while shoulder is<br />
abducted and externally<br />
rotated. Pt. rotates head away<br />
Roos’ Test<br />
“Hostage test”<br />
Wright’s Test<br />
“Hyperabduction test”<br />
Costoclavicular Maneuver<br />
Test<br />
from side being tested.<br />
Pt seated. Abduct both arms to<br />
90, flex elbows to 90 and<br />
externally rotate. Pt<br />
opens/closes fist for 3 min or<br />
until symptoms occur.<br />
Pt seated. Doc palpates Radial<br />
pulse of affected arm. Doc<br />
passively abducts arm to 180<br />
degrees. Note angle of<br />
abduction where pulse<br />
disappears/decreases.<br />
Compare to opposite side<br />
Pt seated with arms on thighs<br />
and palms up. Doc palpates<br />
radial pulse. Pt told to draw<br />
shoulders down and back,<br />
lower chin to chest and take a<br />
deep breath and hold for 10<br />
sec.<br />
Apley's Scratch Test Pt seated. Place affected hand<br />
behind head to touch opposite<br />
superior angle of scapula.<br />
The place hand behind back<br />
and touch inferior angle of<br />
scapula Compare bilaterally.<br />
Apprehension Test Pt seated. Shoulder is abducted<br />
and externally rotated (Ant<br />
Shoulder).<br />
Pt supine. Shoulder flexed &<br />
internally rotated doc applies<br />
Codman’s Drop Arm Test<br />
posterior force (post shoulder)<br />
Pt seated. Doc passively<br />
abducts affected arm. Doc<br />
suddenly removes support at<br />
an angle about 90 degrees<br />
Dawbarn’s Test Pt seated Doc palpates<br />
affected shoulder deeply for<br />
localized tenderness at the<br />
subacromial bursa. Hold<br />
pressure as arm is passively<br />
Dugas Test<br />
abducted.<br />
Pt seated places affected sides<br />
hand on opposite shoulder &<br />
tries to touch chest w/ elbow<br />
Decrease of pulse amplitude<br />
Paresthesia<br />
Decrease of pulse amplitude<br />
Paresthesia<br />
Decrease of pulse amplitude<br />
Paresthesia<br />
Pulse disappears <strong>TO</strong>S<br />
Paresthesia/tingling, pain,<br />
weakness<br />
Loss of pulse / Tingling<br />
(look at amplitude of<br />
symptoms)<br />
Cessation or dampening of<br />
radial pulse, ischemic color<br />
change, paresthesia, radicular<br />
pain in upper extremity.<br />
Neurovascular compromise of<br />
Subclavian A due to Scalenus<br />
Anticus or Cervical Rib – <strong>TO</strong>S<br />
Scalene medius & Cervical<br />
rib <strong>TO</strong>S<br />
Scalene medius & Cervical<br />
Rib <strong>TO</strong>S<br />
<strong>TO</strong>S<br />
Hyperabduction syndrome<br />
(compression of axillary artery<br />
under the pec minor)<br />
Clavicle and first rib <strong>TO</strong>S (due<br />
to poor posture, cervical rib,<br />
bone tumor, or poorly united<br />
fx of clavicle)<br />
Reproduces shoulder pain Exacerbation of pain –<br />
degenerative tendonitis<br />
(especially supraspinatus)<br />
Pain / pay attention to look on<br />
pt face.<br />
*instable shoulder can<br />
dislocated w/ this test<br />
Pt cannot stop arm from<br />
dropping / Pain<br />
Anterior or Posterior Shoulder<br />
Dislocation trauma<br />
Rotator cuff tear / injury<br />
(specifically rupture of<br />
supraspinatus tendon)<br />
Pain disappears. Pain disappears – subacromial<br />
bursitis<br />
Inability to move elbow or<br />
pain<br />
Propensity for shoulder to<br />
dislocate anteriorly.
