Free radicals, oxidative stress and importance of antioxidants in ...
Free radicals, oxidative stress and importance of antioxidants in ...
Free radicals, oxidative stress and importance of antioxidants in ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Kunwar A et al. <strong>Free</strong> <strong>radicals</strong>, <strong>oxidative</strong> <strong>stress</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>antioxidants</strong> <strong>in</strong> human health<br />
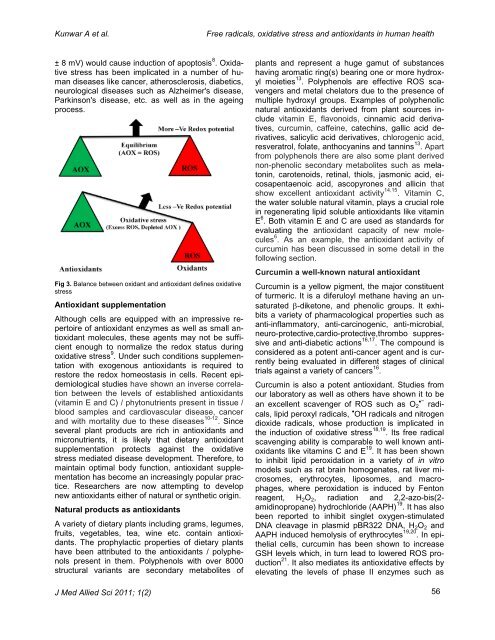
± 8 mV) would cause <strong>in</strong>duction <strong>of</strong> apoptosis 8 . Oxidative<br />
<strong>stress</strong> has been implicated <strong>in</strong> a number <strong>of</strong> human<br />
diseases like cancer, atherosclerosis, diabetics,<br />
neurological diseases such as Alzheimer's disease,<br />
Park<strong>in</strong>son's disease, etc. as well as <strong>in</strong> the age<strong>in</strong>g<br />
process.<br />
Fig 3. Balance between oxidant <strong>and</strong> antioxidant def<strong>in</strong>es <strong>oxidative</strong><br />
<strong>stress</strong><br />
Antioxidant supplementation<br />
Although cells are equipped with an impressive repertoire<br />
<strong>of</strong> antioxidant enzymes as well as small antioxidant<br />
molecules, these agents may not be sufficient<br />
enough to normalize the redox status dur<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>oxidative</strong> <strong>stress</strong> 9 . Under such conditions supplementation<br />
with exogenous <strong>antioxidants</strong> is required to<br />
restore the redox homeostasis <strong>in</strong> cells. Recent epidemiological<br />
studies have shown an <strong>in</strong>verse correlation<br />
between the levels <strong>of</strong> established <strong>antioxidants</strong><br />
(vitam<strong>in</strong> E <strong>and</strong> C) / phytonutrients present <strong>in</strong> tissue /<br />
blood samples <strong>and</strong> cardiovascular disease, cancer<br />
<strong>and</strong> with mortality due to these diseases 10-12 . S<strong>in</strong>ce<br />
several plant products are rich <strong>in</strong> <strong>antioxidants</strong> <strong>and</strong><br />
micronutrients, it is likely that dietary antioxidant<br />
supplementation protects aga<strong>in</strong>st the <strong>oxidative</strong><br />
<strong>stress</strong> mediated disease development. Therefore, to<br />
ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong> optimal body function, antioxidant supplementation<br />
has become an <strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>gly popular practice.<br />
Researchers are now attempt<strong>in</strong>g to develop<br />
new <strong>antioxidants</strong> either <strong>of</strong> natural or synthetic orig<strong>in</strong>.<br />
Natural products as <strong>antioxidants</strong><br />
A variety <strong>of</strong> dietary plants <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g grams, legumes,<br />
fruits, vegetables, tea, w<strong>in</strong>e etc. conta<strong>in</strong> <strong>antioxidants</strong>.<br />
The prophylactic properties <strong>of</strong> dietary plants<br />
have been attributed to the <strong>antioxidants</strong> / polyphenols<br />
present <strong>in</strong> them. Polyphenols with over 8000<br />
structural variants are secondary metabolites <strong>of</strong><br />
J Med Allied Sci 2011; 1(2)<br />
plants <strong>and</strong> represent a huge gamut <strong>of</strong> substances<br />
hav<strong>in</strong>g aromatic r<strong>in</strong>g(s) bear<strong>in</strong>g one or more hydroxyl<br />
moieties 13 . Polyphenols are effective ROS scavengers<br />
<strong>and</strong> metal chelators due to the presence <strong>of</strong><br />
multiple hydroxyl groups. Examples <strong>of</strong> polyphenolic<br />
natural <strong>antioxidants</strong> derived from plant sources <strong>in</strong>clude<br />
vitam<strong>in</strong> E, flavonoids, c<strong>in</strong>namic acid derivatives,<br />
