HOW TO USE FLOODPLAINS FOR FLOOD RISK ... - SGGW
HOW TO USE FLOODPLAINS FOR FLOOD RISK ... - SGGW
HOW TO USE FLOODPLAINS FOR FLOOD RISK ... - SGGW
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
A natural flood defence is an area in which a specific<br />
set of measures has been taken to reduce flood risk<br />
and improve natural floodplain functioning at the same<br />
time. The measures are preventive flood risk reduction<br />
measures that can be aimed at both reducing the<br />
flooding probability and minimising the potential damage<br />
(Table 1). In general, natural flood risk reduction<br />
measures aim to enlarge the discharge capacity of<br />
river channels and the storage capacity of floodplains.<br />
Natural flood risk reduction measures are nontechnical<br />
measures that contribute to the restoration<br />
of the characteristic hydrological and geomorphological<br />
dynamics of rivers and floodplains and ecological<br />
restoration. Changes in land use are often needed for<br />
the implementation of these measures. Therefore spatial<br />
planning and stakeholder involvement are of vital<br />
importance when implementing a natural flood defence<br />
scheme. The protection of existing naturally<br />
32<br />
. / (<br />
Measure Qualitative description of the measure<br />
Protection of existing naturally functioning<br />
river and floodplain systems<br />
Flood bypasses<br />
PART II – Background<br />
functioning river and floodplain systems also can be<br />
regarded as an important natural flood risk reduction<br />
measure.<br />
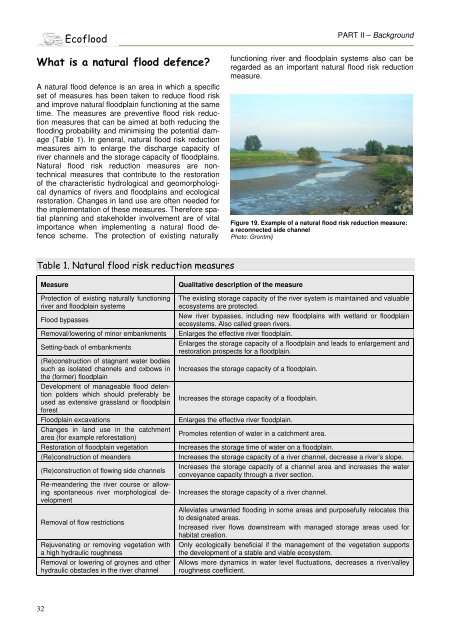
Figure 19. Example of a natural flood risk reduction measure:<br />
a reconnected side channel<br />
Photo: Grontmij<br />
The existing storage capacity of the river system is maintained and valuable<br />
ecosystems are protected.<br />
New river bypasses, including new floodplains with wetland or floodplain<br />
ecosystems. Also called green rivers.<br />
Removal/lowering of minor embankments Enlarges the effective river floodplain.<br />
Setting-back of embankments<br />
(Re)construction of stagnant water bodies<br />
Enlarges the storage capacity of a floodplain and leads to enlargement and<br />
restoration prospects for a floodplain.<br />
such as isolated channels and oxbows in<br />
the (former) floodplain<br />
Development of manageable flood deten-<br />
Increases the storage capacity of a floodplain.<br />
tion polders which should preferably be<br />
used as extensive grassland or floodplain<br />
forest<br />
Increases the storage capacity of a floodplain.<br />
Floodplain excavations Enlarges the effective river floodplain.<br />
Changes in land use in the catchment<br />
area (for example reforestation)<br />
Promotes retention of water in a catchment area.<br />
Restoration of floodplain vegetation Increases the storage time of water on a floodplain.<br />
(Re)construction of meanders Increases the storage capacity of a river channel, decrease a river’s slope.<br />
(Re)construction of flowing side channels<br />
Re-meandering the river course or allow-<br />
Increases the storage capacity of a channel area and increases the water<br />
conveyance capacity through a river section.<br />
ing spontaneous river morphological development<br />
Increases the storage capacity of a river channel.<br />
Alleviates unwanted flooding in some areas and purposefully relocates this<br />
Removal of flow restrictions<br />
to designated areas.<br />
Increased river flows downstream with managed storage areas used for<br />
habitat creation.<br />
Rejuvenating or removing vegetation with Only ecologically beneficial if the management of the vegetation supports<br />
a high hydraulic roughness<br />
the development of a stable and viable ecosystem.<br />
Removal or lowering of groynes and other Allows more dynamics in water level fluctuations, decreases a river/valley<br />
hydraulic obstacles in the river channel roughness coefficient.