Impingement Test Pt seated. Pt’s arm is slightly<br />
abducted and moved fully<br />
through flexion by the doctor.<br />
(Jams greater tuberosity into<br />
ant inf acromial surface).<br />
Speed’s Test Pt seated. Forearm is flexed<br />
and supinated. Pt flexes<br />
shoulder against resistance.<br />
Supraspinatus Press Test Pt seated shoulders are<br />
abducted to 90 degrees. The<br />
shoulders are medially rotated<br />
& angled 30 degrees forward<br />
w/ thumbs pointing to floor.<br />
Doc applies resistance to<br />
abduction while observing for<br />
weakness/pain.<br />
Yergason’s Test<br />
Pt seated w/ elbow flexed. Pt<br />
resists doc pronating and<br />
extending the arm. Doc’s other<br />
hand is palpating the inter-<br />
tubercular groove<br />
Load & Shift Test While stabilizing the scapula,<br />
the doc performs the<br />
following:<br />
Push I-S, P-A for Ant Capsule<br />
Push I-S, A-P for Post Capsule<br />
O’Brien’s<br />
Pull S-I for Inf Capsule<br />
Pt arm flexed forward to 90<br />
degrees w/ elbow extended &<br />
arm adducted to 15 degrees.<br />
Part 1: arm in internal rotation<br />
(thumbs down). Part 2: arm in<br />
external rotation (palm up).<br />
Doc applies downward<br />
pressure while pt resists.<br />
Lift Off Test Pt places dorsum of hand on<br />
low back. Pt then lifts hand off<br />
back as far as possible.<br />
Compare side to side.<br />
Elbow Flexion Test Pt seated and actively flexes<br />
elbow for 5 minutes<br />
Tinel’s test at the Elbow<br />
Cozen’s Test<br />
Pt seated w/ elbow flexed to<br />
90 degrees doc taps groove<br />
between olecranon and lateral<br />
epicondyle. Repeat between<br />
the olecranon and medial<br />
epicondyle.<br />
Pt seated affected elbow<br />
flexed & pronated. Pt makes a<br />
fist. Pt actively extends hand /<br />
wrist. Doc applies pressure<br />
against dorsum of hand<br />
Golfer’s Elbow Test Pt seated w/ elbow flexed &<br />
hand/wrist supinated. Pt makes<br />
a fist and actively flexes the<br />
wrist. Doc applies pressure to<br />
extend wrist and pt resists.<br />
Lift Test Cozens & Golfers Test<br />
performed with weights<br />
instead of pressure<br />
Ligament Instability Test Pt’s elbow slightly flexed. Doc<br />
stabilizes elbow while<br />
applying an adduction (varus)<br />
force to the distal forearm to<br />
test the LCL. Then an<br />
abduction (valgus) force is<br />
applied to test the MCL.<br />
Pain in shoulder Overuse injury of<br />
supraspinatus tendon<br />
(sometimes biceps tendon)<br />
Pain / tenderness in the<br />
bicipital groove.<br />
Bicipital Tendonitis<br />
Pain / Weakness in shoulder Supraspinatus muscle/tendon<br />
tear<br />
Clicking or pain over the<br />
intertubercular groove<br />
Pain = Bicipital Tenosynovitis<br />
Clicking = tear of transverse<br />
humeral ligament<br />
Sulcus Line / Pain / Laxity Shoulder Capsule Instability /<br />
loosening<br />
Propensity to dislocate<br />
Pain on part 1 or part 2 Pain during part 1: anterior<br />
labrum tear, SLAP lesion<br />
Pain during part 2: biceps<br />
tendonitis<br />
Inability to life the hand off<br />
the back as far as the other<br />
side.<br />
Pain on Ant Shoulder<br />
Tingling or paresthesia in<br />
ulnar distribution of<br />
hand/forearm.<br />
Hypersensitivity.<br />
Tingling radiating toward<br />
forearm<br />
* Positive Speeds & O’Briens<br />
indicates Type II SLAP lesion<br />
Subscapularis Tendonitis<br />
Capsulitis<br />
Ulnar paresthesia – Cubital<br />
Tunnel Syndrome<br />
Lateral: Superficial Radial<br />
Nerve Palsy (degeneration)/<br />
neuroma/neuritis<br />
Medial: Ulnar N palsy /<br />
neuroma / neuritis<br />
Pain near Lateral Epicondyle Lateral Epicondylitis “Tennis<br />
Elbow”<br />
Radiohumeral bursitis<br />
Pain near Medial Epicondyle Medial Epicondylitis “Golfers<br />
Elbow”<br />
Pain near Medial / Lateral<br />
Epicondyle<br />
Laxity, decreased mobility,<br />
altered pain.<br />
Medial / Lateral Epicondylitis<br />
Adduction force: medial<br />
collateral ligament instability<br />
(sprain)<br />
Abduction force: lateral<br />
collateral ligament instability<br />
(sprain)
Mills Test<br />
Pt seated w/ forearm, fingers,<br />
and wrist passively flexed. The<br />