curcum<strong>in</strong>, caffe<strong>in</strong>e, catech<strong>in</strong>s, gallic acid derivatives,<br />
salicylic acid derivatives, chlorogenic acid,<br />
resveratrol, folate, anthocyan<strong>in</strong>s <strong>and</strong> tann<strong>in</strong>s 13 . Apart<br />
from polyphenols there are also some plant derived<br />
non-phenolic secondary metabolites such as melaton<strong>in</strong>,<br />
carotenoids, ret<strong>in</strong>al, thiols, jasmonic acid, eicosapentaenoic<br />
acid, ascopyrones <strong>and</strong> allic<strong>in</strong> that<br />
show excellent antioxidant activity 14,15 . Vitam<strong>in</strong> C,<br />
the water soluble natural vitam<strong>in</strong>, plays a crucial role<br />
<strong>in</strong> regenerat<strong>in</strong>g lipid soluble <strong>antioxidants</strong> like vitam<strong>in</strong><br />
E 6 . Both vitam<strong>in</strong> E <strong>and</strong> C are used as st<strong>and</strong>ards for<br />
evaluat<strong>in</strong>g the antioxidant capacity <strong>of</strong> new molecules<br />
6 . As an example, the antioxidant activity <strong>of</strong><br />
curcum<strong>in</strong> has been discussed <strong>in</strong> some detail <strong>in</strong> the<br />
follow<strong>in</strong>g section.<br />
Curcum<strong>in</strong> a well-known natural antioxidant<br />
Curcum<strong>in</strong> is a yellow pigment, the major constituent<br />
<strong>of</strong> turmeric. It is a diferuloyl methane hav<strong>in</strong>g an unsaturated<br />
-diketone, <strong>and</strong> phenolic groups. It exhibits<br />
a variety <strong>of</strong> pharmacological properties such as<br />
anti-<strong>in</strong>flammatory, anti-carc<strong>in</strong>ogenic, anti-microbial,<br />
neuro-protective,cardio-protective,thrombo suppressive<br />
<strong>and</strong> anti-diabetic actions 16,17 . The compound is<br />
considered as a potent anti-cancer agent <strong>and</strong> is currently<br />
be<strong>in</strong>g evaluated <strong>in</strong> different stages <strong>of</strong> cl<strong>in</strong>ical<br />
trials aga<strong>in</strong>st a variety <strong>of</strong> cancers 16 .<br />
Curcum<strong>in</strong> is also a potent antioxidant. Studies from<br />
our laboratory as well as others have shown it to be<br />
an excellent scavenger <strong>of</strong> ROS such as O2 − <strong>radicals</strong>,<br />
lipid peroxyl <strong>radicals</strong>, OH <strong>radicals</strong> <strong>and</strong> nitrogen<br />
dioxide <strong>radicals</strong>, whose production is implicated <strong>in</strong><br />
the <strong>in</strong>duction <strong>of</strong> <strong>oxidative</strong> <strong>stress</strong> 18,19 . Its free radical<br />
scaveng<strong>in</strong>g ability is comparable to well known <strong>antioxidants</strong><br />
like vitam<strong>in</strong>s C <strong>and</strong> E 19 . It has been shown<br />
to <strong>in</strong>hibit lipid peroxidation <strong>in</strong> a variety <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong> vitro<br />
models such as rat bra<strong>in</strong> homogenates, rat liver microsomes,<br />
erythrocytes, liposomes, <strong>and</strong> macrophages,<br />
where peroxidation is <strong>in</strong>duced by Fenton<br />
reagent, H2O2, radiation <strong>and</strong> 2,2-azo-bis(2amid<strong>in</strong>opropane)<br />
hydrochloride (AAPH) 19 . It has also<br />
been reported to <strong>in</strong>hibit s<strong>in</strong>glet oxygen-stimulated<br />
DNA cleavage <strong>in</strong> plasmid pBR322 DNA, H2O2 <strong>and</strong><br />
AAPH <strong>in</strong>duced hemolysis <strong>of</strong> erythrocytes 19,20 . In epithelial<br />
cells, curcum<strong>in</strong> has been shown to <strong>in</strong>crease<br />
GSH levels which, <strong>in</strong> turn lead to lowered ROS production<br />
21 . It also mediates its anti<strong>oxidative</strong> effects by<br />
elevat<strong>in</strong>g the levels <strong>of</strong> phase II enzymes such as<br />
56