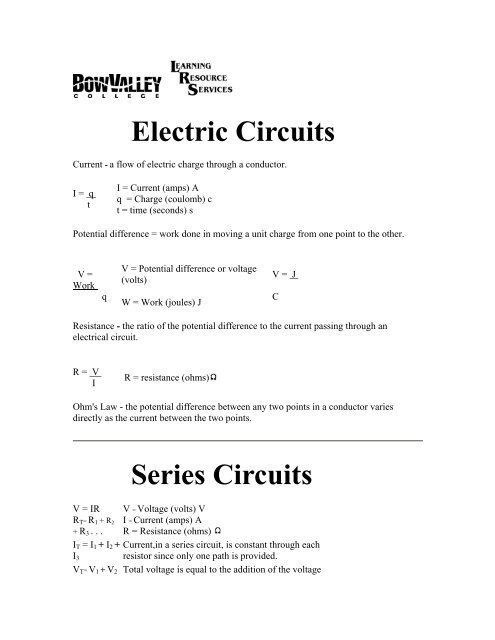
Electric Circuits - Bow Valley College
Electric Circuits - Bow Valley College
Electric Circuits - Bow Valley College
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Electric</strong> <strong>Circuits</strong><br />
Current - a flow of electric charge through a conductor.<br />
I = q<br />
t<br />
I = Current (amps) A<br />
q = Charge (coulomb) c<br />
t = time (seconds) s<br />
Potential difference = work done in moving a unit charge from one point to the other.<br />
V =<br />
Work<br />
q<br />
V = Potential difference or voltage<br />
(volts)<br />
W = Work (joules) J<br />
V = J<br />
Resistance - the ratio of the potential difference to the current passing through an<br />
electrical circuit.<br />
R = V<br />
I<br />
R = resistance (ohms)<br />
Ohm's Law - the potential difference between any two points in a conductor varies<br />
directly as the current between the two points.<br />
V = IR<br />
RT= R1 + R2<br />
+ R3 . . .<br />
IT = I1 + I2 +<br />
I3<br />
Series <strong>Circuits</strong><br />
V = Voltage (volts) V<br />
I = Current (amps) A<br />
R = Resistance (ohms)<br />
Current,in a series circuit, is constant through each<br />
resistor since only one path is provided.<br />
VT= V1 + V2 Total voltage is equal to the addition of the voltage<br />
C
+ V3 drops.<br />
Units<br />
V = A Volt = amp X ohm<br />
Ammeter - measures current in a circuit<br />
Voltmeter - measures the voltage drop<br />
across part of a circuit or an entire<br />
circuit<br />
Resistor<br />
Voltage source - direct current<br />
Battery cells in series<br />
Battery cells in parallel<br />
Transformer<br />
Switch open<br />
Switch closed<br />
Ground<br />
Series <strong>Circuits</strong>
Find:<br />
(a) total resistance<br />
(b) total current<br />
(c) Vdrop at R1, R2, R3, R4<br />
(d) current at R3<br />
(a) RT = R1 + R2 + R3 + R4<br />
RT = 5.0 + 7.0 + 9.0 + 11<br />
RT = 32<br />
(b) VT = IRT<br />
24V = I (32 )<br />
I = 0.75A<br />
(c) Vdrop at R1<br />
Vdrop= IR<br />
Vdrop = (0.75A) (5.0 )<br />
Vdrop = 3.75V<br />
Vdrop at R3<br />
Vdrop= IR<br />
Vdrop = (0.75A) (9.0 )<br />
Vdrop = 6.75V<br />
CHECK: VT = Vl + V2 +V3 +V4<br />
VT = 3.75V + 5.25V + 6.75V + 8.25V<br />
VT = 24V<br />
(d) I = 0.75A (Current is constant in a series circuit)<br />
V = IR<br />
VT= V1 = V2 =<br />
V3<br />
1 = 1 + 1 +<br />
1<br />
RT R1 R2<br />
Parallel <strong>Circuits</strong><br />
Vdrop at R2<br />
Vdrop= IR<br />
Vdrop = (0.75A) (7.0 )<br />
Vdrop = 5.25V<br />
Vdrop at R4<br />
Vdrop= IR<br />
Vdrop = (0.75A) (11 )<br />
Vdrop = 8.25V<br />
Voltage across each resistor is the same in a parallel<br />
circuit.