doc pronates and extends the<br />
forearm.<br />
Tinel’s Test at the Wrist Doc taps over the carpel tunnel Tingling into thumb, index<br />
and middle finger and lateral<br />
Phalen’s Test Doc flexes pt’s wrists and<br />
pushes them together for 1<br />
Froment’s Test<br />
Pinch Grip Test<br />
Bunnell-Littler Test<br />
minute.<br />
Pt. Grasps a piece of paper<br />
between thumb and index<br />
finger. Doc pulls paper away.<br />
Pt asked to pinch tips of index<br />
finger and thumb together.<br />
MCP joint held slightly<br />
extended while doc moves the<br />
PIP joint into flexion.<br />
Finkelstein’s Test Doc stabilizes the forearm and<br />
ulnar deviates the wrist.<br />
Mankopf’s Test<br />
THORACIC <strong>TESTS</strong><br />
Adam’s Position<br />
Amoss Sign<br />
Beevor’s Sign<br />
Take pt’s resting HR. Apply<br />
firm pressure over area of<br />
pain.<br />
Pt has high shoulder &/or<br />
visible scoliosis while standing<br />
/ Doc watches for change in<br />
scoliosis while Pt flexes at<br />
waist<br />
Pt in side lying position is<br />
asked to move to a seated<br />
position. Doc observes for<br />
pain/discomfort or the use of<br />
upper body strength<br />
(hands/arm/abs) to assist in<br />
rising from a supine/side lying<br />
position<br />
Pt supine, does partial crunch<br />
(enough to lift shoulders off<br />
table) doc observes umbilicus<br />
for deviation<br />
Chest Expansion Test Measure chest during maximal<br />
inspiration & maximal<br />
expiration at the 4 th intercostal<br />
space (nipple line).<br />
Forestier Bowstring Lateral bending side to side,<br />
doc observes ROM<br />
Rib Motion Test Pt supine / doc hand on<br />
chest/ribs (Medial to Lateral<br />
Tissue Pull) should<br />
expand/contract<br />
symmetrically.<br />
Also use Rib Spring – pt<br />
prone, press at 45 degrees to<br />
ribs w/ flat broad contact. Feel<br />
for springiness.<br />
Schepelmann’s Pt seated w/ arms extended<br />
overhead & laterally bends to<br />
both sides<br />
Elbow pain increases Lateral Epicondylitis / Tennis<br />
Elbow<br />
half of ring finger.<br />
Tingling into thumb, index and<br />
middle fingers and lateral half<br />
of ring finger.<br />
Distal phalanx of thumb goes<br />
into flexion when paper is<br />
pulled away.<br />
Unable to pinch the tips of the<br />
index finger and thumb<br />
together<br />
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome<br />
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome<br />
Ulnar nerve injury<br />
Pathology of the anterior<br />
interosseous nerve<br />
PIP joint cannot be flexed Osteoarthritis (capsular<br />
contraction)<br />
Pain over the abductor pollicis<br />
longus and the extensor<br />
pollicis brevis tendons at the<br />
wrist<br />
Pulse increase of 10 or more<br />
bpm<br />
High shoulder / High hip upon<br />
flexion<br />
Usually the Rt. side<br />
Rising elicits localized pain in<br />
Thoracics or Thoraco-Lumbar<br />
area or Pt uses upper body to<br />
help themselves up<br />
Deviation of umbilicus (will<br />
deviate in the opposite<br />
direction of weakness)<br />
(Rectus Ab. Innerv T7 – T12)<br />
LUMBAR <strong>TESTS</strong><br />
Adam’s Position<br />
Pt has high shoulder &/or<br />
visible scoliosis while standing<br />
/ Doc watches for change in<br />
scoliosis while Pt flexes at<br />
waist<br />
Amoss Sign Pt in side lying position is<br />
asked to move to a seated<br />
position. Doc observes for<br />
pain/discomfort or the use of<br />
upper body strength<br />
(hands/arm/abs) to assist in<br />
rising from a supine/side lying<br />
position<br />
Antalgia Sign Doc observes an antalgic<br />
posture / lean to one side to<br />
relieve pt’s pain<br />
Straight Leg Raiser (1) Pt supine. Raise leg straight up<br />
on side of pain.<br />
Bechterew’s Test<br />
Braggard’s Sign (2)<br />
Crossed Straight Leg<br />
Raiser (5)<br />
Pt sits w/ hips & knee at 90<br />
degrees. Pt actively extends<br />
leg at knee<br />
Straight Leg Raiser – when<br />
pain is elicited, lower the leg 5<br />
degrees and dorsiflex foot<br />
Pt. Supine. Raise leg straight<br />
up on asymptomatic side.<br />
Fajersztajn’s Test (6) “Well Leg Braggards” –<br />
