Misoprostol: An emerging technology for women's health
Misoprostol: An emerging technology for women's health
Misoprostol: An emerging technology for women's health
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
36<br />
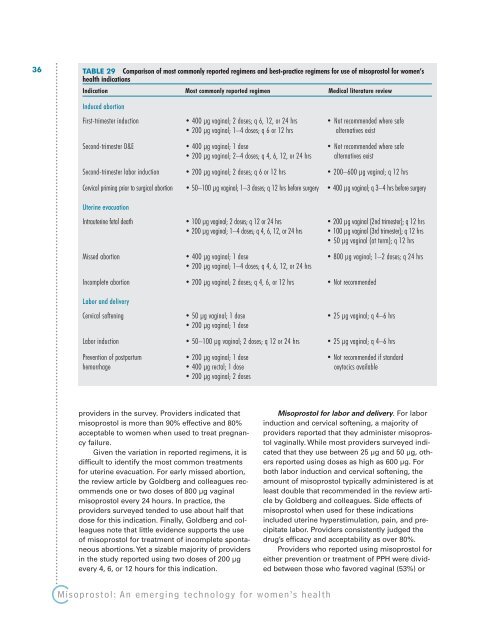
TABLE 29 Comparison of most commonly reported regimens and best-practice regimens <strong>for</strong> use of misoprostol <strong>for</strong> women’s<br />
<strong>health</strong> indications<br />
Indication Most commonly reported regimen Medical literature review<br />
Induced abortion<br />
First-trimester induction • 400 µg vaginal; 2 doses; q 6, 12, or 24 hrs • Not recommended where safe<br />
• 200 µg vaginal; 1–4 doses; q 6 or 12 hrs alternatives exist<br />
Second-trimester D&E • 400 µg vaginal; 1 dose • Not recommended where safe<br />
• 200 µg vaginal; 2–4 doses; q 4, 6, 12, or 24 hrs alternatives exist<br />
Second-trimester labor induction • 200 µg vaginal; 2 doses; q 6 or 12 hrs • 200–600 µg vaginal; q 12 hrs<br />
Cervical priming prior to surgical abortion • 50–100 µg vaginal; 1–3 doses; q 12 hrs be<strong>for</strong>e surgery • 400 µg vaginal; q 3–4 hrs be<strong>for</strong>e surgery<br />
Uterine evacuation<br />
Intrauterine fetal death • 100 µg vaginal; 2 doses; q 12 or 24 hrs • 200 µg vaginal (2nd trimester); q 12 hrs<br />
• 200 µg vaginal; 1–4 doses; q 4, 6, 12, or 24 hrs • 100 µg vaginal (3rd trimester); q 12 hrs<br />
• 50 µg vaginal (at term); q 12 hrs<br />
Missed abortion • 400 µg vaginal; 1 dose • 800 µg vaginal; 1–2 doses; q 24 hrs<br />
• 200 µg vaginal; 1–4 doses; q 4, 6, 12, or 24 hrs<br />
Incomplete abortion • 200 µg vaginal; 2 doses; q 4, 6, or 12 hrs • Not recommended<br />
Labor and delivery<br />
Cervical softening • 50 µg vaginal; 1 dose • 25 µg vaginal; q 4–6 hrs<br />
• 200 µg vaginal; 1 dose<br />
Labor induction • 50–100 µg vaginal; 2 doses; q 12 or 24 hrs • 25 µg vaginal; q 4–6 hrs<br />
Prevention of postpartum • 200 µg vaginal; 1 dose • Not recommended if standard<br />
hemorrhage • 400 µg rectal; 1 dose oxytocics available<br />
• 200 µg vaginal; 2 doses<br />
providers in the survey. Providers indicated that<br />
misoprostol is more than 90% effective and 80%<br />
acceptable to women when used to treat pregnancy<br />
failure.<br />
Given the variation in reported regimens, it is<br />
difficult to identify the most common treatments<br />
<strong>for</strong> uterine evacuation. For early missed abortion,<br />
the review article by Goldberg and colleagues recommends<br />
one or two doses of 800 µg vaginal<br />
misoprostol every 24 hours. In practice, the<br />
providers surveyed tended to use about half that<br />
dose <strong>for</strong> this indication. Finally, Goldberg and colleagues<br />
note that little evidence supports the use<br />
of misoprostol <strong>for</strong> treatment of incomplete spontaneous<br />
abortions. Yet a sizable majority of providers<br />
in the study reported using two doses of 200 µg<br />
every 4, 6, or 12 hours <strong>for</strong> this indication.<br />
<strong>Misoprostol</strong>: <strong>An</strong> <strong>emerging</strong> <strong>technology</strong> <strong>for</strong> women’s <strong>health</strong><br />
<strong>Misoprostol</strong> <strong>for</strong> labor and delivery. For labor<br />
induction and cervical softening, a majority of<br />
providers reported that they administer misoprostol<br />
vaginally. While most providers surveyed indicated<br />
that they use between 25 µg and 50 µg, others<br />
reported using doses as high as 600 µg. For<br />
both labor induction and cervical softening, the<br />
amount of misoprostol typically administered is at<br />
least double that recommended in the review article<br />
by Goldberg and colleagues. Side effects of<br />
misoprostol when used <strong>for</strong> these indications<br />
included uterine hyperstimulation, pain, and precipitate<br />
labor. Providers consistently judged the<br />
drug’s efficacy and acceptability as over 80%.<br />
Providers who reported using misoprostol <strong>for</strong><br />
either prevention or treatment of PPH were divided<br />
between those who favored vaginal (53%) or