Shorted Annular Patches as flexible antennas for space applications
Shorted Annular Patches as flexible antennas for space applications
Shorted Annular Patches as flexible antennas for space applications
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
2. SAP CHARACTERISTICS<br />
SAP antenn<strong>as</strong> have been extensively studied <strong>for</strong> their<br />
property to inhibit surface wave radiation. In [2] it h<strong>as</strong><br />
been demonstrated that an appropriate selection of the<br />
SAP ring external radius inhibits the excitation of the TM0<br />
surface wave mode avoiding the radiation pattern<br />
deterioration due to the surface waves diffraction and<br />
reducing mutual coupling in array <strong>applications</strong> [3]. The<br />
theory h<strong>as</strong> been extended to elliptical SAP, <strong>for</strong> dual band<br />
or circularly polarized antenn<strong>as</strong>, in [4].<br />
Another essential feature of the antenna is that the SAP<br />
pattern can be e<strong>as</strong>ily controlled varying the antenna<br />
geometry without degrading the radiation characteristics.<br />
In order to clarify this <strong>as</strong>pect, let us first consider a<br />
conventional circular patch antenna resonating on its<br />
dominant mode TM11. Once the resonant frequency and<br />
the dielectric characteristics are given, the external radius<br />
of the disk it is uniquely determined and the antenna<br />
radiation pattern, strictly connected to the magnetic current<br />
distribution at the external edge of the patch, can not be<br />
varied.<br />
On the contrary, the shorted annular patch, which h<strong>as</strong> the<br />
same magnetic current distribution of a conventional disk,<br />
offers much more flexibility in shaping the radiation<br />
pattern. In fact, with a proper choice of the external and<br />
internal radii, narrower beams that maintain the radiation<br />
characteristics of a circular disk can be obtained.<br />
As example, three shorted annular patch antenn<strong>as</strong><br />
resonating at the nominal GPS L1 frequency,<br />
1.57542GHz, with an external radius of 35, 45, and 55.7<br />
mm, have been designed considering a substrate with<br />
dielectric constant ε R =2.55 and thickness of 3.2 mm. The<br />
effect of a larger external radius is shown in Fig. 2 where<br />
the co-polar radiation patterns of the three SAP antenn<strong>as</strong><br />
have been compared with the one of a conventional<br />
circular patch resonating at the same frequency and<br />
designed using the same substrate. As expected, a larger<br />
outer radius of the antenna results in a narrower beam.<br />
Fig. 2 – SAP radiation pattern flexibility.<br />
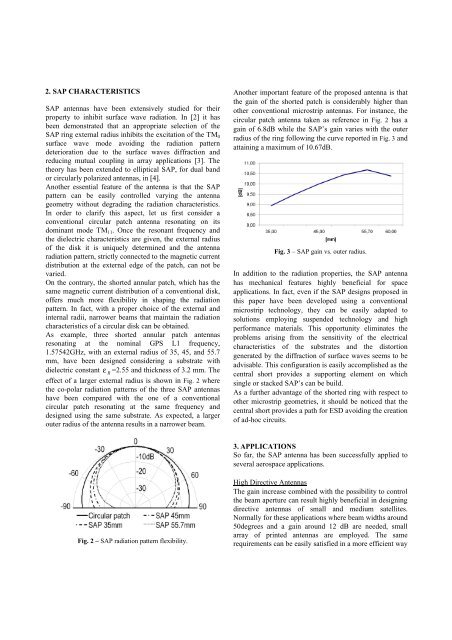
Another important feature of the proposed antenna is that<br />
the gain of the shorted patch is considerably higher than<br />
other conventional microstrip antenn<strong>as</strong>. For instance, the<br />
circular patch antenna taken <strong>as</strong> reference in Fig. 2 h<strong>as</strong> a<br />
gain of 6.8dB while the SAP’s gain varies with the outer<br />
radius of the ring following the curve reported in Fig. 3 and<br />
attaining a maximum of 10.67dB.<br />
Fig. 3 – SAP gain vs. outer radius.<br />
In addition to the radiation properties, the SAP antenna<br />
h<strong>as</strong> mechanical features highly beneficial <strong>for</strong> <strong>space</strong><br />
<strong>applications</strong>. In fact, even if the SAP designs proposed in<br />
this paper have been developed using a conventional<br />
microstrip technology, they can be e<strong>as</strong>ily adapted to<br />
solutions employing suspended technology and high<br />
per<strong>for</strong>mance materials. This opportunity eliminates the<br />
problems arising from the sensitivity of the electrical<br />
characteristics of the substrates and the distortion<br />
generated by the diffraction of surface waves seems to be<br />
advisable. This configuration is e<strong>as</strong>ily accomplished <strong>as</strong> the<br />
central short provides a supporting element on which<br />
single or stacked SAP’s can be build.<br />
As a further advantage of the shorted ring with respect to<br />
other microstrip geometries, it should be noticed that the<br />
central short provides a path <strong>for</strong> ESD avoiding the creation<br />
of ad-hoc circuits.<br />
3. APPLICATIONS<br />
So far, the SAP antenna h<strong>as</strong> been successfully applied to<br />
several aero<strong>space</strong> <strong>applications</strong>.<br />
High Directive Antenn<strong>as</strong><br />
The gain incre<strong>as</strong>e combined with the possibility to control<br />
the beam aperture can result highly beneficial in designing<br />
directive antenn<strong>as</strong> of small and medium satellites.<br />
Normally <strong>for</strong> these <strong>applications</strong> where beam widths around<br />
50degrees and a gain around 12 dB are needed, small<br />
array of printed antenn<strong>as</strong> are employed. The same<br />
requirements can be e<strong>as</strong>ily satisfied in a more efficient way