straight leg raiser on well side.<br />
when pain is elicited lower the<br />
leg 5 degrees and dorsiflex the<br />
foot<br />
Cox’s Sign (4) During the Straight leg raiser<br />
test the pt raises ipsilateral hip<br />
to relieve pain<br />
Ely’s Heel to Buttocks Pt prone. Doc touches foot to<br />
contralateral buttocks<br />
Femoral Nerve Traction<br />
Test<br />
Heel/Toe Walk Test<br />
Pt side lying, bottom leg is<br />
straight, top leg bent at knee,<br />
extend thigh back on affected<br />
side to traction the femoral n<br />
Walk on heels<br />
Walk on toes<br />
Kemp’s Test Pt seated. Doc stabilizes L<br />
spine with one hand and<br />
supports contralateral shoulder<br />
w/ other hand. Pt laterally<br />
flexed away from doc, then<br />
flexed forward , laterally bent<br />
toward doc and brought into<br />
extension in one smooth<br />
motion (circumduction)<br />
High shoulder / High hip upon<br />
flexion<br />
Usually the Rt. side<br />
Rising elicits localized pain in<br />
Thoracics or Thoraco-Lumbar<br />
area or Pt uses upper body to<br />
help themselves up<br />
Pain Relief<br />
Away from side of pain –PLL<br />
Toward side of pain – PLM<br />
Forward w/ little relief –<br />
central “Rhizel”<br />
Pain reproduced (note angle &<br />
location of pain)<br />
Pain from lumbars radiating<br />
down the leg (reproduced)<br />
Scoliosis Remains during<br />
flexion – Structural or<br />
Pathological Scoliosis<br />
Scoliosis disappears during<br />
flexion – Functional Scoliosis<br />
(90% F / functional best<br />
treated w/ chiro care)<br />
AS, IVD syndrome,<br />
sprain/stain<br />
(AS will also have decreased<br />
ROM, decreased chest<br />
expansion, tender sternum & T<br />
spine)<br />
Disc herniation / bulge<br />
(pt is not locked into position -<br />
that would indicated<br />
tortipelvis)<br />
0-30 = SOL (N or N Root<br />
irritation)<br />
30-60 = SIJ inflammation /<br />
sciatica<br />
60+ = Lumbosacral problem<br />
SOL, IVF encroachment,<br />
Radiculopathy, nerve root<br />
tension, sciatica<br />
Radiating Pain (reproduced) SOL, IVF encroachment,<br />
Radiculopathy, nerve root<br />
tension, sciatica<br />
Pain reproduced on the<br />
affected leg (opposite the side<br />
being tested)<br />
Radiating Pain on<br />
symptomatic side (reproduced)<br />
Medial bulge on symptomatic<br />
/ painful side<br />
SOL, IVF encroachment,<br />
Radiculopathy, nerve root<br />
tension, sciatica<br />
Pain at same angle as<br />
Braggards – PLM bulge<br />
Pain at greater angle PLL<br />
bulge.<br />
Pain / Roll to opposite side SOL, IVF encroachment,<br />
Radiculopathy, nerve root<br />
tension, sciatica<br />
Pain in anterior thigh / groin<br />
area (ipsilateral leg testing)<br />
Pain on Ant Thigh<br />
To groin – L3<br />
To mid tibia – L4<br />
Can’t walk on heels<br />
Can’t walk on toes<br />
Radiating leg pain or local low<br />
back pain.<br />
Radiating: Femoral N, or N<br />
root compression<br />
Localized: Quadriceps muscle<br />
contracture.<br />
Anterior thigh pain from L2-4<br />
NR, Hip lesion (rule out AVN,<br />
OA, TB, subluxation)<br />
Femoral N or N root<br />
compression.<br />
If bilateral in elderly – prostate<br />
hypertrophy/cancer<br />
Can’t walk on heels: L5 N -<br />
L4 IVD<br />
Cant walk on toes S1 N - L5<br />
IVD<br />
NR irritation / disc herniation<br />
Radiculopathy<br />
Local pains<br />
Pain w/ slight rotation or on<br />
convexity – capsulitis<br />
Pain on extension or concavity<br />
– facet .<br />
Pain at waist – LS sprain/strain<br />
Pain w/ flexion – IVD lesion
Kernig’s Sign<br />
Brudzinski Sign<br />
Lasegue Test<br />
Pt supine doc flexes pt hip &<br />
knee 90 degrees doc then tries<br />
to extend leg<br />
Supine pt flexes head toward<br />
the xiphoid process<br />
Pt supine doc flexes pt hip &<br />
knee 90 degrees doc then tries<br />
to extend leg<br />
Lindner’s Sign Pt seated/supine. Passively<br />
flex head/neck toward xiphoid<br />
process<br />
Milgram’s Test<br />
Pt Supine and lifts feet 6” off<br />
table (knees in extension) and<br />
told to hold for 30 sec<br />
Minor’s Sign Pt uses upper body strength to<br />
stand from seated position.<br />
Nachlas Test (lumbars)<br />
