Historical Perspective of the Heck Reaction
Historical Perspective of the Heck Reaction
Historical Perspective of the Heck Reaction
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
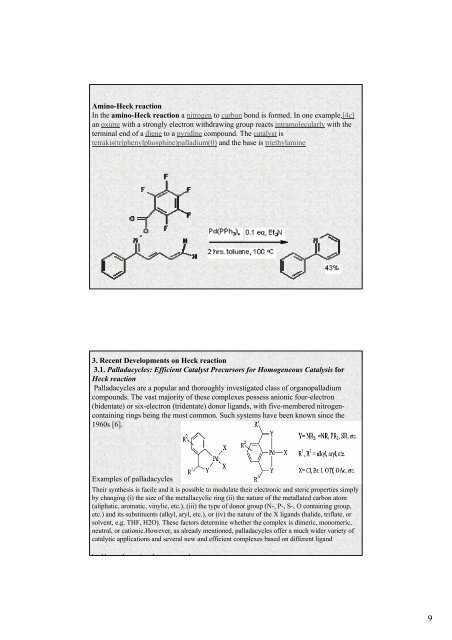
Amino-<strong>Heck</strong> reaction<br />
In <strong>the</strong> amino-<strong>Heck</strong> reaction a nitrogen to carbon bond is formed. In one example,[4c]<br />
an oxime with a strongly electron withdrawing group reacts intramolecularly with <strong>the</strong><br />
terminal end <strong>of</strong> a diene to a pyridine compound. The catalyst is<br />
tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0) and <strong>the</strong> base is triethylamine<br />
3. Recent Developments on <strong>Heck</strong> reaction<br />
3.1. Palladacycles: Efficient Catalyst Precursors for Homogeneous Catalysis for<br />
<strong>Heck</strong> reaction<br />
Palladacycles are a popular and thoroughly investigated class <strong>of</strong> organopalladium<br />
compounds. The vast majority <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se complexes possess anionic four-electron<br />
(bidentate) or six-electron (tridentate) donor ligands, with five-membered nitrogencontaining<br />
rings being <strong>the</strong> most common. Such systems have been known since <strong>the</strong><br />
1960s [6].<br />
Examples <strong>of</strong> palladacycles<br />
Their syn<strong>the</strong>sis is facile and it is possible to modulate <strong>the</strong>ir electronic and steric properties simply<br />
by changing (i) <strong>the</strong> size <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> metallacyclic ring (ii) <strong>the</strong> nature <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> metallated carbon atom<br />
(aliphatic, aromatic, vinylic, etc.), (iii) <strong>the</strong> type <strong>of</strong> donor group (N-, P-, S-, O containing group,<br />
etc.) and its substituents (alkyl, aryl, etc.), or (iv) <strong>the</strong> nature <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> X ligands (halide, triflate, or<br />
solvent, e.g. THF, H2O). These factors determine whe<strong>the</strong>r <strong>the</strong> complex is dimeric, monomeric,<br />
neutral, or cationic.However, as already mentioned, palladacycles <strong>of</strong>fer a much wider variety <strong>of</strong><br />
catalytic applications and several new and efficient complexes based on different ligand<br />
backbones have since been reported<br />
9