KVÄLLSSYMPOSIUM 2008 Vaccinering av hund och katt
KVÄLLSSYMPOSIUM 2008 Vaccinering av hund och katt
KVÄLLSSYMPOSIUM 2008 Vaccinering av hund och katt
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
274 S.M. Moore et al. / Biologicals 33 (2005) 269e276<br />
GMT<br />
260<br />
240<br />
220<br />
200<br />
180<br />
160<br />
140<br />
120<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
PCECV homologous<br />
PCECV heterologous<br />
Low<br />
PVRV homologous<br />
PVRV heterologous<br />
1200<br />
1100<br />
1000<br />
900<br />
800<br />
700<br />
600<br />
appropriate to utilize RVNA assays to measure the<br />
immune response after rabies vaccination rather than<br />
relying on antigen-binding assays, which do not measure<br />
the function of the antibodies produced. Indeed,<br />
currently the most accepted method for measuring the<br />
immune response to rabies antigen is to measure<br />
the amount of RVNA in serum. In the United States,<br />
the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices<br />
(ACIP) recommends that RVNA testing should be<br />
performed using a virus neutralization assay; those<br />
persons at risk of contracting rabies should h<strong>av</strong>e their<br />
RVNA levels measured periodically; and a booster<br />
should be administered to persons at risk of contracting<br />
rabies when their RVNA titer falls below complete<br />
neutralization of a specific quality of rabies virus at a 1:5<br />
500<br />
400<br />
300<br />
200<br />
PCECV homologous<br />
PCECV heterologous<br />
Medium<br />
PVRV homologous<br />
PVRV heterologous<br />
6000<br />
5500<br />
5000<br />
4500<br />
4000<br />
3500<br />
3000<br />
2500<br />
2000<br />
1500<br />
1000<br />
PCECV homologous<br />
PCECV heterologous<br />
High<br />
PVRV homologous<br />
PVRV heterologous<br />
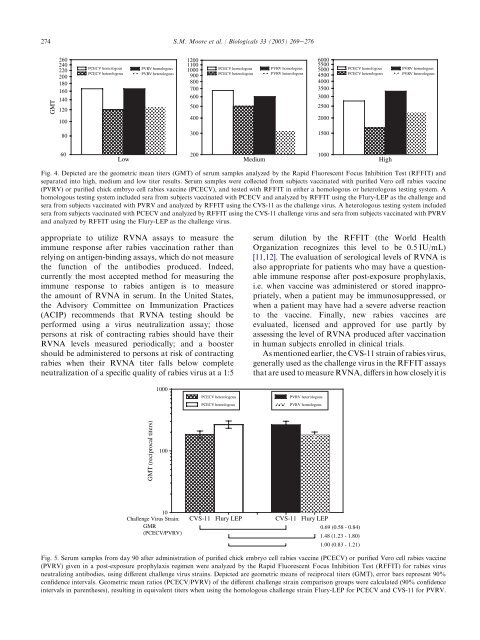
Fig. 4. Depicted are the geometric mean titers (GMT) of serum samples analyzed by the Rapid Fluorescent Focus Inhibition Test (RFFIT) and<br />
separated into high, medium and low titer results. Serum samples were collected from subjects vaccinated with purified Vero cell rabies vaccine<br />
(PVRV) or purified chick embryo cell rabies vaccine (PCECV), and tested with RFFIT in either a homologous or heterologous testing system. A<br />
homologous testing system included sera from subjects vaccinated with PCECV and analyzed by RFFIT using the Flury-LEP as the challenge and<br />
sera from subjects vaccinated with PVRV and analyzed by RFFIT using the CVS-11 as the challenge virus. A heterologous testing system included<br />
sera from subjects vaccinated with PCECV and analyzed by RFFIT using the CVS-11 challenge virus and sera from subjects vaccinated with PVRV<br />
and analyzed by RFFIT using the Flury-LEP as the challenge virus.<br />
GMT (reciprocal titers)<br />
1000<br />
100<br />
10<br />
Challenge Virus Strain:<br />
GMR<br />
(PCECV/PVRV)<br />
PCECV heterologous<br />
PCECV homologous<br />
serum dilution by the RFFIT (the World Health<br />
Organization recognizes this level to be 0.5 IU/mL)<br />
[11,12]. The evaluation of serological levels of RVNA is<br />
also appropriate for patients who may h<strong>av</strong>e a questionable<br />
immune response after post-exposure prophylaxis,<br />
i.e. when vaccine was administered or stored inappropriately,<br />
when a patient may be immunosuppressed, or<br />
when a patient may h<strong>av</strong>e had a severe adverse reaction<br />
to the vaccine. Finally, new rabies vaccines are<br />
evaluated, licensed and approved for use partly by<br />
assessing the level of RVNA produced after vaccination<br />
in human subjects enrolled in clinical trials.<br />
As mentioned earlier, the CVS-11 strain of rabies virus,<br />
generally used as the challenge virus in the RFFIT assays<br />
that are used to measure RVNA, differs in how closely it is<br />
PVRV heterologous<br />
PVRV homologous<br />
CVS-11 Flury LEP CVS-11 Flury LEP<br />
0.69 (0.58 - 0.84)<br />
1.48 (1.23 - 1.80)<br />
1.00 (0.83 - 1.21)<br />
Fig. 5. Serum samples from day 90 after administration of purified chick embryo cell rabies vaccine (PCECV) or purified Vero cell rabies vaccine<br />
(PVRV) given in a post-exposure prophylaxis regimen were analyzed by the Rapid Fluorescent Focus Inhibition Test (RFFIT) for rabies virus<br />
neutralizing antibodies, using different challenge virus strains. Depicted are geometric means of reciprocal titers (GMT), error bars represent 90%<br />
confidence intervals. Geometric mean ratios (PCECV/PVRV) of the different challenge strain comparison groups were calculated (90% confidence<br />
intervals in parentheses), resulting in equivalent titers when using the homologous challenge strain Flury-LEP for PCECV and CVS-11 for PVRV.