Types of Androecium in the Fabaceae of SW ... - Annals of Botany
Types of Androecium in the Fabaceae of SW ... - Annals of Botany
Types of Androecium in the Fabaceae of SW ... - Annals of Botany
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Rodrıguez-Rian o et al.—<strong>Androecium</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Fabaceae</strong> 113<br />
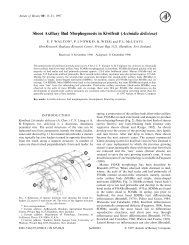
Fig. 2. <strong>Types</strong> <strong>of</strong> androecium: A, monadelphous (Cytisus grandiflorus); B, unfenestrated pseudomonadelphous (Coronilla alent<strong>in</strong>a subsp. glauca);<br />
C, basally fenestrated pseudomonadelphous (Vicia benghalensis); D, diadelphous (Astragalus lusitanicus); E, reduced diadelphous (Biserrula<br />
pelec<strong>in</strong>us); F, free (Anagyris foetida). Bars 1 mm except B and E where bar 05 mm.<br />
formation <strong>of</strong> fenestration at <strong>the</strong> base (Fig. 2B). This appears<br />
only <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> genus Coronilla; (c) pseudomonadelphous, with<br />
basal fenestration: as <strong>the</strong> preced<strong>in</strong>g case, but with <strong>the</strong> free<br />
stamen (A1) present<strong>in</strong>g a curvature at its base permitt<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>the</strong> formation <strong>of</strong> two basal orifices (Fig. 2C). The coupl<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>of</strong> this stamen to <strong>the</strong> stam<strong>in</strong>al tube varies from a simple<br />
superposition (e.g. Lathyrus) to a complete fusion along <strong>the</strong><br />
length <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> tube (e.g. Medicago) except at <strong>the</strong> basal part. It<br />
is also represented <strong>in</strong> Vicia (except V. pubescens), Pisum,<br />
some species <strong>of</strong> Trifolium, Rob<strong>in</strong>ia, Dorycnopsis, Dorycnium<br />
rectum, Anthyllis, Hymenocarpos, Cullen and Bitum<strong>in</strong>aria;<br />
(d) diadelphous (Fig. 2D). It appears <strong>in</strong> some species <strong>of</strong><br />
Trifolium, Melilotus, Trigonella, Astragalus (except A.<br />
epiglottis subsp. epiglottis), Hedysarum, Hippocrepis, Onob-<br />
rychis (at times <strong>the</strong> free stamen is fused to <strong>the</strong> rest),<br />
Ornithopus, Scorpiurus, Lotus, Tripodion, Dorycnium pentaphyllum<br />
and one population <strong>of</strong> D. rectum, and Colutea<br />
atlantica; (e) reduced diadelphous: similar to <strong>the</strong> previous<br />
case but with <strong>the</strong> disappearance <strong>of</strong> all <strong>the</strong> an<strong>the</strong>rs <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
lower whorl with only vestiges persist<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> which it is at<br />
times possible to observe occasional pollen gra<strong>in</strong>s (Fig. 2E).<br />
This type is presented by Biserrula pelec<strong>in</strong>us, Vicia pubescens<br />
and Astragalus epiglottis; (f ) free: all <strong>the</strong> stamens rema<strong>in</strong><br />
free (Fig. 2F). It only appears <strong>in</strong> Anagyris foetida.<br />
The type <strong>of</strong> androecium <strong>of</strong> each taxon is listed <strong>in</strong> Table 1,<br />
toge<strong>the</strong>r with an <strong>in</strong>dication <strong>of</strong> whe<strong>the</strong>r it is nectariferous or<br />
not. The nectar is secreted by an annular nectary which is<br />
most <strong>of</strong>ten <strong>in</strong>trastam<strong>in</strong>al, i.e. situated between <strong>the</strong> andro-