R3<br />
IT = I1 + I2 +<br />
I3<br />
Question 1:<br />
In a parallel circuit the current in must equal the<br />
current out.<br />
Sample Parallel <strong>Circuits</strong>:<br />
Find:<br />
(a) total resistance<br />
(b) total current
(c) Vdrop<br />
(d) I1, I2, I3<br />
(a)<br />
(b) V = IR<br />
(current through<br />
each resistor)<br />
12.0V = I (1.09 )<br />
I = 11.0 A<br />
(c) Vdrop= 12.0 V Voltage drop in parallel must be equal across all branches.<br />
(d) V=I1R<br />
12.0 V = I1 (2.0 )<br />
I1 = 6.00 A<br />
CHECK:<br />
IT = I1 + I2 + I3<br />
IT = 6.00 A + 3.00 A + 2.00 A<br />
IT = 11.0 A<br />
Question 2:<br />
V = I3R<br />
12.0 V = I3R (6.00 )<br />
I3 = 2.00 A<br />
V =I2R<br />
12.0 V = I2 (4.00 )<br />
I2 = 3.00 A
Find:<br />
(a) RT<br />
(b) IT<br />
(c) I1, I2, I3<br />
(d) V1, V2, V3<br />
(a) 1 = 1 + 1<br />
RT 30.0 30.0<br />
RT = 15.0<br />
(b) VT = ITRT<br />
60.0 V = IT(15.0 )<br />
IT = 4.00 A<br />
(c) Current in line<br />
VT = I1R<br />
60.0 V = I1(30.0 )<br />
I1 = 2.00 A<br />
I2 = 2.00 A (same current in line)<br />
CHECK:<br />
(d) V1 = IR<br />
V1 = (2.00 A) (10.0 )<br />
V1 = 20.0 V<br />
IT = I2&3 + I3<br />
IT = 2.00 A + 2.00 A<br />
IT = 4.00 A<br />
VT = I3R<br />
60.0 V = I3 (30.0 )<br />
I3 = 2.00 A<br />
V3 = IR<br />
V3 = (2.00 A) (30.0 )<br />
V3 = 60.0 V<br />
V2 = IR<br />
V2 = (2.00 A) (20.0 )<br />
V2 = 40.0 V
Question 3:<br />
Find:<br />
(a)<br />
(a) total resistance<br />
(b) total current<br />
(c) Vdrop X ----> Y<br />
(d) Vdrop Y ----> Z<br />
(e) Current through each resistor<br />
I1, I2, I3, I4, I5<br />
(b) V = IR<br />
90.0 V = IT (3.65 )<br />
IT = 24.7 A<br />
(c)<br />
CHECK: VT = 22.8 V + 67.3 V<br />
VT = 90.0 V<br />
(d) Current using formula V = IR
IT = I4 + I5<br />
IT = 24.7A<br />
CHECK: IT = I1 + I2 + I3<br />
I4 = 13.5 A I5 = 11.2 A<br />
Combination Series and Parallel <strong>Circuits</strong><br />
Question 1:<br />
Find:<br />
(a) total resistance<br />
(b) total current<br />
(c) Vdrop at parallel<br />
(d) I through 12 resistor<br />
(e) I through 8 resistor
(a) 1 = 1 + 1<br />
R 12.0 8.00<br />
R = 4.80<br />
RT = 4.80 + 20.0 + 7.00 + 0.600<br />
RT = 32.4<br />
(b) V = IR<br />
45.0 V = I (32.4 )<br />
I = 1.39 A<br />
c) V = IR<br />
V = (1.39 A) (4.80 )<br />
V = 6.67 V<br />
(d) I through 12.0 resistor<br />
I = 0.556 A<br />
(e) I through 8.00 resistor<br />
I = 0.833 A<br />
CHECK: IT = 0.5560 A + 0.833 A<br />
IT = 1.39 A<br />
Question 2:<br />
Find:<br />
(a) total resistance<br />
(b) total current<br />
(c)<br />
(d) current<br />
through R1 & R2<br />
(e) current<br />
through R3 & R4
(a)<br />
R = 3.80<br />
RT = 3.80 + 4.00<br />
RT = 7.80<br />
(b) V = IR<br />
24.0 V = IT(7.80 )<br />
IT = 3.08A<br />
(c)<br />
V = IR<br />
V = (3.08 A) (3.80 )<br />
V = 11.7 V<br />
(d) Current through R1 and R2<br />
I = 2.34 A<br />
(e) Current through R3 and R4<br />
I = 0.731 A<br />
CHECK: IT = 2.34 A + 0.731 A<br />
IT= 3.08 A
Question 3:<br />
Find<br />
(a) total resistance<br />
(b) total current<br />
(c) V1, V2, V3, V4<br />
(a) Resistances in parallel<br />
circuits<br />
R = 9.38<br />
RT = 5.00 + 9.38 +<br />
3.00 + 5.45<br />
RT = 22.8<br />
(b) Total current<br />
I = 3.94 A<br />
(c) V1 = IR<br />
V1 = (3.94 A) (5.00 )<br />
V1 = 19.7 V<br />
V3 = IR<br />
V3 = (3.94A) (3.00 )<br />
V3 = 11.8 V<br />
.<br />
R = 5.45<br />
V2 = IR<br />
V2 = (3.94 A) (9.38 )<br />
V2 = 37.0 V<br />
V4 = IR<br />
V4 = (3.94 A) (5.45 )<br />
V4 = 21.5V
CHECK: VT = Vl + V2 +V3 +V4<br />
VT= 90.0 V