MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations Exercises - Millersville ...
MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations Exercises - Millersville ...
MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations Exercises - Millersville ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
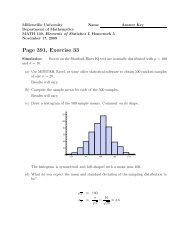
Findthe solution to the wave equation for this initial condition. Discuss the case where<br />
ǫ → 0 + .<br />
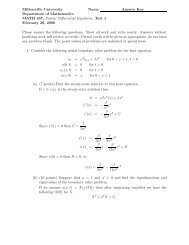
46. Define new coordinates in the xy-plane by<br />
ˆx = ax+by +f<br />
ˆy = cx+dy +g<br />
where a, b, c, d, f, and g are constants with ad−bc = 0. Define û(ˆx,ˆy) = u(x,y).<br />
(a) Show that if u is C 2 , then<br />
uxx +uyy = (a 2 +b 2 )ûˆxˆx +2(ac+bd)ûˆxˆy +(c 2 +d 2 )ûˆyˆy.<br />
(b) Suppose that (ˆx,ˆy) are the new coordinates obtained by rotating the original axes<br />
by some angle θ in the counterclockwise direction. Verify that a = cosθ, b = sinθ,<br />
c = −sinθ, and d = cosθ. Show that in this case<br />
47. Solve the boundary value problem<br />
uxx +uyy = ûˆxˆx +ûˆyˆy.<br />
uxx +uyy = 0 for 0 < x < π and 0 < y < π<br />
u(x,0) = sinx<br />
u(x,π) = sinx<br />
u(0,y) = siny<br />
u(π,y) = siny.<br />
48. Find a function of the form U(x,y) = a + bx + cy + dxy such that U(0,0) = 0,<br />
U(1,0) = 1, U(0,1) = −1, and U(1,1) = 2. Use this function to solve the following<br />
boundary value problem.<br />
uxx +uyy = 0 for 0 < x < 1 and 0 < y < 1<br />
u(x,0) = 3sin(πx)+x<br />
u(x,1) = 3x−1<br />
u(0,y) = sin(2πy)−y<br />
u(1,y) = y +1.<br />
49. Solve the boundary value problem<br />
uxx +uyy = 0 for 0 < x < π and 0 < y < π<br />
u(x,0) = 0<br />
u(x,π) = x(π −x)<br />
u(0,y) = 0<br />
u(π,y) = 0.