Ely’s Test (buttocks)<br />
(walk up legs)<br />
Pt prone. Knee is flexed to<br />
touch foot to ipsilateral<br />
buttocks<br />
Quick Test Pt supports self w/ hand on<br />
table/wall and performs ~5<br />
deep squats<br />
Pain in spine or involuntary<br />
flexion of the opposite<br />
knee/hip<br />
Involuntary hip and knee<br />
flexion<br />
Pain with fever - meningitis<br />
Pain & fever - meningitis<br />
Pain low back, hip or thigh Hip: hip pathology<br />
Thigh: Radiculopathy<br />
Bilateral: tight hamstrings<br />
Pain in L spine or radicular leg Compression of Lumbar NR<br />
pain<br />
Unable to hold Due to low back pain:<br />
herniation or L strain/sprain<br />
No pain – may have weak core<br />
Recruitment of upper body<br />
strength to stand up<br />
Pain in SI/ lumbosacral area.<br />
Radiation of pain down<br />
thigh/leg.<br />
Pain / locking / crepitus in low<br />
back, hips, knees, or ankles<br />
(Helps locate problem along<br />
the kinetic chain)<br />
muscles<br />
SIJ lesion, L5 strain/sprain, LP<br />
fx, IVD syndrome, Muscular<br />
Dystrophy, Sciatica, myotonia<br />
SI or Lumbosacral Problems<br />
(sprain/strain)<br />
Ant thigh pain may be from<br />
inflammation of L2-4 NR’s.<br />
Subluxation of any involved<br />
joints (Problems with joints)<br />
Do not perform on elderly /<br />
pregnant women<br />
Sicard’s Sign (3) Straight leg raise, lower the Radiating Pain (reproduced) Irritation to L5 NR (L4 or S1<br />
leg 5 degrees, dorsiflex big toe<br />
possible too)<br />
Bilateral Leg Lowering Pt supine, Doc flexes hips to Pain in buttocks, SI, lower Lumbosacral sprain/strain,<br />
Test<br />
90 degrees with legs extended. extremity, leg drops due to facet syndrome, IVD lesion…<br />
PELVIS <strong>TESTS</strong><br />
Pt lowers legs to 45 degrees. pain<br />
Anterior Innominate Test Place unaffected foot 2-3 feet Local pain over SI joint. Unilateral forward<br />
(1)<br />
forward. Flex forward at waist<br />
displacement of ilium, sacrum,<br />
to touch toes<br />
SIJ sprain<br />
Belt Test (2) 1) Patient stands, bends Pain in lumbar or sacral If pt had pain in part 1 but no<br />
forward to touch toes – note regions<br />
pain in part 2 or is able to bend<br />
any pain.<br />
further in part 2 before painful<br />
2) Dr. braces hips with hands<br />
= SI joint<br />
and places hip tightly against<br />
If pt had pain in part 1 and<br />
pt sacrum then pt. bends<br />
pain in part 2 at the same or<br />
forward again – note pain.<br />
lesser degree of flexion =<br />
Lumbar involvement.<br />
Erichsen’s Test Pt. prone and dr. compresses Pain around SI joint Usually caused by Ant<br />
SI joint by applying pressure<br />
stabilization ligaments<br />
to area of PSIS with thumbs or<br />
thenars Creates double IN<br />
ilium<br />
weakness<br />
Gaenslen’s Test Pt supine, doc stands on SI joint pain on side being SI joint sprain, instability.<br />
unaffected side and brings extended. Radiating pain to DDx SI pain from<br />
affected knee up toward groin or thigh.<br />
Lumbosacral pain<br />
patient’s chest. Then dr.<br />
slowly hyperextends<br />
unaffected leg (may need to<br />
drop unaffected leg off table to<br />
achieve hyperextension)<br />
If neg L5 lesion possible<br />
Goldthwait’s Sign<br />
Pt. prone while dr. palpates L5 Pain Pain before separation – SI<br />
and S1. Dr uses other hand to<br />
joint<br />
elevated affected leg.<br />
Pain after L5/S1 separation –<br />
Lumbar<br />
Hibb’s Test “Prone Thigh Pt prone, flex knee to 90 Pain Hip (Femoral head or<br />
Roll”<br />
degrees & internally rot femur<br />
(push foot laterally)<br />
acetabular problems)<br />
Iliac Compression Test Pt laying on side, doc<br />
Pain / increase pressure in SIJ Sprain Posterior SI ligament /<br />
compresses iliac crest toward<br />
SI inflammation/subluxation<br />
table (affected side down)<br />
(can also have ilium fx or<br />
Creates double EX ilium<br />
pubic symphysis pain)
Lewin Gaenslen Test<br />
Lewin Standing Test<br />
standing straight leg raiser<br />
Lay on unaffected side. Pt<br />
brings unaffected knee toward<br />
chest. Then dr. slowly<br />
hyperextends affected thigh.<br />
Slightly flex knees & waist<br />
