CASEL-Report-low-res-FINAL
CASEL-Report-low-res-FINAL
CASEL-Report-low-res-FINAL
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
18 the Missing Piece<br />
Survey FindingS 1<br />
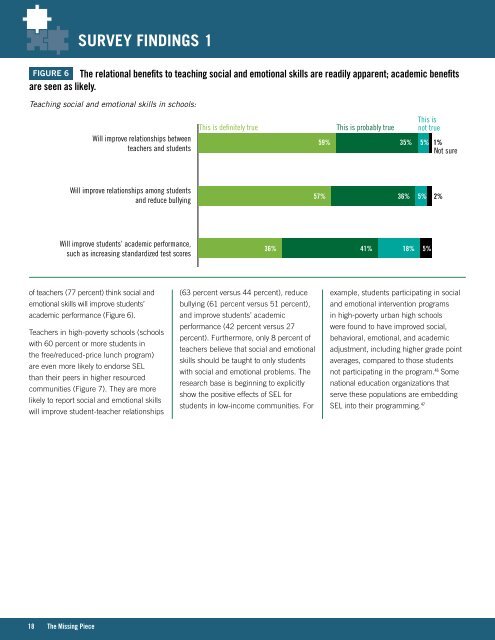
Figure 6 the relational benefits to teaching social and emotional skills are readily apparent; academic benefits<br />
are seen as likely.<br />
Teaching social and emotional skills in schools:<br />
Will improve relationships between<br />
teachers and students<br />
Will improve relationships among students<br />
and reduce bullying<br />
Will improve students’ academic performance,<br />
such as increasing standardized test sco<strong>res</strong><br />
of teachers (77 percent) think social and<br />
emotional skills will improve students’<br />
academic performance (Figure 6).<br />
Teachers in high-poverty schools (schools<br />
with 60 percent or more students in<br />
the free/reduced-price lunch program)<br />
are even more likely to endorse SEL<br />
than their peers in higher <strong>res</strong>ourced<br />
communities (Figure 7). They are more<br />
likely to report social and emotional skills<br />
will improve student-teacher relationships<br />
This is definitely true This is probably true<br />
7%<br />
36%<br />
(63 percent versus 44 percent), reduce<br />
bullying (61 percent versus 51 percent),<br />
and improve students’ academic<br />
performance (42 percent versus 27<br />
percent). Furthermore, only 8 percent of<br />
teachers believe that social and emotional<br />
skills should be taught to only students<br />
with social and emotional problems. The<br />
<strong>res</strong>earch base is beginning to explicitly<br />
show the positive effects of SEL for<br />
students in <strong>low</strong>-income communities. For<br />
59% 35% 5% 1%<br />
Not sure<br />
57% 36%<br />
26%<br />
41% 18%<br />
This is<br />
not true<br />
30%<br />
5%<br />
5%<br />
2%<br />
example, students participating in social<br />
and emotional intervention programs<br />
in high-poverty urban high schools<br />
were found to have improved social,<br />
behavioral, emotional, and academic<br />
adjustment, including higher grade point<br />
averages, compared to those students<br />
not participating in the program. 46 Some<br />
national education organizations that<br />
serve these populations are embedding<br />
SEL into their programming. 47