slightly, cross arms, bend pt<br />
forward to point before pain,<br />
put 1 leg into extension when<br />
stabilizing sacrum<br />
Yeoman’s Test Pt prone. Dr. applies pressure<br />
to PSIS with one hand and<br />
places other hand under<br />
ipsilateral knee and lifts flexed<br />
knee off table (extending the<br />
thigh)<br />
HIP <strong>TESTS</strong><br />
Actual Leg Length Test<br />
Apparent Leg Length Test<br />
Allis’ Sign / Saleazzi’s<br />
Sign<br />
Anvil Test<br />
Pt supine w/ feet together,<br />
knees & hips straight. Doc<br />
measures apex of ASIS to<br />
center of medial malleolus<br />
Same as above – measure<br />
made from umbilicus to<br />
medial maleolus<br />
Pt supine, Knees/Hips flexed,<br />
feet flat on table and medial<br />
malleoli & big toes are aligned<br />
side by side – doc stands at<br />
foot of table and observes<br />
knees for any height<br />
discrepancy. Dr. then stands<br />
at side of table and looks for<br />
one knee to be more anterior<br />
than the other.<br />
Pt supine, doc elevates straight<br />
leg & hits bottom of<br />
calcaneous w/ clenched fist<br />
Gauvain’s Sign Pt lays on side w/ affected side<br />
up doc grasps above ankle and<br />
abducts leg & then internally<br />
and externally rotates thigh<br />
Hip Telescoping Test Pt supine doc passively flexes<br />
knee & hip of affected side to<br />
90 degrees , grasp calf with<br />
one hand and place other hand<br />
on thigh just proximal to knee<br />
– push femur into table and<br />
distract femur away from<br />
Patrick’s Test (mnemonic<br />
FABERE)<br />
Ober’s Test<br />
Thomas Test<br />
table.<br />
Pt supine, doc on unaffected<br />
side and patient instructed to<br />
cross legs into a “figure 4”.<br />
Dr. then stabilizes<br />
contralateral ASIS on table<br />
and puts downward pressure<br />
on knee of affected side<br />
Pt lies w/ affected side up, doc<br />
stands behind pt & stabilizes<br />
pelvis – doc uses other hand to<br />
abduct & extend thigh at hip<br />
(holding at knee) with knee<br />
bent to 90 degrees – doc then<br />
slides hand from knee to ankle<br />
keeping knee bent<br />
Pt supine & actively pulls<br />
unaffected knee to chest while<br />
keeping the other leg straight.<br />
SI joint pain on side being<br />
extended<br />
Muscle tightness<br />
Knee flexes or pt tries to stand<br />
up b/c of pain / tightness<br />
Pain in SI joints<br />
Muscle tightness<br />
Difference of more than 6mm<br />
from side to side<br />
Difference of more than 6mm<br />
from side to side<br />
(adds in L3-5 discs w/ sublux<br />
the leg lengths could change)<br />
One knee is lower compared to<br />
the other.<br />
One knee is more anterior<br />
compared to the other<br />
Pain in kinetic chain heel to<br />
acetabulum<br />
Ipsilateral contraction of<br />
abdominal muscles / pain in<br />
hip / referred pain to groin, ant<br />
thigh,<br />
Excess joint play and or<br />
palpable click in joint<br />
Pain in hip or inability to<br />
perform<br />
Affected thigh remains<br />
abducted may be painful or<br />
may drop w/ spastic jerks<br />
(clonus)<br />
L spine maintains lordosis or<br />
pt is unable to keep affected<br />
thigh flat on the table<br />
SI joint sprain, arthritis.<br />
Iliopsoas muscle contracture<br />
DDx SI pain from<br />
Lumbosacral pain<br />
Herniation , SOL, Bulge<br />
SI lesion esp Anterior SI ligs<br />
Pain into ant thigh/groin –<br />
Femoral N irritation (L2-4), or<br />
prostate problems<br />
Iliopsoas or rectus femoris<br />
muscle contracture<br />
Hip joint of long bone<br />
deficiency (accurate to 1 cm<br />
need x-rays for higher<br />
accuracy)<br />
Pelvic Subluxation<br />
Ipsilateral femoral length<br />
discrepancy (protrusion<br />
acetabuli, hip dislocation PS,<br />
dysplasia, fx)<br />
Hip pain – arthritis, femoral<br />
neck fx, infection<br />
Heel pain – calcaneus fx, tibia<br />
fx, fibula fx (depending on<br />
point of pain)<br />
AVN, Infection, Fx, gout,<br />
Hernia, hip tuberculosis (rare)<br />
Hip dislocation / hip dysplasia<br />
MC – women (Mediterranean<br />
& Scandinavian)<br />
Hip Pathology (DJD, OA, RA,<br />
SCFE, AVN, Fx, sprain/strain,<br />
tight hip adductors)<br />
ITB contracture<br />
Common in runners<br />
Flexion contracture or<br />
shortening of iliopsoas on<br />
affected side
Trendelenburg’s Test<br />
Pt stands on affected foot and<br />
raises unaffected foot off the<br />
ground. (pt can brace<br />
themselves against doc/table)<br />
Dr. observes for any pelvic<br />
unleveling.<br />
Ortolani’s Test Infant supine. Dr. grasps both<br />
thighs at level of lesser and<br />
greater trochanters between<br />
thumbs and fingers. Dr then<br />
flexes and abducts the thighs<br />
bilaterally.<br />
Iliac crest high on supported<br />
leg and low on lifted leg.<br />
Paralysis / weakness of hip<br />
abductors on affected side<br />
(gluteus medius)<br />
Hip dysplasia<br />
Palpable click/clunk Congenital femoral<br />
dislocation, instability
<strong>NMS</strong> II <strong>Orthopedics</strong><br />
KNEE <strong>TESTS</strong><br />
Abduction (Valgus) Stress<br />
Test<br />
Adduction (Varus) Stress<br />
Test<br />
Pt. supine with legs<br />
straight, Dr. stabilizes the<br />
medial ankle and pushes<br />
lateral to medial at the<br />
knee. Procedure is then<br />
repeated w/ knee slightly<br />
flexed (25°).<br />
Pt. supine with legs<br />
straight, Dr. stabilizes the<br />
lateral ankle and pushes<br />
medial to lateral at the<br />
knee. Procedure is then<br />
repeated w/ knee slightly<br />
flexed (25°).<br />
Apley’s Compression Test Pt. prone with knee flexed<br />
to 90°. Dr. pushes down on<br />
the foot with leg neutral,<br />
then medially rotated and<br />
laterally rotated.<br />
Patellar Ballottement Test Pt supine w/ leg straight,<br />
Dr. pushes down on the<br />
patella and moves it lateral<br />
and medial, palpating for<br />
motion<br />
Bounce Home Test Pt. supine and relaxed. Dr.<br />
lifts leg and bends knee to<br />
20°. Dr. then allows the<br />
knee to drop into full<br />
extension.<br />
Clark’s Sign (Patellar<br />
Scrape Test)<br />
Push down on the patella<br />
and ask the patient to<br />
contract the quadriceps.<br />
McMurray’s Sign Pt supine, hip and knee<br />
flexed to 90°. Dr. stabilizes<br />
knee and grips heel with<br />
the other hand. Dr. rotates<br />
the tibia internally while<br />
applying a varus force<br />
while extending the leg.<br />
Repeated with tibia rotated<br />
externally and Dr. applying<br />
a valgus force while<br />
Lateral Pivot Shift<br />
Maneuver<br />
extending the leg.<br />
Pt. supine, w/ hip and knee<br />
flexed. Adduction, internal<br />
rotation, valgus stress and<br />
flex knee.<br />
Lachman’s Test Drawer test with knee<br />
flexed to 25°.<br />
Drawer Test Pt. supine with knee flexed<br />
to 90°. Dr. pulls the tibia<br />
anterior and then pushes it<br />
posterior feeling for<br />
excessive motion.<br />
Pain or increased<br />
motion/gapping<br />
Pain or increased<br />
motion/gapping<br />
Pain or crepitus with<br />
compression (usually<br />
relieved by distraction)<br />
Patella is slow to return to<br />
resting position. Increased<br />
motion or spongy joint<br />
feel.<br />
Joint line pain<br />
Inability to fully extend<br />
knee:<br />
1. Spongy end feel<br />
2. Rubbery end feel<br />
3. Hard end feel<br />
Medial Collateral<br />
Ligament strain or rupture.<br />
Lateral Collateral<br />
Ligament strain or rupture.<br />
Internal rotation = lateral<br />
meniscus<br />
External Rotation = Medial<br />
Meniscus<br />
Retropatellar<br />
effusion/Intraarticular knee<br />
swelling.<br />
Meniscal tear<br />
1. swelling/edema<br />
2. meniscal tear<br />
3. intra-articular<br />
fragment<br />
Retropatellar pain Chondromalacia patella,<br />
degeneration of<br />
patellofemoral joint<br />
Pain or crepitus Int. rot. w/ valgus stress &<br />
extend = lateral meniscus<br />
Ext. rot. w/ varus stress &<br />
extend = medial meniscus<br />
Knee gives out Anterior Cruciate Lig.<br />
Pain w/ or w/o increased<br />
anterior (ACL) and<br />
posterior (PCL) translation.<br />
Pain w/ or w/o increased<br />
anterior (ACL) and<br />
posterior (PCL) translation.<br />
Pain w/ normal translation:<br />
sprain. Pain w/ increased<br />
translation: rupture.<br />
Pain w/ normal translation:<br />
sprain. Pain w/ increased<br />
translation: rupture.
Q-Angle Test Pt. standing. Draw a line<br />
for ASIS through midpoint<br />
of patella and another line<br />
from tibial tuberosity<br />
through the midpoint of the<br />
patella. The angle is<br />
measured between these 2<br />
lines.<br />
LOWER EXTREMITY VASCULAR & ANKLE EXAMS<br />
Anterior Drawer Sign Pt. supine or seated. Dr.<br />
places one hand on anterior<br />
tibia and the other on<br />
posterior calcaneus and<br />
pulls the foot anteriorly.<br />
Calf Circumference Test Measure the calf at the<br />
widest point.<br />
Claudication Test Pt. walks at 2 steps/sec<br />
(120/min) for one minute<br />
while Dr. observes<br />
Homan’s Sign Pt. supine – raise leg up to<br />
10° , squeeze calf and<br />
Angle is less than 13°. Genu varum<br />
Excessive anterior<br />
movement/translation<br />
Increased or decreased<br />
diameter comparing side to<br />
side<br />
Muscle weakness,<br />
cramping, pain, discomfort<br />
or color change (palor)<br />
Short duration, deep calf<br />
pain<br />
Persistent achy calf pain<br />
Short duration, deep calf<br />
pain<br />
Anterior talofibular<br />
ligament instability<br />
↑ = acute compartment<br />
syndrome<br />
↓ = muscle atrophy<br />
Peripheral vascular disease,<br />
intermittent vascular<br />
claudication, popliteal a.<br />
entrapment syndrome,<br />
atherosclerosis<br />
Thrombophlebitis<br />
quickly dorsiflex the foot<br />
Gastrosoleus strain<br />
Moses’ Test Pt. prone, flex knee to 90°<br />
LE vascular insufficiency,<br />
and squeeze calf.<br />
thrombophlebitis,<br />
arteriosclerosis obliterans<br />
Persistent achy calf pain Gastrosoleus strain<br />
Thompson’s Test Pt. prone, flex knee to 90° No plantar flexion Ruptured Achilles tendon<br />
and squeeze the calf Localized pain<br />
Gastroc/soleus sprain<br />
FOOT <strong>TESTS</strong><br />
Short, deep pain<br />
thrombophlebitis<br />
Duchenne’s Sign Apply upward force to<br />
head of 1 st Supination of foot with Superficial peroneal n.<br />
metatarsal attempted plantar flexion lesion or L4-S1 lesion<br />
Helbing’s Sign Pt stands – Dr. observes Medial curving of Achilles Overpronation syndrome –<br />
the Achilles tendon<br />
Common with Cerebral<br />
Palsy<br />
Morton’s Test Squeeze foot around the Pain Morton’s neuroma (usually<br />
metatarsal heads<br />
between 3 rd and 4 th digits),<br />
arthritis, stress fx of<br />
metatarsal heads,<br />
Metatarsalgia (less<br />
localized/generalized pain)<br />
Strunsky’s Sign Rapidly flex patients toes Forefoot pain Metatarsalgia, OA<br />
Tinel’s Foot Tap posterior aspect of Pain in the toe, arch, or Nerve compression<br />
medial malleolus (post. heel<br />
syndrome, Tarsal Tunnel<br />
Tibial n./medial plantar n.)<br />
Syndrome (Post. Tibial<br />
and dorsum of foot (deep<br />
peroneal n)<br />
nerve)
MISC<br />
Burn’s Bench Test Stand, bend, and note angle<br />
of pain<br />
Kneel on bench and bend<br />
forward<br />
MannKopf’s Test Take pt’s resting HR.<br />
Apply firm pressure over<br />
area of pain.<br />
Libman’s Test Pt. seated, Dr. standing<br />
behind pt. Dr. applies<br />
pressure on the pt’s<br />
mastoid process with<br />
thumbs until pt reports<br />
pain/discomfort. Compare<br />
side to side.<br />
Should be able to bend<br />
farther when kneeling<br />
because the tension is off<br />
of the sciatic n.<br />
Pulse increase of 10 or<br />
more bpm.<br />
Indicates malingering –<br />
“objective findings to not<br />
match the subjective<br />
complaint”<br />
Pain is real – They are not<br />
faking/malingering.<br />
Pain/Uncomfortable Tests the pt’s pain<br />
tolerance – useful for later<br />
procedures and to<br />
determine malingering.